
What are two ways did the Crusades affect Europe?
Two major effects of the Crusades were that the kings' authority increased and the Europeans learned about new things from the Muslims they encountered. During the Crusades, the kings increased taxes to fund the cause. Many peasants also left their land to fight, and when they died, the land went to the king.
Why were the Crusades significant to the future of Europe?
What followed was a series of nine Crusades which altered history for people throughout both Europe and the Middle East. In general, the Crusades were significant because it involved increased interaction between groups of people who previously had limited contact.
What reasons did Europeans have to go on the Crusades?
Why did people go on a crusade?
- Positive Impacts Of The Crusades. The Crusades resulted in a more negative way. ...
- The Crusades Were A Series Of Sacred Wars. Jamie K. ...
- Causes And Effects Of The Crusades. the Crusades would both be lasting and surprising. ...
- The Story of the Crusades
How did the Crusades affect the life of the Europeans?
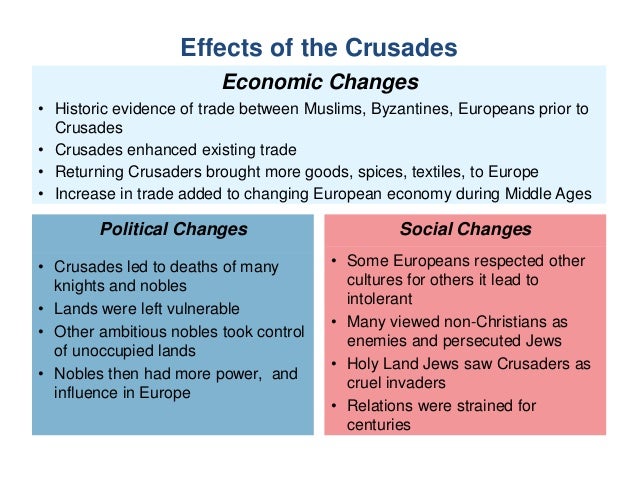
These effects profoundly changed the lives of Western Europeans. One of the many effects of the Crusades was that the pope and the kings of Western Europe became more powerful. In addition, Europeans began to trade with the Middle East. Trade increased as Western Europeans began to buy products like sugar, lemons, and spices.
What foods did the Crusades bring?
What was the bed made of before the Crusades?
What games were brought back to the Holy Land?
Did Muslims keep the medical knowledge of the Romans alive?
How did the Crusades influence Europe?
Crusading in northern and eastern Europe led to the expansion of kingdoms like Denmark and Sweden, as well as the creation of brand-new political units, for example in Prussia. As areas around the Baltic Sea were taken by the crusaders, traders and settlers—mostly German—moved in and profited economically.
What was one of the effects of the Crusades on European society?
After four Crusades, the Muslims won control of the Holy Lands. However, the crusades resulted in increased trade in Europe and the development of towns. Trade routes needed to be protected, which led to the rise of power of Kings and the decrease of power of the nobles.
What ideas did the Crusaders bring back to Europe?
WHAT DID THE CRUSADERS BRING BACK TO EUROPE? Crusaders returned with apricots, lemons, rice, dyes, spices, perfume, soap, and glass mirrors. They also brought back a musical instrument, the ancestor of the modern guitar.
What was a lasting effect on European culture after the Crusades?
Through the stabilization of societies, people became more independent and opened their eyes to new cultures. In the later years, this led to the thriving period in European history known as the Renaissance.
What was one direct result of the Crusades?
The immediate geopolitical results of the crusades was the recapture of Jerusalem on 15 July 1099 CE, but to ensure the Holy City stayed in Christian hands it was necessary that various western settlements were established in the Levant (collectively known as the Latin East, the Crusader States or Outremer).
What were the effects of the Crusades on Europe?
As a result of the Crusades, Europe saw tremendous intellectual growth, a strengthening of the merchant class through expansion in trade and the rise of new banking institutions. Unfortunately, all of these benefits came at the tremendous cost of lost lives and fortunes.
Why did the Crusades need supplies?
