Why do tax cuts stimulate the economy?
Yet most economists seem to agree that tax cuts really do provide a stimulus. The real reason may be that they provide flexibility:people who want to consume more can use their tax cut for that purpose;people who want to save more can use theirs to buy up the new government bonds.
How do tax cuts affect the economy?
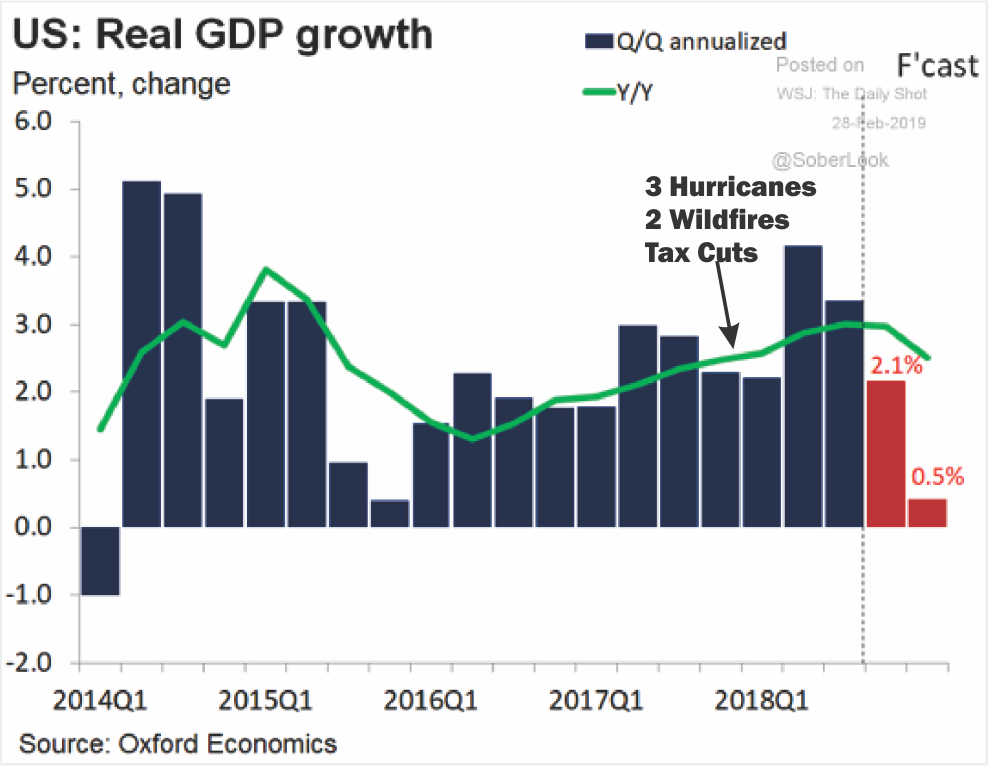
The Bush tax cuts may have boosted the economy in the short-term:
- 1.7%
- 2.9%
- 3.8%
- 3.5%
Do tax cuts stimulate the economy?
at least if they are in a strong enough economic position to do so. Is Utah in a strong enough economic position to push back against the tax cut competition, or are we still so vulnerable that we have no choice in the matter? A generation or two ago ...
What is the result of cutting taxes?
Cut taxes too much too quickly and an increase may be necessary ... and $62,000 for those filing jointly. The result: More people who rely on Social Security benefits and live on fixed incomes will be eligible for tax relief. Critics of the tax reform ...
How does cutting taxes affect the economy?
Why are tax cuts important in 2021?
What is shifting tax burden?
How does reducing taxes affect aggregate demand?
What is the largest source of income for the federal government?
What happens if you tax cigarettes?
Why is cutting income tax so emotional?
See more
About this website
Is tax cut good for the economy?
Contrary to claims from the law's proponents and neoclassical economic models, cutting dividend taxes more than in half did not boost economic growth but did reduce government revenue and increase inequality.
How does tax cuts affect the economy?
They found that marginal rate cuts led to both increases in real GDP and declines in unemployment. A 1 percentage-point decrease in the tax rate increases real GDP by 0.78 percent by the third year after the tax change.
Why should we not cut taxes?
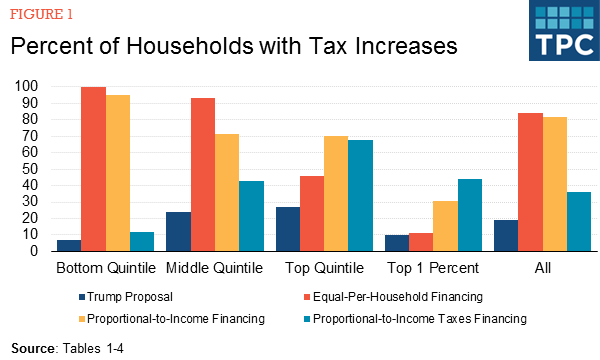
The government faces a large, long-term deficit, and tax cuts would make this problem worse. The proposed 10-percent income tax rate cut would provide disproportionately large benefits to wealthy households and little to lower income households.
