There are certainly benefits to Chinese investment in Africa, such as improvements in infrastructure and economic development. As economies grow, poverty decreases and populations become better educated and more politically involved, leading to better governance.
Who is benefiting more from Chinas relationship with the African continent?
eNCAs Yusuf Omar explains who is benefiting more from Chinas relationship with the African continent. JOHANNESBURG - South Africa is the biggest recipient of Chinese investment on the continent, and that relationship is likely to grow. The China-Africa Cooperation Forum is being held in Johannesburg this week.
How much money does China give to Africa?
Estimates vary wildly—data on Chinese financing is scant and must be collected indirectly—but a report written in 2016 by Deborah Brautigam, a professor of international political economy at John Hopkins, estimated that Chinese banks, contractors, and the government lent approximately $86 billion to Africa between 2000 and 2014.
How does China finance its projects in Africa?
China has used a form of financing that functions like a bartering system: In return for investment capital and infrastructure development projects, some sub-Saharan African countries grant China resource concessions. (Such was the case with the Sicomines copper project in the Democratic Republic of Congo and in various oil projects in Angola.)
What is China’s role in the United Nations doing in Africa?
Through large-scale economic and personnel engagement in the UN’s military operations, China hopes to be seen as a responsible actor for maintaining order in the region. In times when other countries have reduced such support, China’s increased involvement has mainly been viewed positively in Africa.

Why does Africa trade with China?
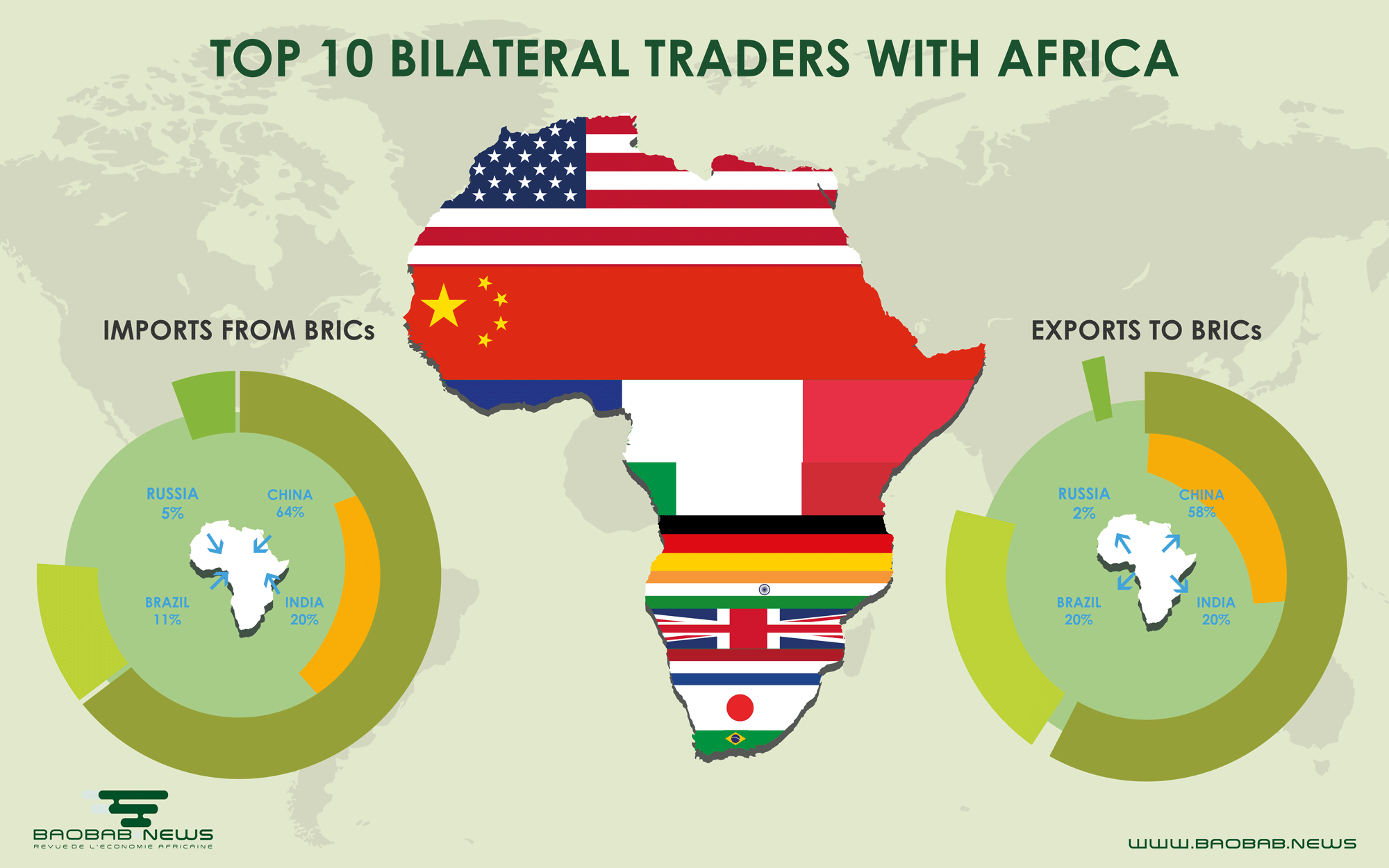
China-Africa trade still has a deficit problem And Kenya is creating an online platform to sell agricultural products. China, on its part, wants to import more goods, especially agricultural products, from Africa.
