
Some advantages of bioplastics are:
- Reduced carbon footprint.
- Savings in energy during production.
- Non-renewable sources are not consumed.
- Reduction of non-biodegradable waste, which pollutes the environment.
- No health-damaging additives are contained, like phthalates or bisphenol-A.
- They do not alter the flavour and smell of food they store.
What are the advantages of bioplastic products?
What are the advantages of bioplastic products? Bio-based plastics can help to reduce the dependency on limited fossil resources, which are expected to become significantly more expensive in the coming decades. Bio-based plastics are made from renewable sources instead of oil and that way gradually substitute fossil resources used to produce ...
What are bioplastics and why is it confusing?
The term “bioplastics” is actually used for two separate things: bio-based plastics (plastics made at least partly from biological matter) and biodegradable plastics (plastics that can be completely broken down by microbes in a reasonable timeframe, given specific conditions).
Why are bioplastics good?
- Burning
- Bacterial decay
- Conversion to a gas or liquid fuel
How much does bioplastic cost?
The cost of some next-generation bioplastics are now even with those derived from oil —a milestone Renmatix says it can meet even at today’s oil price of around $50 per barrel (other companies have said their break-even figure is closer to $130, a price last seen in 2008 ).
How does bioplastic impact society?
The increased use of bioplastics is reducing landfill waste, utilizing renewable feedstocks, recycling petroleum based plastics and limiting the use of finite resources to create products that perform just as well, if not better, than traditional plastics in many applications.
What are the benefits of bioplastics?
The often-cited advantages of bioplastic are reduced use of fossil fuel resources, a smaller carbon footprint, and faster decomposition. Bioplastic is also less toxic and does not contain bisphenol A (BPA), a hormone disrupter that is often found in traditional plastics.
How do bioplastics help the environment?
Bioplastics come from natural sources including crops like corn and switch grass. This makes them conserve non-renewable sources of energy such as petroleum. One of the main advantages of using biodegradable plastic is a significant reduction in carbon emissions during the manufacturing process.
How are bioplastics promising for humankind?
For more than a decade, bioplastics, which can be completely biodegradable, have been a promising alternative to plastic – particularly PET used for the ubiquitous plastic bottles that contain water and soda. Many companies have experimented with bioplastic packaging.
What are advantages of biodegradable?
Biodegradable plastic's ability to break down within a year means it has several advantages over traditional plastics: It decreases the waste sent to landfills or incinerators. It takes less energy to manufacture. It releases fewer harmful substances when breaking down.
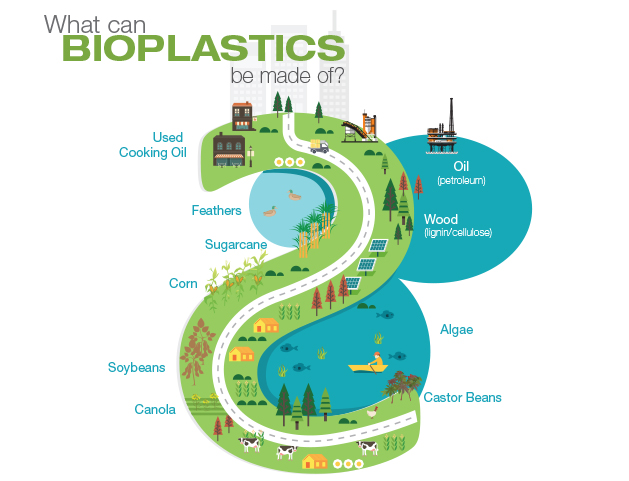
What are bioplastics made of?
Bioplastics are, in simple terms, plastics made from renewable feedstocks, which can include corn, sugar cane, potatoes, coconuts, mushrooms, wheat, wood, or soy beans to name a few. (Conventional plastics are made from crude oil.) Like conventional petrochemical-produced plastics, there are several types of bioplastics: Some ...
Is plastic made of oil?
As we reported in the Nov/Dec 2011 Green American, plastics are rarely just made out of oil—the y’re mixed with a host of chemical additives to enhance their capabilities, i.e. make them more flexible or less flammable, to prevent them from degrading or to tint them pretty colors, write Mike Neal and Dr. Anthony Andrady in a 2009 research paper published in the Royal Society’s Philosophical Transitions B. The same holds true for bioplastics—they aren’t just made from plants. They may have the same toxicity issues that a conventional plastic does.