Does cutting taxes increase inflation?
That really would drive prices down and slow inflation. Cutting taxes, by contrast, will boost demand for products already in short supply. And that is likely to only increase prices—exactly the opposite effect of what these pols claim to want.
The Disadvantages of Tax Cuts | Sapling
Tax cuts reduce the tax obligations of taxpayers who meet specific criteria, or of all taxpayers in a country. Lower taxes almost always seem desirable from the taxpayer's point of view, and there are arguable benefits of cutting taxes in different areas, but tax cuts also come with a distinct set of disadvantages.
How do taxes affect the economy in the long run? | Tax Policy Center
Primarily through the supply side. High marginal tax rates can discourage work, saving, investment, and innovation, while specific tax preferences can affect the allocation of economic resources. But tax cuts can also slow long-run economic growth by increasing deficits. The long-run effects of tax ...
What Are Tax Cuts?
Tax cuts are changes in the law that reduce your tax payment along with government revenue.
How does the Small Business Tax Cuts work?
Small business tax cuts help entrepreneurs starting new businesses. This can help add jobs since small businesses create roughly 64% of all new private-sector jobs. 3. Corporate tax cuts lower corporate income taxes. That gives corporations more money to invest back into their businesses, which could, in turn, help create jobs.
How does capital gains tax affect investors?
Capital gains tax cuts reduce taxes on sales of assets. That gives more money to investors.
Why is payroll tax cut important?
That gives corporations more money to invest back into their businesses, which could, in turn, help create jobs. Payroll tax cuts lower the payments made to Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment taxes. Businesses and employees share this cost, so a payroll tax cut helps both parties.
How does income tax affect consumers?
Income tax cuts reduce the amount individuals and families pay on wages earned. When people can take home more of their paychecks, consumer spending increases.
Why do economists use the Laffer curve?
Economists use something called the "Laffer Curve" to measure this relationship between current tax rates, the proposed tax cuts, and the expected economic growth. 1.
What does inheritance tax cut mean?
Inheritance or estate tax cuts reduce the amount paid by heirs on their parents' assets.
Why is cutting taxes good for growth?
There's a simple logic behind the idea that cutting taxes boosts growth: Cutting taxes gives people more money to spend as they like, which can boost economic growth.
What did the moderators ask Donald Trump about his tax reform pans?
Moderator John Harwood asked Donald Trump about the idea that his massive tax cuts would make the economy take off "like a rocket ship" (an idea that Trump staunchly defended).
How much gap does Ben Carson have in taxes?
Ben Carson's tax plan, for example, appears to leave a $2 trillion gap between spending and revenue, according to math from CNBC debate moderator Becky Quick this week (and Carson's math — in which he seemed to say he would somehow tax all of GDP, not just income — is not how taxes currently work).
What did Ted Cruz say about the tax plan?
Ted Cruz got at a similar idea, referencing the tax plan he unveiled Thursday: " [I]t costs, with dynamic scoring, less than $1 trillion. Those are the hard numbers. And every single income decile sees a double-digit increase in after-tax income. ... Growth is the answer. And as Reagan demonstrated, if we cut taxes, we can bring back growth."
Can tax cuts boost economic growth?
The Long Answer: Tax cuts can boost economic growth. But the operative word there is "can.". It's by no means an automatic or perfect relationship. We know, we know. No one likes a fact check with a nonfirm answer. So let's dig further into this idea.
What is Break It Down on NPR?
Have something you want us to fact check? Put it in the comments section or send us an email at [email protected].
Do tax cuts boost the economy?
But in practice, it's not always clear that tax cuts themselves automatically boost the economy, according to a recent study. " [I]t is by no means obvious, on an ex ante basis, that tax rate cuts will ultimately lead to a larger economy," as the Brookings Institution's William Gale and Andrew Samwick wrote in a 2014 paper.
Why are tax cuts important?
First, tax cuts boost business everywhere. Employers who are struggling to pay their bills (including national and local taxes), are not likely to think about hiring more people. But a tax cut would make a crucial marginal difference to them.
What happens if taxes are higher?
If it comes from higher taxes, that depresses business and employment all round. If it comes from increased borrowing, that just monopolizes investment funds that could have gone to – more productive – private businesses. And it adds to the debt and to the interest payments that burden taxpayers.
