What are the 4 types of symbiotic relationships?
What are the 6 symbiotic relationships?
- Competition (-/-) Ernest Wolfe.
- Predation (+/-) Definition: an interaction in which one animal typically kills and consumes another animal.
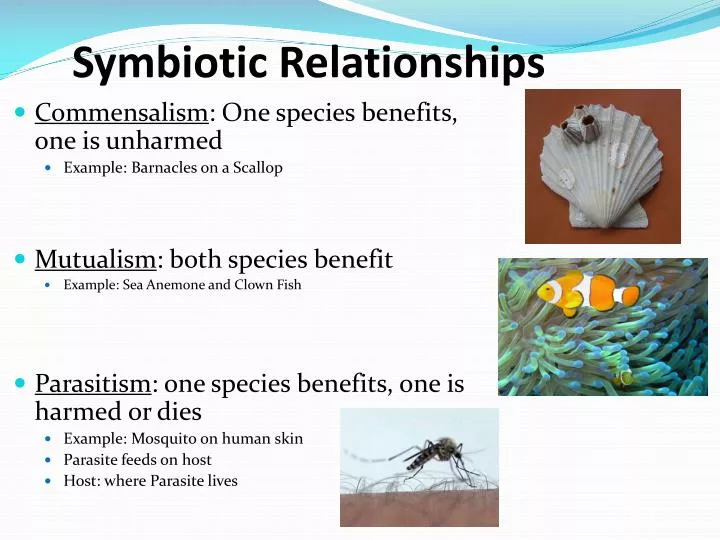
- Parasitism (+/-) Definition: an interaction in which one organism (the parasite) lives on or in another organism (the host)
- Herbivory (+/-)
- Mutualism (+/+)
- Commensalism (+/0)
What are some examples of symbiotic relationships?
What are the 3 types of symbiotic relationships and give an example for each?
- mutualism – a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship.
- commensalism – a one-sided symbiotic relationship.
- parasitism – one species lives on, in or with a host species.
- competition – relationship in which organisms compete for resources.
What are the different types of symbiotic relationships?
What are the three types of symbiosis quizlet?
- parasitism. A relationship between two organisms where one benefits and the other is harmed.
- commensalism. A relationship between two organisms where one benefits and the other is unharmed.
- mutualism. A relationship between two organisms where both benefit.
Do plants and animals have a symbiotic relationship?
Symbiotic relationships between plants and animals provide the cornerstone of pollination syndrome. Symbiotic relationships between fauna and flora are key aspect for gardeners looking to create a naturescape. While citrus farms, are just one of the few fruit and vegetable farms that rely on bees for pollination.

What is a symbiotic relationship?
Symbiotic relationships are a special type of interaction between species. Sometimes beneficial, sometimes harmful, these relationships are essential to many organisms and ecosystems, and they provide a balance that can only be achieved by working together. Updated: 07/12/2020. Create an account.
What is a good example of mutualistic symbiosis?
Defense symbiosis is another mutualistic symbiosis. A good example of this is the relationship between clownfish and sea anemones.
What is the purpose of cleaning symbiosis?
Cleaning symbiosis is a facultative mutualistic symbiosis. In this case, one organism cleans parasites off another organism's body, which in turn provides a source of food.
Why is mutualism beneficial?
Mutualism occurs when both species benefit from the interaction. Because mutualism is beneficial to both species involved, there are a wide variety of mutualistic interactions, and these are most common in nature. For example, there may be a nutritional benefit to be gained from the symbiosis, such as with lichen.
What is the third type of symbiosis?
The third main type of symbiosis is parasitism. This is when one species benefits from the interaction and the other species is harmed. A parasite is an organism that lives on or within a host species. The host provides food and shelter to the parasite, but at a cost to the host itself.
What are some examples of birds that live with cattle?
This is when one species benefits and the other does not gain or lose anything. A good example of this is cattle and cattle egrets. Cattle egrets are birds that are often seen in cattle pastures. They live with the cattle because as the cattle walk around they stir up insects, which the birds can eat.
What is competition in symbiosis?
Lesson Summary. Symbiosis describes close interactions between two or more different species.
What are the five symbiotic relationships?
There are five main symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalism, predation, parasitism and competition. To explore these relationships, let's consider a natural ecosystem such as the ocean. Oceanic environments are known for their wide variety of species.
What are some examples of symbiosis?
The last example of symbiosis we will explore on our imaginary dive is competition, or the struggle among organisms for the same limited resources in an ecosystem. Competition can happen between members of the same species, called intraspecific competition, and between different species, known as interspecific competition. An example of interspecific competition in the ocean is the relationship between coral and sponges. Sponges are ancient sea organisms that are abundant in coral reefs. If they become too successful, they take much of the food and other resources that coral need to survive. Sponges may beat out coral for resources in the short term, but if too many coral die, the reef itself becomes damaged. That is because coral are responsible for building reefs out of calcium, and if coral disappear, the reef will too. Sponges may therefore start to die off until the reef is balanced again.
