
California Business Journal – August 25, 2020 Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) were created to be the middleman and negotiate drug prices. Working with the health care providers, pharmacies and the pharmaceutical companies determine reimbursements and what they’d charge the pharmacies.
What does a pharmacy benefit manager do?
Key Takeaways
- Pharmacy benefit managers serve as the middlemen between drug companies and insurers.
- They negotiate discounts with drug makers and pass the cost savings on to insurers.
- These companies make money by up-charging the drugs or keeping some of the rebates.
- This sector of the industry is highly competitive and is characterized by consolidation.
What are the responsibilities of a pharmacy manager?
- Program, direct, review, and rectify pharmacy procedures.
- Render assistance to the technical and professional personnel in mixing, compounding and dispensing of various medications utilized by and sold to hospital patients.
- Make formal requests for all supplies needed.
Who is the largest pharmacy benefit manager?
In 2020, the top pharmacy benefit managers included CVS Health, Express Scripts, and OptumRx, to name a few. CVS Health had the largest share of the pharmacy benefit manager market in 2020. In total CVS Health held 32 percent of the market at that time. Pharmacy benefit managers are an important part of the prescription drug supply chain.
How do PBMs get paid?
Policymakers have considered three principal reforms to regulate PBMS:
- Require greater transparency around rebates. Federal and state policymakers likely need more data on the rebates PBMs receive to gain a more complete understanding of pharmaceutical spending and where reforms ...
- Ban spread pricing. ...
- Require PBMs to pass through rebates to payers or to patients. ...
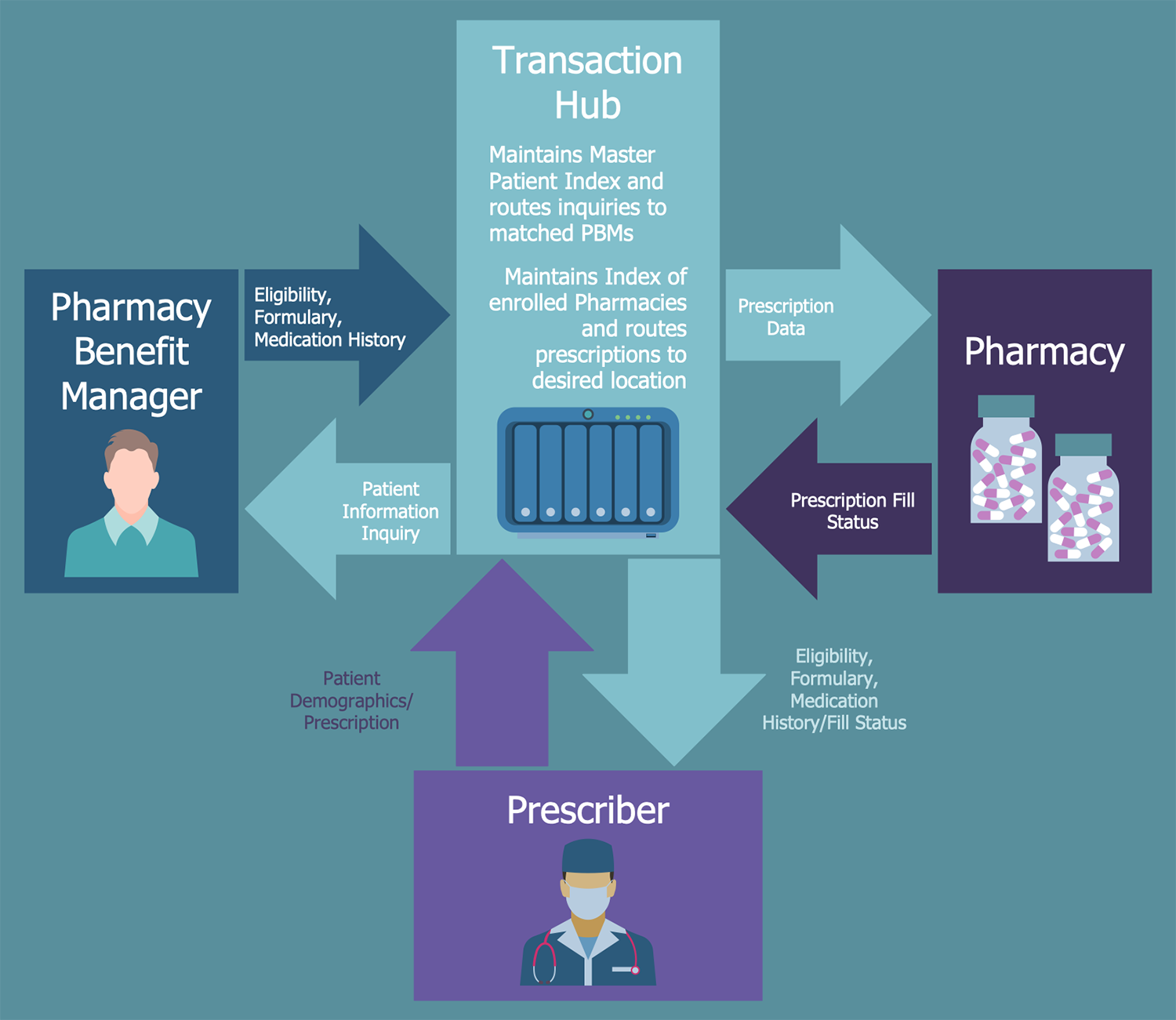
What is a role of a pharmacy benefit manager PBM )?
