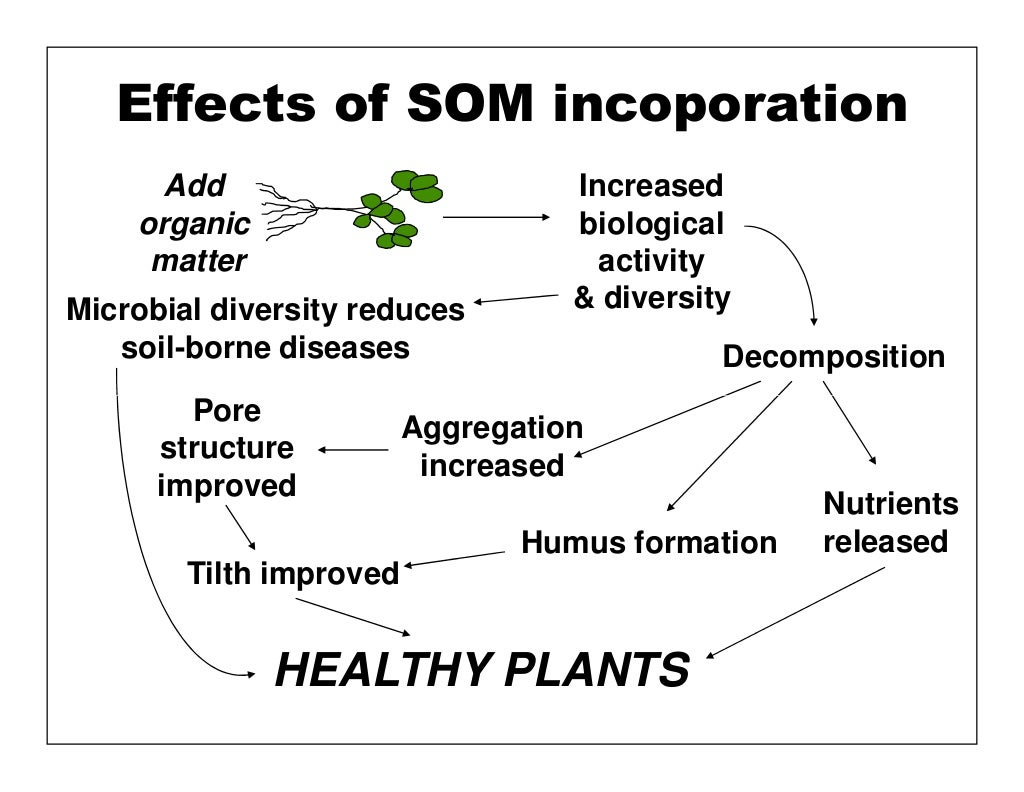
Here are just a few of its top contributions to soil:
- It provides nutrients for plants as microbes break down and release nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
- It stores nutrients in soil and increases soil’s cation exchange capacity, or CEC. Organic matter has a negative charge,...
- It helps sandy soil retain water and clay soil drain excess water. As a result,...
How do you add organic matter to soil?
You can:
- add tougher organic matter with a high carbon-to-nitrogen ratio like straw, paper crumble, sawdust or wood chips
- switch to min-till or no-till farming, to disturb soil less
- reduce soil compaction from livestock and machinery
- manually disrupt tramlines to reduce soil erosion and runoff
What is the importance of organic matter in soil?
- When cropland is fertilized, the crops don't need to trade soil organisms for nutrients so they reduce their rate of exuding carbon from their roots.
- And then, most cropland globally is left bare fallow most of the year. No growing roots in the soil means no carbon root exudes going into the soil.
- Overgrazing by livestock or he
How to increase organic matter?
- Regular application of lime and other needed minerals, including supplement to the cattle which they spread.
- Management for a highly diverse plant community that is high in biomass and root growth and root depth.
- Dissolving of any hardpan with boom-and-bust grazing followed by complete plant recovery.
Why nutrients in soil are important?
Why are nutrients in soil important? Soil is a major source of nutrients needed by plants for growth. Other important nutrients are calcium, magnesium and sulfur. … Plants also need small quantities of iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron and molybdenum, known as trace elements because only traces are needed by the plant.

How Much Organic Matter Is in The Soil?
An acre of soil measured to a depth of 6 inches weighs approximately 2,000,000 pounds, which means that 1 percent organic matter in the soil would...
What Are The Benefits of Organic Matter?
1. Nutrient Supply Organic matter is a reservoir of nutrients that can be released to the soil. Each percent of organic matter in the soil releases...
How Can I Maintain Or Improve Soil Organic Matter Levels?
Building soil organic matter is a long-term process but can be beneficial. Here are a few ways to do it. 1. Reduce or Eliminate Tillage Tillage imp...
Why is it important to consider organic matter in soil?
In addition to providing the resources to support microbial activity , considering the quality and quantity of organic matter inputs into a soil is important. As mentioned earlier, a healthy soil has a steady supply of active and stable forms of organic matter.
What is the organic matter level of soil?
Soil Organic Matter Levels. The soil organic matter level in most mineral soils ranges from trace amounts up to 20%. If a soil has 20% or more organic material to a depth of 16 inches, then that soil is considered organic and is termed a peat or muck, depending on the extent of decomposition.
How does tillage affect the soil?
Tillage affects the amount of residue that can be harvested. With more aggressive tillage, more residue and air are incorporated into the soil. This, in turn, promotes the decomposition of crop residues and soil organic matter by soil microorganisms (especially bacteria). Figure 17.
What is the organic fraction of soil?