Is it possible to recycle bioplastics?
Recycling bioplastics isn’t always an easy accomplishment. Recyclers fear that non-petroleum-based plastics will corrupt their streams (many bioplastics have lower heat resistance—and that whole biodegrading thing they might do is not desirable in the eyes of recycled plastics manufacturers for fear that the recycled plastic will degrade prematurely).
What is DBI bioplastics?
DBI Bioplastics is 90% pure biomaterial from Brazilian sugar canes. Farmed under strict sustainable guidelines in respect of natural resources, biodiversity and crop rotation. Being a by-product derived from food and fuel extraction and production, the raw material used for Bioplastics is an extremely efficient and sustainable raw material. The Bioplastics end product is fully recyclable and can be included in a closed loop system for maximum sustainable impact.#N#An estimated 99% of all plastic is made from fossil fuels such as oil and gas. The remaining 1% is made from natural raw materials such as corn, cane sugar and sugar beet.
What is plastic made of?
An estimated 99% of all plastic is made from fossil fuels such as oil and gas. The remaining 1% is made from natural raw materials such as corn, cane sugar and sugar beet.
What are the benefits of biobased plastics?
Another huge benefit of biobased plastics is their possibility of using a local resource like plants or other kind of biomass (e.g. corn, crab shells, straws, hemp fibers etc…) for the production. This fits totally into the concept of 3d printing and the circular economy. Production material does not need to be shipped around the world anymore but plastics can be produced closer where consumption is. Furthermore, plastics that are bio-based and compostable can help to divert biowaste from landfill and increase waste management efficiency.
Why are bioplastics not being adopted?
One of the main reasons why bioplastics have not been adopted more yet, is that often they can’t compete on price with fossilbased materials (at least this goes for the traditional manufacturing technologies). That means they need to offer other benefits, let’s have a look into these benefits.
What are the environmental issues associated with growing plants for bioplastic?
Among them: pollution from fertilizers and land diverted from food production.
What is bio plastic made of?
It is also often called bio-based plastic. It can either be made by extracting sugar from plants like corn and sugarcane to convert into polylactic acids (PLAs), or it can be made from polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) engineered from microorganisms.
Why is industrial composting necessary?
Industrial composting is necessary to heat the bioplastic to a high enough temperature that allows microbes to break it down . Without that intense heat, bioplastics won't degrade on their own in a meaningful timeframe, either in landfills or even your home compost heap.
What is BPI in composting?
The Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) is a non-profit formed to advocate for biodegradable products and waste infrastructure. They see bioplastics and industrial composting as untapped potential. “Composting is inherently local,” says Rhodes Yepsen, the executive director of BPI.
How much plastic is in the ocean?
More than eighteen trillion pounds of plastic have been produced to date, and eighteen billion pounds of plastic flows into the ocean every year. It ensnares the marine animals we cherish and the fish we put on our plates, it appears in the table salt we use, and it’s even found in our own bodies. As more research on the impact ...
Where does Eco Products buy their PLA?
They buy raw corn-based PLA from NatureWorks, a chemical manufacturer in Blair, Nebraska. Eco Products deferred questions about their products to the Plastics Industry Assocation (PLASTICS), who said that demand for bioplastics has increased in the past decade or so.
Where does PLA come from?
Because PLA often comes from the same large industrial facilities making products like ethanol , it’s the cheapest source of bioplastic. It’s the most common type and is also used in plastic bottles, utensils, and textiles.
What is bioplastics?
1. Bioplastics are plastics that are made from a renewable resource and/or are able to break down naturally. 2. The first-ever man-made plastic was actually a bioplastic. 3. Bioplastics can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels, support sustainability in the industry and allow manufacturers to diversify feedstocks.
Why is plastic packaging important?
Plastic packaging protects products in transit and with a lower environmental impact than alternatives. With more consumers using e-commerce than ever before, industry is leading the way in developing new recycling initiatives that address waste challenges.
When was plastic invented?
The first man-made plastic, introduced in 1862, was a bioplastic, meaning it was made from a renewable resource. Bioplastics can be biobased (made from a renewable resource), biodegradable (able to break down naturally) or both.
Can bioplastics be biodegradable?
Biodegradable bioplastics can be just as durable as other types of plastic, as they only break down in specific conditions. There’s no need to worry about a bioplastic container breaking down on the shelf. The way they biodegrade depends on their intended use.