Pharmacy benefit managers, or PBMs, are companies that manage prescription drug benefits on behalf of health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, large employers, and other payers.
What does a pharmacy benefits manager do quizlet?
pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) are organizations that deliver, monitor & manage prescription drug benefits on behalf of a plan sponsor.
How did PBMs get started?
Background: When insurance companies began offering prescription drugs as a health plan benefit in the 1960s, PBMs were created to help insurers contain drug spending. Originally, PBMs decided which drugs were offered in formularies and administered drug claims.
What is an example of a pharmacy benefit manager?
Example of PBMs: CVS/caremark According to the CVS/caremark website: "Whether plan members access their prescriptions by mail or in one of our national network's more than 68,000 retail pharmacies, we provide the service and support needed to make sure the process goes smoothly.
Why is prescription management an important cost control quizlet?
Why is prescription management an important cost control? Prescription management is an important cost control because it increases the use of a formulary, a list of prescription drugs that health insurance will cover, to an inclusive approach to medications and medication administration.
What is the purpose of a drug benefit plan?
Alberta's supplementary health plans will pay for the lowest priced drug product where interchangeable products can be used to fill a prescription. Beneficiaries who choose higher cost alternatives are responsible for paying the difference in price.
When were PBMs created?
In 1968, the first PBM was founded when Pharmaceutical Card System Inc. (PCS, later AdvancePCS) invented the plastic benefit card. By the "1970s, [they] serve[d] as fiscal intermediaries by adjudicating prescription drug claims by paper and then, in the 1980s, electronically".
How does a PBM operate?
PBMs manage Medicaid and Medicare prescription plans and bill the government the same way they bill their private insurance clients. PBMs own their own pharmacies - both retail stores and mail order - and make money when patients are forced to use mail order or only purchase from a PBM-owned pharmacy, such as CVS.
How do PBMs increase drug prices?
PBMs often use a practice called “spread pricing” to artificially inflate generic drug prices. PBMs practice “spread pricing” when they charge their clients more for a prescription drug than they are actually paying. Bloomberg examined the prices of the 90 best-selling generic drugs that were used by Medicaid in 2017.
What is one benefit health and wellness services provide to pharmacies?
In addition to the convenient access and established relationships across a community, pharmacists also have access to prescription data, which can potentially be leveraged to identify patients who would benefit from wellness-related services.
What is pharmacy benefit vs medical benefit?
Medical benefit drugs are ones that are injected or infused by a healthcare professional in an out-patient clinic or infusion centers. Whilst, pharmacy benefit drugs are self-administered and include orals, self-injectable, or a route of administration a patient can manage at home.
What is PBM in pharmacy?
Updated: Jul 21, 2017 at 12:05PM. A pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) is a third-party administrator of prescription-drug programs for end payers, such as private insurers, and Medicare Part D plans.
What is a pharmacy benefit manager?
A pharmacy benefit manager is essentially a middleman service between the world's drugmakers and U.S. end payers, but healthcare investors need to understand far more about the unusual PBM industry. A pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) is a third-party administrator of prescription-drug programs for end payers, such as private insurers, ...
What is OptumRx?
The next largest PBM, OptumRx, is a subsidiary of UnitedHealth Group, America's largest healthcare provider. Pharmacy benefit managers point to expert understanding of prescription-drug markets as a source of value for their customers. However, it's sheer size that gives them power to negotiate discounts and rebates from drugmakers.
What is PBM insurance?