What does Africa buy from China?
The main products China exports to Africa are machinery and electronics, textile and apparel, hi-tech products and finished goods, while imports from Africa concentrate on crude oil, iron ore, cotton, diamond and other natural resources and primary goods.
Which African country owes China the most money?
Between 2020 and 2022, Angola will get $6.9 billion in debt relief, mostly from China. Chinese banks have offered significant debt restructuring both before and during the coronavirus era acting within and outside of the G-20 arrangements.
How much money does Africa owe China?
Africa's rising debt: Chinese loans to continent exceeds $140 billion.
Why is China a good partner for Africa?
For Africans, China has four major attractions: Unconditional soft loans and access to capital; quick delivery of services and cheap goods; funding of peacekeeping; and an alternative development model.
What is China's investment in Africa?
The other two-thirds of China’s investment in Africa is in infrastructure, construction, electricity production, manufacturing and finance. In fact, compared with the US and other developed countries, China’s share in extractive investments in Africa, in the form of mining, for example, is lower.
Why does Africa love China?
Why Africa loves China. Contrary to what the West believes, Africans do not see themselves as victims of Chinese economic exploitation. Mehari Taddele Maru. Dr Mehari Taddele Maru is a scholar of peace and security, law and governance, and human rights and migration issues. 6 Jan 2019.
How much did China trade with Africa in 2016?
In 2016, the trade between China and Africa reached $128bn, a drastic surge from $1bn in 1980. At FOCAC in Beijing this year, China offered $60bn for development financing until 2021. While the financial crises in the US and EU limited their investments in Africa, China committed to investing more in the continent.
What is Kagame's view on Africa?
Kagame argued that the cooperation between China and Africa is based on mutual respect and is for the benefit of both partners. This sentiment is perhaps shared by most African heads of states and governments if their attendance of the summit is anything to go by.
How many people did China lift out of poverty?
According to the World Bank, in about 40 years, China has lifted about 800 million people out of poverty through its untraditional path of development.
How has China aided African governments?
Second, China has aided African governments to meet their people’s rapidly growing demands for services and infrastructure more quickly. Many people in Africa are now used to quick delivery of services – such as transportation, education, health and telecommunication – by Chinese companies.
What are the concerns of China and Africa?
To ensure the sustainability of the Africa-China partnership, three key concerns need to be addressed: Corruption, personal safety, and language and cultural barriers. Corruption has thrived in Africa’s current climate of political and economic impunity. Corruption creates and increases poverty and exclusion.
What were the first examples of China's zero interest loan?
One of the first famous examples is the Tanzania-Zambia Railway built between 1970 and 1975, for which China provided a zero-interest loan of RMB980 million ($150 million). Sectors including agriculture, banking, insurance, transport and logistics, housing, information communications technology and telecommunications are poised to see significant ...
Is China a part of Africa?
By Forbes Africa. The past three decades have seen a marked step change in Africa’s international relations. While geography historically favoured a European focus – especially in North Africa – the continent has shifted its gaze to the East. China has catapulted from being a relatively small investor in the continent to becoming Africa’s largest ...
Abstract
Since arriving in Africa in the 1800s, the trading relationship between Africa and China has evolved and intensified in many ways. As this relationship intensifies, so do the discussions of the opportunities and challenges of this relationship. Much of these discussions and debates point to China’s exploitation of the relationship.
About this chapter
Adekunle B., Korzun M. (2017) Trading with China: How can Africa Benefit?. In: Odularu G., Adekunle B. (eds) Negotiating South-South Regional Trade Agreements. Advances in African Economic, Social and Political Development. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45569-3_3
What is the China-Africa Cooperation Forum?
The China-Africa Cooperation Forum, or FOCAC, was set up about 15 years ago. China is committing a trillion dollars in financing to Africa by 2025. Critics say, however, that Chinese state-owned enterprises create jobs with the lowest wages, and haven’t done much about transferring skills.
Which country is the biggest recipient of Chinese investment?
