Genetics helps explain a lot of things, like what makes you unique, why you look like other members of your family, and why some diseases run in your family. Taking time to learn about genetics can help you understand your own health and make healthy choices. Genes that do not work correctly can cause problems.
Why learn about genetics?
Why learn about genetics? Why learn about genetics? How does genetics work? Why learn about genetics? Why Does Genetics Matter for Me? Genetics helps explain a lot of things, like what makes you unique, why you look like other members of your family, and why some diseases run in your family.
What are the benefits of genetic testing?
What are the benefits of genetic testing? From Genetics Home Reference. Learn more Genetic testing has potential benefits whether the results are positive or negative for a gene mutation. Test results can provide a sense of relief from uncertainty and help people make informed decisions about managing their health care.
What are the benefits of from genetics home reference?
From Genetics Home Reference. Learn more Genetic testing has potential benefits whether the results are positive or negative for a gene mutation. Test results can provide a sense of relief from uncertainty and help people make informed decisions about managing their health care.
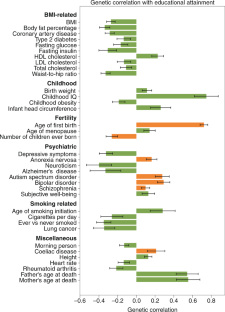
Does genetics affect choice of academic subjects and achievement?
Genetics affects choice of academic subjects as well as achievement. Sci. Rep.6:26373. 10.1038/srep26373 [PMC free article][PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]

Why is learning about genetics important?
Taking time to learn about genetics can help you understand your own health and make healthy choices. Genes that do not work correctly can cause problems. A group of rare diseases are caused when a single gene stops working normally.
What do you learn in genetics?
Genetics is the scientific study of genes and heredity—of how certain qualities or traits are passed from parents to offspring as a result of changes in DNA sequence. A gene is a segment of DNA that contains instructions for building one or more molecules that help the body work.
How is genetics used in everyday life?
Scientific research has today advanced further and identified genes coding for the way muscles in our body respond to diet and training, skin types and their response to nutrition, the control of hair fall, risk of diabetic complications, obesity, addictions and a lot more. “This actually came to us from the public.
Aneuploidy – anomaly in a whole chromosome or part of it
Supernumerary chromosome: Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) or Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) Missing chromosome: Turner’s syndrome (45,X) Missing part of...
Genetic mutation – gene anomaly
Substitution (change of one “letter” to another) Deletion (a portion of the gene is absent) Duplication (a portion of the gene is repeated) Some mu...
Genetic Diseases
There are thousands of genetic diseases, most often rare (affecting less than one in 2,000 people). Among the most common are: Cystic fibrosis (or...
Diagnostic Test
As the name suggests, this type of test is performed for the purpose of diagnosing and determining a genetic cause that explains symptoms or a dise...
Screening Test
The term “genetic screening” is used when the test identifies individuals who are more likely to have a genetic disease. However, further testing i...
Research Test
These tests are similar to diagnostic tests. However, the tests are conducted as part of a research protocol and, according to the study, the resul...
Proactive or Preventive Test
Advances in technology now allow several genes (panels) to be tested at the same time. Currently there are two types of clinical offers: Extended c...
Recreational Tests (directly to the consumer)
In recent years, a number of genetic tests offering information on genetic factors that have no health impact have been marketed. These tests estab...
Types of Technology
Not all genetic tests are equal and different technologies offer sometimes different results. Main technologies include: Caryotype: chromosome stru...
Why is it important to learn about genetics?
Taking time to learn about genetics can help you understand your own health and make healthy choices. Genes that do not work correctly can cause problems. A group of rare diseases are caused when a single gene stops working normally.
Why do we need genetics?
Genetics helps explain a lot of things, like what makes you unique, why you look like other members of your family, and why some diseases run in your family.
Genes and Health
Family members share genes, habits, lifestyles, and surroundings. These things can affect health and the risk for illness. Most people have a relative with a chronic disease or a health condition such as high cholesterol. If you have a close family member with a chronic disease, you may be more likely to get that disease.
Ian's Story
All my male relatives died at an early age, and heart disease is to blame. I had high cholesterol all my life, but because I exercised regularly and did not drink or smoke like my father and uncle, who died of heart attacks at age 53 and 63, respectively, I believed my risks were low. At age 49, I had a heart attack.
