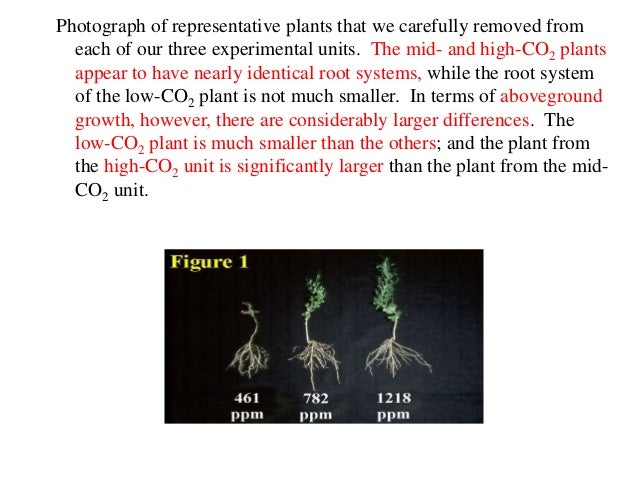
How does increased CO2 affect plant growth?
More CO2 in the atmosphere hurts key plants and crops more than it helps
- Fertilizer alone does not make a successful garden. A lot of myths have a grain of truth to them. ...
- CO2 is natural, but can also be harmful. ...
- It’s all about balance. ...
- Climate change is hard on plants. ...
- Agricultural experiments show negative effects. ...
- Bad news can lead to our making needed changes. ...
What is the relationship between plants and CO2?
What is the relationship between plants and animals in the carbon dioxide oxygen cycle? Plants and animals are linked to each other through the carbon dioxide and oxygen cycle. Plants produce oxygen, a gas that animals and other living things need.
What is the optimal CO2 for plants?
lower levels of carbon dioxide than ambient can decrease plant growth 30-40% (at 150 ppm) Conversely, with a CO2 level about 500 ppm plant growth increased by 15-25%. Between 340 ppm – 700 ppm, CO2 can increase growth by 30-40%. The wide band is due to variation between crops and to conditions. This graph is based on data from about 60 ...
Can plants survive without carbon dioxide?
The reaction is powered by sunlight, and uses a combination of CO2 and water. Oxygen is the natural by-product. So, without carbon dioxide, a plant would basically starve even if you had a sunny spot, lots of water and even extra fertilizer.

How does increased CO2 affect plant growth?
Studies have shown that higher concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide affect crops in two important ways: they boost crop yields by increasing the rate of photosynthesis, which spurs growth, and they reduce the amount of water crops lose through transpiration.
Does CO2 speed up plant growth?
Writing in the journal Science, researchers concluded that elevated atmospheric CO2 actually reduces plant growth when combined with other likely consequences of climate change -- namely, higher temperatures, increased precipitation or increased nitrogen deposits in the soil.
What does CO2 help plants with?
Photosynthesis acts as the lungs of our planet – plants use light and carbon dioxide (CO₂) to make the sugars they need to grow, releasing oxygen in the process.
Is too much CO2 bad for plants?
High CO2 levels cause plants to thicken their leaves, which could worsen climate change effects, researchers say. Plant scientists have observed that when levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere rise, most plants do something unusual: They thicken their leaves.
Can you have too much CO2 in your grow room?
Too much CO2 can be a problem, and this is not only an issue for your plants in a grow room, it also has negative effects for you. As mentioned, plants need CO2 to live, but give them too much and the vital nutrients they produce, become depleted.
What happens when CO2 rises?
Likewise, when carbon dioxide concentrations rise, air temperatures go up, and more water vapor evaporates into the atmosphere—which then amplifies greenhouse heating.
How do you feed CO2 to plants?
Using exhale CO2 bags are the natural and easiest way of adding CO2 to your grow room. The Exhale CO2 bag cultivates carbon dioxide 24 hours a day with no need to refill bottles or use expensive production units. They work through photosynthesis – photosynthesis is the process by which plant leafs make carbohydrates.
How much CO2 do plants need?
Plants during photosynthesis use carbon dioxide. Rate of consumption varies with crop, light intensity, temperature, stage of crop development and nutrient level. An average consumption level is estimated to be between 0.12–0.24 kg/hr/100 m2.
How does carbon dioxide affect crops?
Studies have shown that higher concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide affect crops in two important ways: they boost crop yields by increasing the rate of photosynthesis, which spurs growth, and they reduce the amount of water crops lose through transpiration. Plants transpire through their leaves, which contain tiny pores called stomata ...
Why do plants release water vapor?
During that process they release water vapor. As carbon dioxide concentrations increase, the pores don’t open as wide, resulting in lower levels of transpiration by plants and thus increased water-use efficiency.
How much does rainfed wheat increase yield?
For rainfed wheat grown in more arid climates, such as southern Africa and India, results show that doubled carbon dioxide levels, and their associated climate change impacts, increase yield by 8 percent, an increase that’s driven by improved crop water productivity of up to 50 percent.
Does maize have carbon dioxide?
Results show that maize suffers yield losses with doubled carbon dioxide levels, due in large part to the plant’s already greater efficiency at using carbon dioxide for photosynthesis compared with the other crops. Maize yields fall by 15 percent in areas that use irrigation and by 8 percent in areas that rely on rain.
Why are C4 plants so productive?