JOHANNESBURG - South Africa is the biggest recipient of Chinese investment on the continent, and that relationship is likely to grow. The China-Africa Cooperation Forum is being held in Johannesburg this week.
What is the Asian powerhouse?
The Asian powerhouse grapples with this perception that it has imperial ambitions, boosting investments in exchange for Africa’s natural resources -- with projects like the Zambian power plants, Egyptian trade deals, mines in the DRC, and laying railway tracks across East Africa.
Does China have a non-interference policy?
While many Western countries continue to have a more extractive and exploitative relationship with African economies, China professes to have a non-interference policy, although they are planning a naval base in Djibouti. So, it’s in the hands of Africa’s political and business leaders to determine its future.
Is China industrializing Africa?
China is committed to industrializing the continent, and like all investors, want to benefit from it. Africa has every reason to be suspicious. The continent’s history is riddled w ith failed economic relations with the rest of the world, from the exploitations, to colonialism, to disastrous structural adjustment programs and aid packages.
What are the pros and cons of Chinese investment in Africa?
Thanks to billions of dollars from China, new roads, bridges, stadiums and other projects are being built all over Africa. Even the building of the $200 million headquarters of the African Union was funded entirely by the Chinese. China is also making industrial investments all over the continent, ...
Is China a trading partner in Africa?
As a result, China has now become Africa’s most important trading partner, passing the United States. There are certainly benefits to Chinese investment in Africa, such as improvements in infrastructure and economic development.
What was the public sector debt in Africa in 2016?
Median public-sector debt in sub-Saharan Africa was 48 percent in 2016. The current situation resembles the African debt crisis of the 1980s. In the time leading up to the debt crisis, many sub-Saharan African countries similarly took advantage of lower interest rates and took on more debt.
What would happen if China defaulted on its debt?
Defaulting on their debt would cause foreign investment to dry up. China’s willingness to accept repayment in commodities would leave it as one of the few remaining options for countries struggling to build infrastructure. Beijing could, therefore, drive as hard a bargain as it wanted.
What happened to the dollar when interest rates went up?
When interest rates in the United States went up, the dollar appreciated relative to local currencies in sub-Saharan Africa, making repayment even costlier. Meanwhile, the price of the commodities on which so many of these countries depend fell, decreasing the amount of money they had to pay back their loans.
Will China mine Africa?
China will continue to mine Africa for its resource needs. The only thing that will constrain its behavior in that regard is its own capital needs. It will, in other words, have to determine how much to spend as its own economic problems continue to mount.
Introduction
China’s relations with the African continent [a] date back to the 15th century. In the Ming Imperial Tomb in Beijing is a wall painting of a giraffe—it was the famous Chinese admiral and seafarer Zheng He who brought it to the court in Nanjing during one of several expeditions to the Arab world and the east coast of Africa between 1413 and 1419.
Analysis
One can identify three more or less explicitly stated Chinese goals when it comes to economic relations with Africa: [13] access to the continent’s natural resources; export markets for Chinese manufactured goods; and sufficient economic and political stability for China to safeguard its citizens and pursue its economic and commercial interests.
Focus on Lending
In addition to trade and FDI, loans comprise an increasingly important component of China’s economic relations with Africa.
China as a Political Factor in Africa
The Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) held its first ministerial conference in Beijing in October 2000. The forum’s objectives include the promotion of political cooperation, and creating a favourable environment for China-Africa business and trade.
Conclusion
How should other stakeholders interpret China’s increased activity in Africa?

Valuable Infrastructure
- A spokesman for the ministry in Beijing cited a survey published in November 2021 by the pan-African institute Afrobarometer, which states 63% of Africans believe China has had a positive influence in their country. "I see the influence of the Chinese," admitted Bamidele Adekunle, adju…
The Fallout of Hidden Debt
- But analyst Asche scoffed at the notion. "I sincerely doubt that it is a conscious policy. China has no interest to see African countries caught in a trap," even if the Chinese strategy of swapping infrastructure projects for mineral resources, known as the 'Angola-mode', has resulted in financial troubles for many African countries. The problem lies in the lack of transparency. "Half of the Ch…
The 'Angola-Mode'
- Chinese interests in Africa are focused on the acquisition of commodities. According to Chinese data, the country has turned into the continent's largest trading partner, with direct trade amounting to more than $200 billion in 2019. The trade imbalance is enormous. African products represent around 4% of China's overall imports. However, Nigerian economist and consultant To…
The Need to Eradicate Corruption
- That presupposes the will of African leaders to act and negotiate for the benefit of the people, said economist Fasua. He sees a new opportunity for the continent in the increased competitionbetween the East and the West in Africa. Expert Adekunle, who teaches at the Ted Rogers School of Management, Ryerson University, is cautious. First, corruption will need to be …