What are the benefits of a biosimilar drug?
BC The only benefit is that they are less expensive. Otherwise, there is no particular benefit. As I mentioned before, if the drug is actually more efficacious, it is not considered a valid biosimilar. The availability of biosimilars will have an impact on drug costs.
What is the difference between biosimilar and bio-better?
In one case, the European Medicines Agency had a drug undergoing review as a biosimilar that was actually a “bio-better,” that is, the newer agent had better efficacy than the original agent. This drug was not approved because it was not biosimilar.
Why are biosimilars so difficult to make?
For this reason, the process of making biosimilars is not easy and can be fraught with problems. In fact, one of the issues with biologics has been that there are significantly more lot-to-lot variations than with small molecule drugs, even among the original proteins.
Why is consistency of dose so important in biosimilars?
Consistency of dose is especially important for certain agents, such as those that affect blood clotting. This is one reason why the area of biosimilars is more fraught than many people realize. H&O What is the difference between biosimilars and bioidenticals?

What are the benefits of biosimilars?
Biosimilars may offer a number of potential benefits to various stakeholdersIncreased use. of biologics. Additional treatment choices at lower cost to the health care system.Improved access. and outcomes. ... Health care system. efficiency. ... Expanded options. for patients.
What are biosimilars and are they important?
Biosimilars use the exact same starting materials and similar manufacturing processes as the original biologic. They are designed and developed to be highly similar to the original drug upon which they are based, and they will not be approved as a biosimilar if they are not.
What is biosimilar used for?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved biosimilar medications to treat conditions such as cancer, diabetes, Crohn's disease, colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and more.
Why do we need biosimilars?
Biosimilars increase the number of treatment options available, which in turn increases competition. This can reduce the cost of high-value medicines, and free up valuable funds for healthcare systems. With the help of biosimilars, new treatments can be reimbursed or become available.
Why are biosimilars better than generics?
Biosimilars also have significantly higher research and development costs and risks and are more complex to manufacture than small-molecule generics. Biosimilars have the potential to provide additional treatment options at lower cost, but development requires significant investment.
Are biosimilars effective?
While it is possible that minor structural differences among biosimilars could lead to variable effectiveness and safety, studies to date have found no meaningful differences between a biosimilar and its respective originator biologic with respect to safety and efficacy.
What are examples of biosimilars?
FDA-Approved Biosimilar ProductsBiosimilar NameApproval DateReference ProductAmjevita (Adalimumab -atto)September 2016Humira (adalimumab)Erelzi (Etanercept-szzs)August 2016Enbrel (etanercept)Inflectra (Infliximab-dyyb)April 2016Remicade (infliximab)Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz)March 2015Neupogen (filgrastim)33 more rows•May 26, 2022
What is biosimilar development?
The goal of a biosimilar development program is to demonstrate biosimilarity between the proposed biosimilar product and the reference product, not to independently establish the safety and effectiveness of the proposed product.
Which of the following is example of biosimilar?
An example of an approved biosimilar is Amjevita (adalimumab-atto), the first biosimilar approved for the blockbuster Humira (adalimumab) used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis, among many other uses.
What are biosimilar biological products?
A biosimilar is a biological product that is highly similar to and has no clinically meaningful differences from an existing FDA-approved reference product.
How are biosimilars different from generics?
Generic drugs are chemically identical to the original branded drug and, as such, cost significantly less because they don't require much testing. Because biosimilars are made from living organisms, though, and don't contain identical ingredients to their name-brand counterparts, they still require some testing.
How are biosimilars approved?
The FDA approves a biosimilar after a manufacturer establishes that the product is highly similar to a previously approved originator biologic reference product without any clinically meaningful differences in safety, purity, and potency.
What are biologic agents?
Biologic agents generally contain proteins that are made synthetically. Now that the patents have expired on a number of these agents, pharmaceutical companies are attempting to make off-patent biologics—new agents that act the same as the biologics that are already on the market. To provide an overly simplified definition, ...
What is BC biologics?