Is a tax cut a general or a quick cut?
A tax cut is both general and quick in its effect. Government spending, however, is not general. It is concentrated in sectors like road building and bureaucracy. It takes time for spending in the former to trickle out to the rest of the economy; and as for spending on the latter, well, we have too much of that anyway.
Does a tax cut increase the stimulus?
Sure, a tax cut might produce a short-term cut in government revenues that has to be funded, too. But the higher your taxes are, and the deeper you cut tax, the greater and quicker the stimulus. It also helps if people figure you really mean it and aren't going to raise taxes again.
Can you cut welfare benefits again?
But while it is very easy to boost welfare spending, it is nigh impossible to cut benefits again when the economy has righted itself. So you just end up increasing government welfare spending over the long term, which isn't likely to make your economy any more dynamic.
What are the advantages of tax cuts?
The real advantage of tax cuts is that they’re quick – taxpayers immediately have more money in their paychecks and companies often begin investing before the cuts have taken effect – while the impact of infrastructure or other spending takes much longer, even years, to work its way through the economy. But they both have their place in good economic policy.
Why did the 1980s have tax cuts?
In the past few decades, however, beginning with President Ronald Reagan and the advent of supply-side economics in the 1980s, governments have increasingly toyed with tax cuts to change aggregate demand in part because they are more likely to have an immediate effect on consumer and business expectations and incentives.
What did Donald Trump promise to do during his campaign?
During the presidential campaign, Donald Trump promised to boost the economy both by cutting taxes and investing more money in infrastructure. Usually, however, politicians and policymakers have favored one type of stimulus over the other. Conservatives like tax cuts, while liberals favor more spending. In the Trump administration, tax cuts appear ...
Who was the first economist to suggest that an economy's ills could be traced to the misalign?
British economist John Maynard Keynes was the first to suggest in the 1930s that an economy’s ills could be traced to the misalignment of what he called aggregate demand, which is made up of consumption, investment, government spending and net exports. So if there’s trouble in the economy, a government could try to move the needle by spending more ...
Do conservatives like tax cuts?
Conservatives like tax cuts, while liberals favor more spending. In the Trump administration, tax cuts appear to have won the argument for now. Republicans unveiled the blueprint of a major tax overhaul, which White House officials predict will boost economic growth to more than 3 percent a year. In the meantime, infrastructure investment remains ...
Do tax cuts pay for themselves?
Very often those advocating significant tax cuts claim that the cuts will pay for themselves in terms of ultimate tax revenues. That, of course, is an empirical issue but it misses the point. No one ever claims that expenditure increases pay for themselves (in terms of future tax revenues). The relevant point is how much does each encourage economic growth.
When did the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act go into effect?
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA)—reflecting President Trump's plan—was ultimately signed into law on Dec. 22, 2017. It went into effect on Jan. 1, 2018.
How much less are middle income families expected to pay in taxes?
While middle-income families were expected to pay about $900 less in taxes, those in the top 0.1% of earners were expected to receive an average tax cut of about $190,000. Those estimates appear to be playing out as expected.
How many tax brackets did Trump propose?
President Trump initially proposed to lower income taxes and reduce the number of tax brackets from seven to three—12%, 25%, and 35%. 3 That didn't happen. The TCJA still provides for seven brackets, but they've been reduced somewhat: 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35%, and 37%. 4
How much did the TCJA add to the federal deficit?
The Effect on the Federal Deficit. Official estimates found that the TCJA would have been expected to add between $1 trillion and $2 trillion to the federal deficit before 2025. 14 However, the COVID-19 pandemic and federal spending in response increased the federal deficit much more quickly.
How much was the TCJA tax reduction?
Before the TCJA took effect, the Tax Policy Center estimated that the tax cuts would result in an average tax reduction of $1,600. 8 However, most of those benefits were expected to be enjoyed by high-income families with more than $300,000 in annual income.
How much is the deficit in 2020?
It's now much more difficult to determine what the deficit would have been as a result solely of the TCJA. As of October 2020, the federal deficit was more than $3.1 trillion. 15 In 2017, the deficit was $665 billion.
How much is the average tax wedge in 2020?
9 The average tax wedge was 29.8% in 2019, compared to 31.8% in 2017.
What were the effects of Bill Clinton's tax policies?
President Bill Clinton's tax policies provided insight into the impact of both tax increases and decreases. The Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act was passed in 1993 and it included a series of tax increases. It hiked the top income tax rate to 36%, with an additional surcharge of 10% for the highest earners. It removed the income cap on Medicare taxes, phased out certain itemized deductions and exemptions, increased the taxable amount of Social Security, and raised the corporate rate to 35%. 1
Why did Obama push for higher taxes?