How do genetic variations affect people?
Also, genetic variations can influence how people respond to certain medicines or a person’s likelihood of developing a disease. Because parents pass their genes on to their children, some diseases tend to cluster in families, similar to other inherited traits. In most cases, multiple genes are involved. Researchers can use DNA sequencing ...
Why do researchers use DNA sequencing?
In most cases, multiple genes are involved. Researchers can use DNA sequencing to identify variations in a person’s genome. Some variations between individuals result from epigenetic differences. These are changes in gene function, some of which can be inherited but are not the result of changes in DNA sequence.
How many genes are there in the human genome?
Researchers estimate that humans have about 20,000 genes. All of an organism ’s genetic material, including its genes and other elements that control the activity of those genes, is its genome. An organism’s entire genome is found in nearly all of its cells.
What is the scientific study of genes and heredity?
Fold1 Content. What is genetics ? Genetics is the scientific study of genes and heredity—of how certain qualities or traits are passed from parents to offspring as a result of changes in DNA sequence. A gene is a segment of DNA that contains instructions for building one or more molecules that help the body work.
What is the name of the structure of DNA that contains instructions for building one or more molecules that help the body work?
A gene is a segment of DNA that contains instructions for building one or more molecules that help the body work. DNA is shaped like a corkscrew-twisted ladder, called a double helix. The two ladder rails are called backbones, and the rungs are pairs of four building blocks (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) called bases.
Why do scientists study bacteria?
Scientists also study the genes of bacteria, viruses, and fungi for solutions to prevent or treat infection. Increasingly, these studies are offering insight into how microbes on and in the body affect our health, sometimes in beneficial ways.
Do all living things have the same genes?
All living things evolved from a common ancestor. Therefore, humans, animals, and other organisms share many of the same genes, and the molecules made from them function in similar ways. Scientists have found many genes that have been preserved through millions of years of evolution and are present in a range of organisms living today.
What is additive genetic effect?
An additive genetic effect is the linear combination of the individual genetic effects.
What are the functions of the brain?
Mental functions, including most if not all aspects of human behavior, such as those related to learning, arise from the activity of the brain. Neural connections that generate and support mental functions are formed throughout life, which enables lifelong learning of new concepts and skills.
What is the significance of heritability?
Heritability is a statistic that, as commonly interpreted, captures how much of the variation of a trait is due to genetic differences. (It does not, however, capture how many genes or which genes/alleles are involved, or how much of the trait relies exclusively on the genome).
What are cognitive functions?
Cognitive functions, such as working memory, cognitive control, attention, intelligence and executive functions, as well as other related functions such as motivation and resilience, develop through the activity of the brain, which in turn depends on neural connectivity and function. Both the construction of the brain and the functioning ...
What is learning capacity?
Biologically, learning capacity allows behavioral responses to adapt progressively, modifying aspects that may favor the survival of the individual in a complex, dynamic and changing environment. Education relies on this learning capacity and it should optimize cognitive functions taking into account human culture.
Is negative affect heritable?
Conversely, negative affect is moderately heritable, as it yields a heritability value of 0.53. Interestingly, both positive and negative affect fluctuate over monthly periods, and these fluctuations show a significant heritability: 0.34 and 0.54, respectively.
Is a cognitive function heritable?
Put concisely, psychological traits, including cognitive functions that are indispensable for learning, are partially heritable. To quantify how much of the variation of a trait that is found among people in a given population is due to genetic differences, we use the heritability statistic.
What do geneticists believe?
Geneticists believe that the methods and techniques of genetics are applicable throughout the spectrum of biological activity , and are as relevant to molecular biology as to population studies.
What is the purpose of genetic variants?
Classically this involved the use of genetic variants (mutants) to upset the biological function of the cells or organisms and , from the effect of these mutations, to make deductions about the way cells and organisms worked.
Why did Sydney Brenner predict that genetics would disappear by the year 2000?
Sydney Brenner, writing in the 100th issue of Trends in Genetics in 1993, made the prediction that genetics as a separate subject would have disappeared by the year 2000, because all biology would be gene-centred and all biologists would be geneticists. The prediction may have been realised because of the advances in sequencing genomes ...