What are bioplastics made of?
Bioplastics are either: 1) made from a renewable resource such as corn or sugar cane (biobased), 2) break down completely via a natural process (biodegradable) 3) are both biobased and biodegradable. They are used in the same ways as other plastics: packaging, agriculture, medical, automotive parts, 3D printing and more.
What is the Bioplastics Division?
The Bioplastics Division of PLASTICS works to promote the development of bioplastics as an integral part of the plastics industry by: Educating the plastics industry, federal, state and local governments, and the value chain. Articulating clear and consistent descriptions of the different bioplastics options.
What is biodegradable plastic?
Biodegradable bioplastics are plastics that will be consumed completely with the assistance of microorganisms and converted into natural products, such as biomass, water, and carbon dioxide. There are different ways to be biodegradable, with the most common being industrial composting.
How many tons of plastic were produced in 2014?
Globally, over 1.7 million metric tons were produced in 2014 and contributed to $4.4 billion and 32,000 jobs in the U.S. Bioplastics are one of the fastest growing sectors of the plastics industry, with an anticipated 20-30% annual growth.
Why are bioplastics important?
Traditional plastics come from heating and treating oil molecules until they turn into polymers. Bioplastics come from natural sources including crops like corn and switch grass.
Why are biodegradable plastics good for the environment?
This is achieved when the bacteria and fungi present in the surrounding environment naturally metabolizes the plastics.
Why do we need to compost biodegradable plastic?
Biodegradable plastics require composting or recycling to ensure proper breakdown of the plastic pieces. The requirement to properly dispose of biodegradable plastic products automatically reduces the amount of waste. This waste would otherwise be sent to landfills in order to discard them.
Why do plastics turn into compost?
They also help to further break down the structure of a biodegradable plastic. Created to address the plastic waste problem, these plastic types will turn to compost after a certain period of time.
Why is biodegradable plastic important?
As you can see, biodegradable plastic is extremely significant and proves to be of great importance when it comes to reducing waste and helping the environment. With the increased use and manufacturing ...
What are the advantages of biodegradable plastic?
One of the main advantages of using biodegradable plastic is a significant reduction in carbon emissions during the manufacturing process. Furthermore, since the materials used to create biodegradable plastics are plant-based, minimal carbon is emitted during the composting process. 3. Consumes Less Energy.
Do biodegradable plastics need fossil fuels?
The manufacturing process of biodegradable plastics requires fewer amounts of energy. Also, they do not need fossil fuels to be recycled. Since the energy requirement is less, the pollution and environmental impact are significantly reduced.
Can bioplastics be the environmental answer?
Enter bioplastics: much like classic plastic in their appearance and usage, but considerably different when it comes to their impact on the planet.
What is bioplastic made from?
Whether you’re dealing with PET plastic, PVC, polysytrene, or polyethylene (PE), you’ll always find two key ingredients creating the base structure for all polymers: Crude oil (petroleum) or natural gas.
Advantages and disadvantages of bioplastics for the environment
Now that you know how these ingenious materials are made, let’s get to the crucial issue: Are bioplastics good for the environment?
Disadvantages of bioplastics
Despite all the positives, there are a number of negative associations from using using bioplastics.

What Is Bioplastic?
Plants, Oil, and The Fight For Food Security
- “The argument [for bio-based plastics] is the inherent value of reducing the carbon footprint,” says chemical engineer Ramani Narayanfrom Michigan State University, who researches bioplastic. About eight percent of the world’s oil is used to make plastic, and proponents of bioplastic often tout a reduction in this use as a major benefit. This argum...
What Happens When We're Done with It?
- Depending on the type of polymer used to make it, discarded bioplastic must either be sent to a landfill, recycled like many (but not all) petroleum-based plastics, or sent to an industrial compost site. Industrial composting is necessary to heat the bioplastic to a high enough temperature that allows microbes to break it down. Without that intense heat, bioplastics won't degrade on their o…
So, Should You Use It?
- One of the largest manufacturers of bioplastic in the U.S. is Colorado’s Eco Products. They buy raw corn-based PLA from NatureWorks, a chemical manufacturer in Blair, Nebraska. Eco Products deferred questions about their products to the Plastics Industry Assocation(PLASTICS), who said that demand for bioplastics has increased in the past decade or so. Consumer interest in sustai…