President Barack Obama consistently pushed for higher taxes on the rich to help reduce the deficit. Later, President Donald Trump got a substantial tax decrease across the board, with the bulk of the cuts benefitting upper-income taxpayers.
What was the tax rate in the 1980s?
GDP hit a low of 9.9% and a high of 12.9%. 9 This indicates that the best way to jump-start revenues is to grow the economy through stimulative tax policies.
Why did Reagan believe that lower rates would translate into higher revenue?
Reagan also believed that, over time, lower rates would translate into higher revenue because more jobs mean more taxpayers. He essentially put into practice the economic theories of Arthur Laffer, who summarized the hypothesis in a graph known as the " Laffer Curve .".
What did Ronald Reagan say about the economy?
He said that the way to promote economic growth was to gradually reduce taxes by 30% over three years, concentrating most of it in the higher income brackets. It was known as " supply-side " or " trickle-down " economics, but the media dubbed it " Reaganomics ."
How long did the recession last under Reagan?
Initially, inflation was reignited and the Federal Reserve hiked interest rates. This caused a recession that lasted for about two years. But once inflation was brought under control, the economy began to grow rapidly and 16.5 million jobs were created during Reagan's two terms. 3.
What was the tax relief act?
When the Newt Gingrich-led Republicans wrested control of the House of Representatives in 1994, they ran on a platform known as the Contract with America. The provisions included commitments to reduce taxes, shrink the federal government, and reform the welfare system.
What was the corporate tax rate in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act?
One of the central features of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act was a drop in the corporate income tax rate, from 35% to 21%.
How much did the JPMorgan tax cut add to the profit?
Jamie Dimon says tax cuts added $3.7 billion to JPMorgan's profit. Congress has yet to take up spending cuts to big-ticket items like Medicare and Social Security that the White House had proposed to curb deficits. Still, mounting debt makes conversations around future expenditures more difficult.
How much did the federal tax bill decline in 2018?
About 66% of taxpayers saw their federal tax bill decline by more than $100 in 2018, the congressional Joint Committee on Taxation reported in March. And according to the tax preparation giant H&R Block, total liabilities are down by nearly 25%.
Why do employers use pass through deductions?
According to Nancy Abramowitz, head of the federal tax legal clinic at American University, employers have used it as a reason to encourage low-wage workers to become independent contractors, which also comes with the loss of many rights and benefits.
Why are lawmakers choking on passing infrastructure packages?
Lawmakers have choked on passing a large infrastructure package, for example, because there's no plan to pay for it. "In some ways, our economy is held back by the public investments that we are not making," said Steve Wamhoff, director of federal tax policy for the left-leaning Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy.
Why is it good to have better factories?
That's a good sign because better factories, equipment and tools are supposed to boost productivity, which in some cases allows workers to make more money . Wages did start to grow a bit faster at the end of 2018, at least by some measures, especially for workers on the lower end of the income spectrum.
When is the first tax day in 2019?
Charts by Caroline Matthews, CNN Business. Updated 10:42 AM ET, Mon April 15, 2019. Monday is the first Tax Day under the new rules of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, but Americans have been adapting to the law since it passed in late 2017.
What would be the effect of cutting FICA taxes?
An alternative to a broad income tax cut would be cutting FICA taxes, the bulk of the payroll tax , which would help employees and employers. Reducing FICA taxes from 12.4 percent to 6 percent would reduce both the employee paid tax and the employer match by 3.2 percent, increasing take-home pay and leaving companies more money to create jobs or reinvest in production. Cutting payroll taxes also circumvents government bureaucracy because the IRS doesn’t have to process income tax adjustments or issue credit checks.
What was the economy like in the 1970s?
The U.S. economy stagnated during the 1970s but was revived from its intense inflation, unemployment, and recession by the pro-growth policies of the Reagan era, not stimulus spending. Tax cuts and appropriate monetary policy improved the economy after spending increases under former Presidents Ford and Carter had failed.
What is the fastest way out of economic downturns?
Well, the historical and empirical data proves that the fastest way out of economic downturns is letting individuals and businesses keep more of their money, creating more incentives to produce.
What is the road out of recession?
The road out of this recession is one that creates sustained economic growth, not short-term spending increases. It’s the difference between eating healthy with daily exercise and drinking a Red Bull: one offers a lifetime of benefits, the other causes a burst of energy and then a crash.
Can you cut taxes and spend too?