What are some examples of interspecific competition in the ocean?
An example of interspecific competition in the ocean is the relationship between coral and sponges. Sponges are ancient sea organisms that are abundant in coral reefs. If they become too successful, they take much of the food and other resources that coral need to survive.
How do sea anemones benefit from a mutualistic relationship?
They trap their prey with stinging cells, which are located on their tentacles. The cells release poisons when a small animal touches an anemone's tentacle. This paralyzes the stung animal, allowing the anemone to easily bring the animal into its mouth.
What is the relationship between barnacles and humpback whales?
Commensalism. As we continue our voyage, we discover the commensalistic relationship between barnacles and humpback whales. Commensalism happens when one species lives with, on or in another species, known as the host. The host species neither benefits from nor is harmed by the relationship. For example, various species ...
What is the relationship between a parasite and a host?
Parasitism. Another harmful relationship is parasitism. This happens when one species, the parasite, lives with, on or in a host species, at the expense of the host species. Unlike in predation, the host is not immediately killed by the parasite, though it may sicken and die over time.
Do symbiotic relationships cause harm?
Of course, some symbiotic relationships do cause har m. In predation, one species, the predator, hunts and kills another species, the prey. One of the better studied ocean predators is the orca, or killer whale. Found in every ocean on Earth, orcas are known as apex predators.
What is the relationship between two organisms?
An ecological interaction between two organisms. A symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other organism neither benefits nor is harmed. A symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit. A symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other organism is harmed.
What is the mutualistic relationship between a clown fish and a sea anemone?
Explain the mutualistic relationship that exists between a clown fish and a sea anemone. Clown fish excretes nutritional waste and eats algae and needs a place to hide and be protected. The sea anemone has stinging tentacles, requires nutrients and protection from competition with algae.
What happens when a bee lands on a flower?
When a bee lands on a flower, it gets some pollen on its body. Then, when the bee lands on the next flower, some of the pollen from the first flower rubs off, pollinating the plant. Commensalism. Whales and Barnacles- Barnacles create home sites by attaching themselves to whales. Commensalism.
What are the two things that fungi do to plants?
The fungus helps the plant absorb inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus from the soil. Some fungi also secrete antibiotics, which can help protect the plant from parasitic fungi and bacteria. Mutualism. Bees and Flowers- Bees fly around to various flowers and gather nectar, which they use to make food.
What is the relationship between ostriches and gazelles?
Mutualism. Ostrich and Gazelle- Ostriches and gazelles feed next to each other. They both watch for predators and alert each other to danger. Because the visual abilities of the two species are different, they each can identify threats that the other animal would not see as readily. mutualism.
Do algae and fungi live together?
algae and fungi (lichen). algae and fungi can live together , forming lichen. the algae produce carbohydrates through photosynthesis, providing nutrients to both the algae and the fungi. the fungi provide moisture for the algae. Black wasp and Aphids- Black wasps plant eggs in aphids.
What is a one sided relationship where one of the organisms benefits greatly from the symbios
Commensalism. Commensalism is a one-sided relationship where one of the organisms benefits greatly from the symbiosis. The other is not helped, but it is not harmed or damaged from the relationship either.
Why is symbiosis important?
Whether it’s a mutually beneficial relationship, a parasitic relationship or a competitive relationship, symbiosis is an important part of our natural world. Without symbiosis in nature, many ecosystems would suffer and cease to flourish.
What are the different types of symbiosis?
The most common types of symbiosis include: mutualism - a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship. commensalism - a one-sided symbiotic relationship. parasitism - one species lives on, in or with a host species. competition - relationship in which organisms compete for resources. predation and herbivory - symbiosis where one organism feeds on ...
What does symbiosis mean?
Symbiosis comes from two Greek words that mean "with" and "living.". It describes an ecological relationship between two organisms from different species that is sometimes, but not always, beneficial to both parties. Keep reading to learn about the different types of symbiosis and how they provide balance in various ecosystems around the world.
What is the relationship between organisms that compete for resources?
competition - relationship in which organisms compete for resources. predation and herbivory - symbiosis where one organism feeds on another. These symbiotic relationships are different based on which species benefits the most and whether they can live without each other.
What is a mutualistic relationship?
Mutualism is a close, long-lasting relationship where both parties benefit. Organisms can use other organisms for cleaning, protection or gathering food. In some mutualistic relationships, the organisms can’t survive without each other.
What are some examples of parasitic symbiosis?
Examples of parasitic symbiosis include: Fleas and mosquitoes feed on blood from other organisms. In this type of parasitic relationship, the host needs to stay alive and it is not damaged greatly. Barnacles attach to the bodies of whales.