Because the Crusades went on for over two centuries, there was a need for goods and supplies. Merchants returning from the East brought spices, fruit and other commodities, while raw materials were sent back to the Holy Land to aid the Crusaders who remained.
How did the Crusades affect the feudal system?
The Crusades provoked the weakening of the feudal system as many of the hereditary lords died with their sons during the campaigns. With no one left to inherit, the lands were returned to the Crown. The Crusades saw massive casualties on both sides.
What was the flow of traffic from Europe to the Holy Land?
The flow of traffic from Europe to the Holy Land opened the doors to expansion in the trade of goods and ideas. While Europe was just emerging from the Dark Ages, the East was experiencing an intellectual Golden Age. Europeans were exposed to new concepts in mathematics, engineering and warfare, and they brought these ideas home when they returned.
How did the Crusades affect the Church?
While the Crusades enhanced the authority of the Church in Europe, they also caused a great deal of social chaos. Nowhere was this more immediate than in the Holy land itself. Between 1095 and 1291, various cities in the Holy Land repeatedly changed hands between Christian and Muslim invaders, usually with considerable violence involved. In 1099, for instance, Crusaders overran Jerusalem and conducted a citywide massacre of men, women and children. The Crusades also generated unrest in Europe. It now became acceptable to persecute and massacre Jews, who were also seen as enemies of the Church.
What were the consequences of the Crusades?
Although they ultimately failed to drive the Muslims from either Jerusalem or Byzantium, the Crusades had considerable social consequences for Europe and the Holy Land alike. They also prompted the expansion of trade and learning in Europe.
What did the Christian invaders do to the Holy Land?
Christian invaders introduced European-styled feudal estates across the Holy Land, overseeing both trade and agricultural production. They also left behind a considerable architectural imprint. In Jerusalem alone, they built numerous churches, a city gate, a public market and even a hospital.
What did the Crusaders take with them?
They took possession of Middle Eastern furniture and other items, some of which traveled back to Europe with them.
What was the Holy Land like in the 8th century?
As early as the 8th Century, the Muslim world had developed dynamic centers of learning and scholarship. Now the Holy Land became an intellectual crossroads, where the Crusaders encountered Islamic learning and carried it back to Europe with them.
What were the first cities to benefit from the Arabian trade?
A new interest in Arabian goods helped spark a growth in trade between Europe and Asia. The first to benefit were Italian port cities like Pisa and Genoa, since they were entry points into Europe. Gradually, though, the Italian monopoly was broken as trade made its way north.
What happened in 1099?
In 1099, for instance, Crusaders overran Jerusalem and conducted a citywide massacre of men, women and children. The Crusades also generated unrest in Europe. It now became acceptable to persecute and massacre Jews, who were also seen as enemies of the Church.
What were the positive impacts of the Crusades?
Some positive impacts were felt in Italy; although they had been trading with the East prior to the Crusades, they essentially dominated the entire Mediterranean by the end of them. One of the more lasting impacts was on the relationship between the Greek and Latin churches.
What did the Romantics point to in the Crusades?
And those versions inform how we view the Crusades today. The Romantics idealized the Middle Ages, pointing to the chivalry of knights and the piety of the people. During the rise of French nationalism in the 1800's, the French highlighted the Crusades as the country's first attempt to bring western civilization to the world.
What did Marxists see in the Crusades?
Marxists saw the Crusades as an attempt to address a shortage of resources in Europe and strip ped the Crusaders of any religious motivations. History books cemented the reputation of Crusaders as barbarians.
Was religion a central identifying force in the Crusades?
In Europe, religion was no longer a central identifying force. And as it emerged from the Dark Ages, the Crusades were seen as nothing more than the hysteria of the time. Each succeeding generation has presented its own version of the story of the Crusades. And those versions inform how we view the Crusades today.
Did the Crusades change the world?
After all this fighting , you'd think that the Crusades would have left immense impacts on the world. However, historians today attribute very little of what happened next in Europe or the Middle East to the Crusades [source: Madden ]. They generally believe that while the Crusades were significant at the time, they didn't really change the face ...