But just like the value of exercise would be negated by poor eating habits, you can’t cut taxes and spend too. Fiscal stimulus might be politically advantageous, but a sweeping array of tax cuts, targeted to reach all sectors of the market, would do far more to restore the economy to long-term health.
Will tax cuts improve the economy?
Tax cuts will not bring immediate improvement. However, if appropriately used, they will help the economy much faster than stimulus by paving the way for long-term, sustained growth.
Is FICA cut bad for Social Security?
There are downsides to the FICA cut however. Social Security is already in financial trouble, and cutting its revenue stream would require a complete revamping of the social safety net system (a good, though complicated thing to do).
How does cutting taxes affect the economy?
Cutting taxes reduces government revenues, at least in the short term, and creates either a budget deficit or increased sovereign debt. The natural countermeasure would be to cut spending. However, critics of tax cuts would then argue that the tax cut is helping the rich at the expense of those with fewer resources because the services that would likely get cut are beneficial to those in a lower income bracket. Proponents argue that by putting money back in consumer's pockets spending will increase; hence, the economy will grow and wages will rise. At the end of the day, the outcome depends on where the cuts are made.
Why are tax cuts important in 2021?
Updated Jun 30, 2021. Advocates of tax cuts argue that reducing taxes improves the economy by boosting spending. Those who oppose them say that tax cuts only help the rich because it can lead to a reduction in government services upon which lower-earning individuals rely.
What is shifting tax burden?
A shifting tax burden describes the situation where the economic reaction to a tax causes prices and output in the economy to change, thereby shifting part of the burden to others.
How does reducing taxes affect aggregate demand?
Reducing taxes thus pushes out the aggregate demand curve as consumers demand more goods and services with their higher disposable incomes. Supply-side tax cuts are aimed to stimulate capital formation. If successful, the cuts will shift both aggregate demand and aggregate supply because the price level for a supply of goods will be reduced, which often leads to an increase in demand for those goods.
What is the largest source of income for the federal government?
The federal tax system relies on a number of taxes to generate revenue. By far the largest source of funds is the income tax that individuals, estates and trusts pay. In 2018, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) collected a net $1.57 trillion in personal income taxes, or 52.4% of the total. 1 Personal income taxes are levied against wages, interest, dividends and capital gains. Ordinary income rates are marginal based on income, while long-term capital gains enjoy preferential treatment. 2 3
What happens if you tax cigarettes?
If a tax is levied on a non- price sensitive good or service such as cigarettes, it wouldn't lead to big changes such as factory shutdowns and unemployment. Studies have shown that a 10% increase in the price of cigarettes only reduces demand by 4%. 6 The tax imposed on luxury goods in 1991 was also 10%, but left yacht makers claiming an 86% drop in sales and thousands of lost jobs. 5 Regardless, tax shifting should always be considered when setting tax policy.
Why is cutting income tax so emotional?
Cutting income taxes is more emotional because of the progressive nature of the tax. Reducing taxes on a family with a small adjusted gross income (AGI) will save them less in total dollar amounts than a slightly smaller tax cut on a family with a much higher salary.

The Tax System
A Shifting Tax Burden
- The federal government uses tax policy to generate revenue and places the burden where it believes it will have the least effect. However, the "flypaper theory" of taxation (the belief that the burden of the tax sticks to where the government places the tax), often proves to be incorrect. Instead, tax shifting occurs. A shifting tax burden describes the situation where the economic re…
Gross National Product
- Gross national product (GNP), a measure of a nation's wealth, is also directly affected by federal taxes An easy way to see how taxes affect output is to look at the aggregate demandequation: GNP=C+I+G+NXwhere:C=Consumption spending byindividualsI=Investment spending (business…
Tax Equity?
- Because of the ideal of fairness, cutting taxes is never a simple task. Two distinct concepts are horizontal equity and vertical equity. Horizontal equity is the idea that all individuals should be taxed equally. An example of horizontal equity is the sales tax, where the amount paid is a percentage of the article being purchased. The tax rate stays the same whether you spend $1 or …
The Optics and Emotions of A Tax Cut
- Reducing taxes becomes emotional because, in simple dollar terms, people who pay the most in taxes also benefit most. If you cut the sales tax by 1%, a person buying a Hyundai may save $200, while a person buying a Mercedes may save $1,000. Although the percentage benefit is the same, in simple dollar terms, the Mercedes buyer benefits more. Cutting income taxes is more emotion…
A Taxing Decision
- Cutting taxes reduces government revenues, at least in the short term, and creates either a budget deficit or increased sovereign debt. The natural countermeasure would be to cut spending. However, critics of tax cuts would then argue that the tax cut is helping the rich at the expense of those with fewer resources because the services that would likely get cut are beneficial to thos…