Pharmacy benefit management (PBM) companies serve as the middlemen between insurance companies, pharmacies, and manufacturers securing lower drug costs for insurers and insurance companies. PBMs do this through negotiating with pharmacies and drug manufacturers to secure discounts on drug prices, then pass these discounts along to insurance ...
What are PBMs?
PBMs exploit several revenue streams. They charge service fees for negotiating with pharmacies, insurance companies, and drug manufacturers, and for processing prescriptions and operating mail-order pharmacies .
How much money does PBM make in 2020?
As of 2020, pharmacy benefit management (PBM) companies collectively bring in over $449.12 billion in revenues each year. 3 Since drug costs have exploded over the years, insurance companies have relied more on PBMs to control costs.
Do PBMs have fiduciary duty?
In addition, there has been pressure to force fiduciary duty onto PBMs which would require them to act in the best interest of insurers and insurance plans, similar to financial advisors ' legal obligation to act in the best interest of their clients.
Defining the PBM
A pharmacy benefit manager is a corporation that manages prescription drug benefits on behalf of an insurance company. Express Scripts, CVS/Caremark, and OptumRx are examples of PBMs. PBMs negotiate with drug manufacturers and pocket the savings. Savings that ought to be passed on to the patient.
Why do Pharmacy Benefit Managers Exist?
Because health insurers have inserted themselves so deep into American healthcare, they struggle to perform basic functions. Something so basic as prescription drug coverage. Rather than simplify mercurial eligibility requirements wholly designed to limit their need to spend money, insurers sell off this function to a PBM.
How do PBMs Make Money?
Remember when the only financial transactions in healthcare were between a patient and his doctor or pharmacy? No? Neither do I. American healthcare is the most opaque and complex financial system on the planet.
Why are PBMs so Bad?
Pharmacy benefit managers are the ultimate middlemen. They take advantage of a complex system and add to the bloat. And this all goes on behind closed doors. Forget about getting an itemized statement from your dictatorial PBM.
Pharmacy Benefit Managers Increase the Cost of Drugs
Conceived in the 1960s to process drug claims, PBMs are now partly responsible for rising drug prices. There is no competition. Express Scripts and CVS alone feed off 240 million Americans. Mergers and acquisitions ensure that monopolies stay in power.
More Problems with Pharmacy Benefit Managers
PBMs make your healthcare provider’s life miserable, too. If you are a doctor or PA, you know this firsthand.
Your Doctor Hates PBMs
If there’s one thing that clinicians shouldn’t spend more time on, it’s filling out paperwork. Prior authorizations must be completed by hand, through the EMR, or through third-party services like Cover My Meds. Coverage decisions are instantaneous, right? Wrong again. It can take days to weeks for a PBM to respond to a prior authorization.
A Basic Guide to Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs)
According to IQVIA, Americans paid $67 billion in out-of-pocket costs for prescriptions filled by retail pharmacies in 2019.
What are Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs)?
PBMs have been around a lot longer than many realize. When insurance companies added prescription drugs to many health care benefits in the 1960s, the PBM role was created. Initially, PBMs would process claims for insurance claims. However, their role has evolved tremendously over the years.
How PBMs work with insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, and pharmacies
PBMs help insurance companies manage costs by negotiating with pharmaceutical manufacturers for discounts on medications. PBMs get the manufacturer’s drugs in front of millions of customers in exchange.
Final thoughts
The continual increase in prescription drug costs will emphasize managing the prescription drug benefit for employers.

What Is The Pharmacy Benefit Management (PBM) Industry?
Understanding The Pharmacy Benefit Management (PBM) Industry
- Just like other subsectors of the economy, insurance is a multilayered business with many players serving a variety of interests and purposes. This means that insurance companies aren't the only entities that operate in this industry. In fact, it also includes reinsurers, underwriters, and pharmacy benefit management companies. Insurance companies rely on PBMs to manage cost…
Special Considerations
- The cost of drugs has exploded over the years, leading insurance companies to rely heavily on PBMs to control and reduce their liabilities. As such, the industry has seen increased competition among PBMs as well as consolidation. Mergers and acquisitions(M&A) allow PBMs to increase in size and boost their negotiation power. In addition to M&A deals among PBMs, there has also be…
Criticism of The PBM Industry
- As the sheer nature of the business likely implies, PBMs are common targets of lawsuits and government scrutiny.6 As third-party negotiators, many of their business practices are opaque, so PBMs haven’t always disclosed rebates, discounts, itemized billing statements, or the percentage of savings passed on to insurers. State legislatures have been pushing for greater transparency …