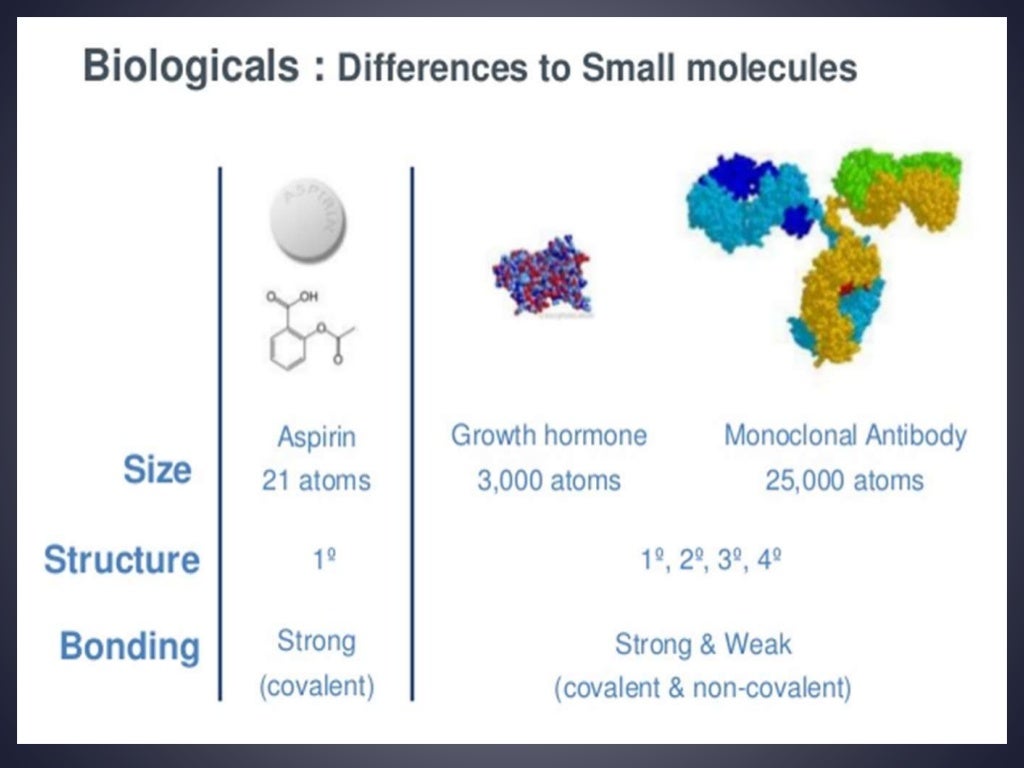
BC Biologics are large and complex molecules that have very specific effects. They are antibodies in many cases, or proteins such as G-CSF. The main concern is that some modifications might occur during the manufacturing process that will be undetectable and will lead to altered efficacy, immunogenicity, or toxicity.
Why is consistency of dose important?
One reason for this regulation is to keep the doses consistent, so that the physicians who are used to giving the drug will know how much is required. Consistency of dose is especially important for certain agents, such as those that affect blood clotting.
Can insurance companies change biosimilars?
Another worry is that different insurance companies will have contracts with different manufacturers of the biosimilar drugs. As patients change insurance companies, they will receive whichever drug their insurance company will pay for, meaning they may change biosimilars over the course of treatment.
Can a pharmacist substitute a generic for a brand name?
This distinction is important. A pharmacist can substitute a generic drug for a brand-name drug, but this is not appropriate for the biosimilars because they are not identical.
Can a protein be identical to a biologic?
By contrast, it is not clear that any protein or peptide made, for example, in a different cell line or by a different company in a different process will be identical to the original biologic agent. For example, there can be differences in the sugar residues that are attached to the protein.
Will the new drug be effective?
Most likely, the new drug will be effective and will not cause problems; however, if this is not the case, there is a chance that the patient will never respond to this type of therapy again. This is a major concern for many physicians.
What is the FDA's action plan?
The FDA has laid out a multifaceted action plan to foster biologic innovation and further biosimilars development. Key measures range from the development and implementation of new FDA review tools to providing revised guidance on biosimilar topics and the establishment of a new Office of Therapeutic Biologics and Biosimilars (OTBB).