C4 plants can be much more productive, especially under hot and dry conditions. They came to dominate Earth’s tropical grasslands from 5m to 10m years ago, probably because the world became drier at this time and their water use is more efficient.
Will fossil fuels make it harder to grow food?
Many projections suggest that burning fossil fuels and the resulting climate change will make it harder to grow enough food for everyone in the coming decades.
Is photosynthesis flawed?
Unfortunately, photosynthesis is flawed. Molecules of CO₂ and oxygen are similar shapes and the key mechanism that harvests CO₂, an enzyme with the catchy name of RuBisCO, sometimes mistakes an oxygen molecule for one of CO₂. This wasn’t a problem when RuBisCO first evolved.
Does C3 affect photosynthesis?
But, as we know, C3 plants waste a lot more resources at higher temperatures, so any increase in photosynthesis from rising CO₂ levels seems likely to be at least cancelled out by the effects of the global warming it will cause. And that’s without factoring in changes to rainfall patterns such as more frequent droughts.
What happens to a tree when carbon dioxide levels are high?
But when carbon dioxide levels are high, the leaf pores shrink. This causes less water to be released, diminishing the tree’s cooling power. The warming effects of carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas have been known for a long time, says Caldeira.
Why do we need to take great care in considering what kind of changes we make to forests and other ecosystems?
We need to take great care in considering what kind of changes we make to forests and other ecosystems, because they are likely to have important climate consequences. ”. The study is published in the May 3-7 online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
How do plants give off water?
Plants give off water through tiny pores in their leaves, a process called evapotranspiration that cools the plant, just as perspiration cools our bodies. On a hot day, a tree can release tens of gallons of water into the air, acting as a natural air conditioner for its surroundings.
Does carbon dioxide reduce evaporative cooling?
Previous work by Carnegie’s Chris Field and Joe Berry had indicated that the effects were important. “There is no longer any doubt that carbon dioxide decreases evaporative cooling by plants and that this decreased cooling adds to global warming,” says Cao.
Why are farmers producing more food on less land?
Thanks in large part to longer growing seasons, fewer frost events, more precipitation, and the fertilization effect of atmospheric carbon dioxide, farmers are producing more food on less land, allowing them to feed a growing global population.” (Read more) The Center for the Study of Carbon Dioxide and Global Change provides summaries ...
What is the Heartland Institute website?
The Heartland Institute has created a new website (Climate at a Glance) which “puts frequently argued climate issues into short, concise, summaries that provide the most important, accurate, powerful information.) Their section on crop production begins:
Does warming the Earth affect plants?
Increasing CO2 and warming have enhanced plant growth and makes plants more water-efficient. And, according to NASA, “greening of the Earth mitigates surface warming” (Link). NASA writes: “A new study reports that increased vegetation growth during the recent decades, known as the ‘Greening Earth’, has a strong cooling effect on ...
Is carbon storage good for plants?
Rather, it will likely be a major benefit, enhancing plant growth and soil organic carbon storage, which (in addition to their own virtues) will provide significant negative feedback to global warming as the Greening of the Earth continues!
Why aren't plants growing faster?
Here's Why Plants Aren't Just Growing Faster With All The CO2 in The Atmosphere. Rising atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) is warming our climate , but it also affects plants directly. A tree planted in the 1850s will have seen its diet (in terms of atmospheric carbon dioxide) double from its early days to the middle of our century.
How many gigatons of CO2 are released by humans?
This stands against over 11 gigatons of human-induced release of CO2. It is also unclear what fraction of the three gigatons plants are taking up due to rising levels of CO2.
Why do plants close their leaf pores?
Plants tend to close their leaf pores slightly under elevated levels of CO2, leading to water savings. In certain (dry) areas, this may indeed lead to more plant growth. But again, things are much more complex and we don't always see positive responses.
Do plants have shorter lifespans?
Even if plants grow more and faster, some studies show there is a risk for them to have shorter lifespans. This again can have negative effects on the carbon locked away in biomass and soils. In fact, fast-growing trees (e.g. plantation forests) store a lot less carbon per surface area than old, undisturbed forests that show very little growth.
Does photosynthesis increase biomass?
But things are a lot more complex than that. Higher levels of photosynthesis don't necessarily lead to more biomass production, let alone to more carbon dioxide sequestration. At night, plants release CO2 just like animals or humans, and if those respiration rates increase simultaneously, the turnover of carbon increases, ...
Why is carbon dioxide increasing?
While rising carbon dioxide concentrations in the air can be beneficial for plants, it is also the chief culprit of climate change. The gas, which traps heat in Earth’s atmosphere, has been increasing since the industrial age due to the burning of oil , gas, coal and wood for energy and is continuing to reach concentrations not seen in ...
What causes plant growth?
Carbon dioxide fertilization isn’t the only cause of the increased plant growth—nitrogen, land cover change and climate change by way of global temperature, precipitation and sunlight changes all contribute to the greening effect.
What is greening in plants?
The greening represents an increase in leaves on plants and trees equivalent in area to two times the continental United States. Green leaves use energy from sunlight through photosynthesis to chemically combine carbon dioxide drawn in from the air with water and nutrients tapped from the ground to produce sugars, which are the main source of food, ...
What percentage of Earth's surface is covered by vegetation?
About 85 percent of Earth’s ice-free lands is covered by vegetation. The area covered by all the green leaves on Earth is equal to, on average, 32 percent of Earth’s total surface area — oceans, lands and permanent ice sheets combined.