Why were the Crusades important?
In conclusion, the crusades were a vitally important event to European and Middle Eastern History. They were centered on a clash between different religions and helped transform Europe and the Middle East during the years of the Middle Ages. As well, many historians consider the effects of the crusades as an important event in the emergence ...
How did the Crusades affect the lives of Europeans?
A third major impact of the crusades was the effect it had on the role of feudalism in the lives of Europeans. Feudalism was a form of government common during medieval Europe that involved society being structured in a very rigid and hierarchical way. It was popular in European society from the 9th century until the 15th century and was ...
Why did the Crusaders wear crosses?
In fact, many of the crusaders wore crosses on their clothing and armor as they made their pilgrimage to the Holy Land. 'Knights of the Holy Ghost embarking on the Crusades' by Jacob, P. L. (1870) The crusades were a major event in the Middle Ages and had a profound impact on the world at the time. For example, one of the first major impacts ...
What was the Crusades?
The Crusades are one of the most significant events in the history of Europe and the Middle East. They were a series of religious wars carried out by Christian crusaders from Europe during the timeframe of the Middle Ages .
What was the Middle East like during the Crusades?
At the outbreak of the crusades in the 11th century, the Middle East was a major center of learning and knowledge. Due to its geographical location, the major Middle Eastern civilizations were at the crossroads of the Silk Road and therefore benefitted greatly from having access to both European and Asian knowledge.
How did feudalism affect the Renaissance?
As a result, the feudal system began to lose its hold on society which eventually led to the ideals of the Renaissance and the emergence of powerful city-states instead of absolute monarchs.
What was the target of the Crusades?
Jerusalem, the place holy to Islam, Christianity and Judaism was the target region. The Christians, Muslims and Jews had their share of positive and negative effects during the crusades. The bloody battles were fought for holy rights and with an aim to maintain sanctity, but in reality they were meaningless acts initiated by inhuman feelings ...
What were the negative effects of the Crusades?
Jews were hit the hardest during the crusades. When crusaders crossed the north of France and Germany, a lot of Jews were killed without cause. Their temples and books were destroyed. Their synagogues were in peril. By the end of the war, Jews had no land to call their own.
Why was the standing army important to Muslims?
The concept of standing army was introduced to them. Also, it was a great opportunity for Muslims to show their unity. They also promoted schools and mosques heavily during that period of the history. Feudalism was a huge issue in Europe at that time which was solved due to the crusades.
What did Christians learn about the Middle East?
When Christians moved to the Middle East, they learned a lot about the new culture. The West and the East merged their food, culture and ethics for the first time. They learned about a number of new things that were otherwise unknown to them. Also, the economy and trade sectors of both countries flourished.
How long was the Crusades?
The 196 year long battle was won by the Muslims, but not in a satisfactory form.
Why did the monarchy increase taxes?
Monarchy became dominant and the kings increased taxes in order to get funds for the crusades. The Christian and Muslim soldiers were killed in equal numbers. Bloodshed and unrest engulfed the continent. Feudalism ended but the heavy taxes levied by the Monarchs were a burden.
What foods did the Crusades bring?
Food: The Crusades brought about trade in many unusual exotic foods. Sugar, spices, dates, coffee, rice and apricots were now available, and rich Europeans could now present new foods on their dinner table as a sign of their wealth and importance.
What was the bed made of before the Crusades?
Bedding would have consisted of straw, with a bare wooden, stone or straw floor.
What games were brought back to the Holy Land?
Games like chess were also brought back, and medieval European farmers were glad to learn how to irrigate (water) their fields in a better way. Concentric (circular) walls for castles were first used in the Holy Land, as were water wheels and water clocks.
Did Muslims keep the medical knowledge of the Romans alive?
The Muslims kept alive the medical knowledge of the Romans after the Roman Empire collapsed in Europe (in 476AD), a time when literacy (reading and writing) was only common among Christian priests. The Muslim doctor, Avicenna, had written down all the ideas of the great Roman and Greek doctors like Galen and Hippocrates ...