Why is biosimilar adoption important?
Biosimilar adoption could help lay the groundwork for future generations of breakthrough treatments.
Why are biologics not exact replicas?
Because of the complexity of their creation, biosimilars may not be exact replicas of the formulations they are designed to replace: As proteins, biologics are subject to certain kinds of modification because they are produced by cells.
What is a granulocyte colony stimulating factor?
Filgrastim, a granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, was the first approved biosimilar in the United States. Filgrastim stimulates bone marrow following chemotherapy. Biosimilars are reviewed under an abbreviated FDA review process known as the 351 (k) pathway.
When was Infliximab-Dyyb approved?
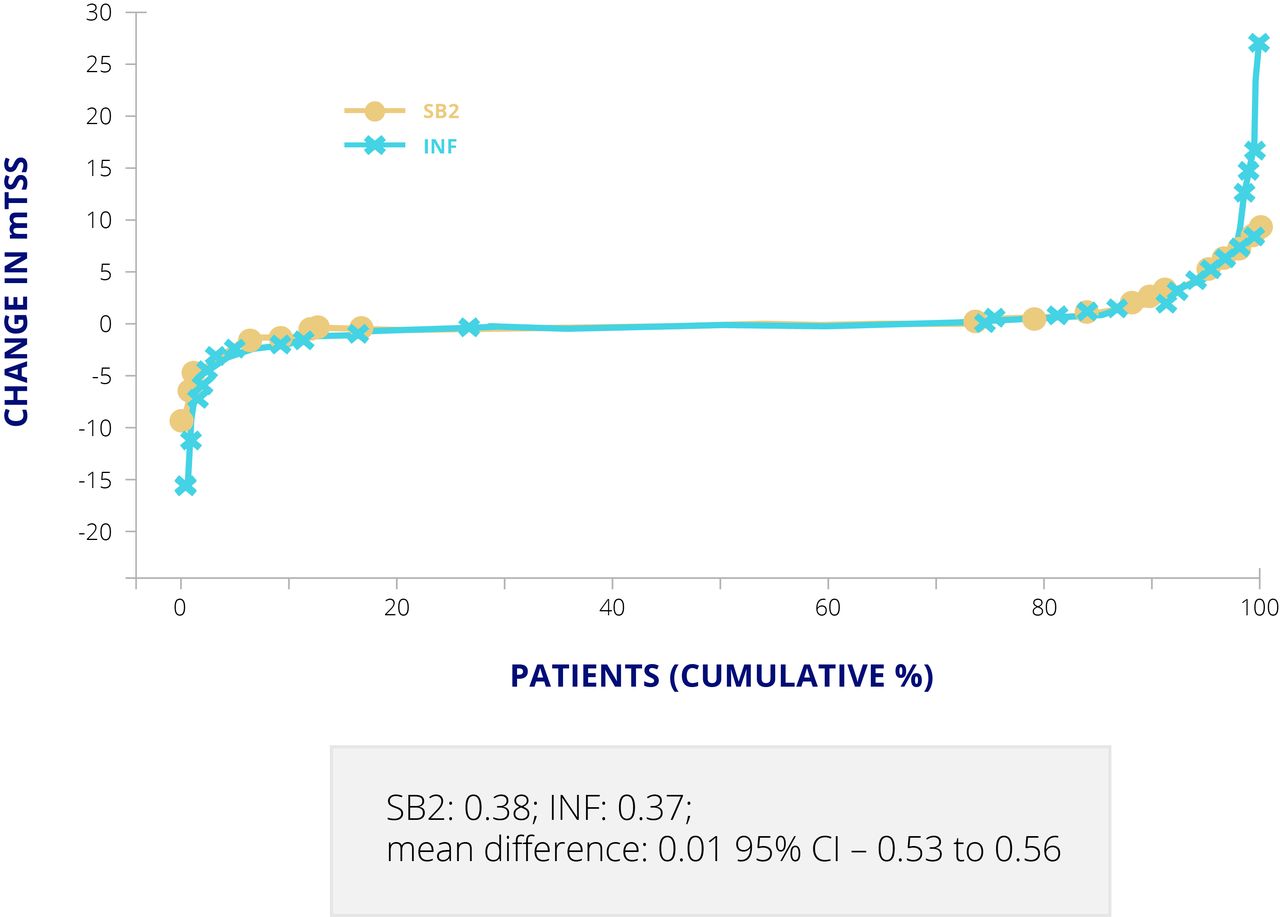
The approval by the US Food and Drug Administration of the first biosimilar monoclonal antibody (infliximab-dyyb) in the United States in April 2016 intensified discussion among rheumatologists about the future of this type of formulation and its significance in medical therapy.
Is there a cost savings for infliximab?
The availability of 2 biosimilars for infliximab has led to significant cost savings; however, it's not yet known whether the savings will allow more patients to be treated with infliximab and its biosimilars.
Is Infliximab a biosimilar?
With the approval of a fifth biosimilar in April 2017, biosimilars are beginning to enter rheumatology practice in the United States, physicians say, and should offer advantages in cost. Infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker for which 2 biosimilars are now available, is FDA approved to treat rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, ...
Can biosimilars be substituted for reference?
Physicians prescribing biosimilars must look for an interchangeability designation, Pisetsky says, which means the biosimilar can be substituted for the reference product by a pharmacist. State laws may also affect the use of biosimilars.
What is a biosimilar?
Biosimilars benefit everyone. Biosimilars are FDA-approved alternatives to reference biologics – much like generic drugs – that provide treatment options for patients who need biologic medicines to manage their conditions.
What is the Biosimilars Council?
The Biosimilars Council is a leading source for information about the safety and efficacy of more affordable alternatives to costly brand biologic medicines. Areas of focus include public and health expert education, strategic partnerships, government affairs, legal affairs and regulatory policy. More information is available on our about page.
When did biosimilars start?
The European Medicines Agency (EMA), the European Union’s equivalent of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), developed a biosimilars approval pathway in 2003 and approved the first biosimilars products for use in the EU in 2006.
How many biosimilars are there in Europe?
As of publication of this brief, Europe has approved 67 biosimilars, all of which entered the market (nine have since been withdrawn for commercial reasons). While experience has varied across countries and molecules, biosimilars attained the majority of the market share. 9.
What is biologic medicine?
Biologic drugs, or biologics, are products derived from living organisms or their components that treat a number of conditions such as diabetes, cancer, and immune disorders. Biologics range from relatively small molecule insulins, to monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), to cell and gene therapies and include some of the most expensive ...
What are biologics used for?
Many biologics were developed to treat conditions that previously proved difficult to treat effectively, including cancers, autoimmune, and inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
How much of the US drug budget is spent on biologics?
Although they constitute only about 2% of all prescriptions in the U.S., biologics account for 43% of total drug expenditures ,2.
When did the US start approving biosimilars?
The United States (U.S.) adopted legislation to create a process for regulating and approving biosimilars in 2010. The law raised expectations that billions of dollars would be saved annually as multiple competitor biologics came onto the market at prices below those of the original drugs.
What is the FDA requirement for interchangeability?
To achieve interchangeability, the FDA requires a manufacturer to provide data and information to evaluate the risk, in terms of safety and decreased efficacy, of alternating or switching between the products, if the product is administered to a patient more than once.
What are the benefits of biosimilars?
Biosimilars may offer additional treatment options that may increase savings and efficiencies to health care systems and expand the use of biologic therapies, which may lead to better overall health outcomes.
Why are biosimilars important?
Biosimilar medicines may provide cost savings for patients who can benefit from biologic medicines. By potentially providing more affordable options, biosimilar medicines can allow for the reallocation of resources to other areas of patient care.
How much will biosimilars save?
to health care systems due to biosimilars may be substantial. RAND corporation estimates that biosimilars may lead to savings of up to $150 billion in direct spending on biologic drugs between 2017 and 2026.*