One textbook definition is: The organic fraction of the soil that includes plant, animal, and microbial residues in various stages of decomposition, biomass of soil microorganisms, and substances produced by plant roots and other soil organisms (Weil and Brady, 2017).
Why is topsoil black?
The dark brown or black color of topsoil is caused by organic matter coatings on soil particles.
How does rotation affect residue quality?
The selection of crops in a rotation, use of cover crops, or added composts and manures can influence residue quality. What makes sense is that more types of food will support more types of microbes, which will work hard to turn that food into stable organic matter.
What is the best way to maintain healthy soil?
Healthy soil has a mix of active and stable soil organic matter. A steady supply of organic inputs, such as crop residues and manure, helps build and maintain active and stable organic matter pools, which provide a wide array of benefits to the soil.
Why is organic matter important?
Though small in proportion by weight, organic matter is linked to important functions in the soils and is critical to maximizing biological activity within the soil. Humus along with clay particles provide cation exchange sites in soils, reducing nutrient leaching losses. Microorganisms using organic matter as a food source promote aggregation ...
Why do microorganisms use organic matter?
Microorganisms using organic matter as a food source promote aggregation of soil particles, resulting in improved structure ( Figure 2 ), soil water infiltration, and holding capacity. It reduces the potential for runoff and erosion as well. Higher organic matter levels also result in favorable soil temperatures, improved plant root growth, ...
What are the things that contribute to the formation of organic matter?
It can be present in soils under various stages of decomposition. Crop and plant residue, tree litter, livestock manure ( Figure 1 ), animals and different types of soil organisms, their by-products and to a lesser extent human waste contribute to form organic matter.
How to increase biomass in soil?
crops/plants that produce greater biomass. Incorporate straw/crop residues. Reduce tillage to minimize soil carbon losses and to slow organic matter decomposition processes. Apply fertilizers on cover crops and legumes to produce more biomass. Apply manure, plant material, or other carbon-rich waste.
What is the active fraction of soil?
The active fraction (roots and residue) is the food source of soil microorganisms. The stable fraction (humus), stores carbon and reduces loss of organic carbon to decomposition.
How old are the Great Plains soils?
Soils of the Northern Great Plains are relatively young (11,000 to 14,000 years old) and have some of the highest organic matter levels (4% to 7%) of all mineral soils in the United States ( Overstreet and DeJong-Huges, 2009 ).
How much carbon do microorganisms need to produce protein?
On average microorganisms require 25 to 30 parts of carbon for every part of nitrogen they consume.
How does organic matter help soil?
Organic matter acts like a lubricant between the physical, chemical, and biological properties of a healthy soil functioning well. In summing up how organic matter builds healthy soil, high soil organic matter feeds and supports high populations of soil organisms. High soil organism populations produce ‘microbial glue’ through their bodily ...
What are the physical properties of soil?
Soil layers, texture, and structure are physical soil properties. Soil layers are distinct horizontal zones in the soil, arranged like layers of lasagna, from the topsoil down to the bedrock. Soil texture is determined by the proportion of sand, silt, and clay mineral particles.
What is soil structure?
Soil structure refers to the aggregation of soil particles and the arrangement of those aggregates with each other. Well aggregated soil drains water properly and exchanges air with the atmosphere providing an ideal home for plant roots.
What is composting in soil?
Home compost is a perfect source of organic matter to add to the soil. For more information about composting, visit HGIC 1600, Composting. The physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil work together to make it a complex, dynamic, and living substance. The role of organic matter in soil health is vital.
What are the nutrients that are needed for a garden?
Most gardeners are aware of the roles mineral nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium play in plant health. However, CEC and soil pH determine the amount of mineral nutrients the soil can hold and whether soil nutrients present in the soil are available to the plant.
What are the benefits of soil?
4. Air quality, water quality, and agricultural productivity improve. Dust, allergens, and pathogens in the air immediately decline.
How does soil change?
3. Soil properties change 1 Surface structure becomes more stable and less prone to crusting and erosion. 2 Water infiltration increases and runoff decreases when soil structure improves. 3 Soil organic matter holds 10 to 1,000 times more water and nutrients than the same amount of soil minerals. 4 Beneficial soil organisms become more numerous and active with diverse crop rotations and higher organic matter levels.
Why are crops better able to withstand drought?
Crops are better able to withstand drought when infiltration and water holding capacity increase. Organic matter may bind pesticides, making them less active. Soils managed for organic matter may suppress disease organisms, which could reduce pesticide needs. Crop health and vigor increase when soil biological activity and diversity increase.
Why does surface water quality improve?
Ground and surface water quality improve because better structure, infiltration, and biological activity make soil a more effective filter.
How does surface structure affect water infiltration?
Surface structure becomes more stable and less prone to crusting and erosion. Water infiltration increases and runoff decreases when soil structure improves. Soil organic matter holds 10 to 1,000 times more water and nutrients than the same amount of soil minerals.
What is organic matter?
Many times we think of organic matter as the plant and animal residues we incorporate into the soil. We see a pile of leaves, manure or plant parts and think, "Wow! I'm adding a lot of organic matter to the soil." This stuff is actually organic material, not organic matter.
How much organic matter is in the soil?
An acre of soil measured to a depth of 6.67 inches weighs approximately 2 million pounds, which means that 1 percent organic matter in soil weighs about 20,000 pounds.
What are the benefits of organic matter?
Nutrient supply Organic matter is a reservoir of nutrients released to the soil. Each 1 percent of soil organic matter releases 20 to 30 pounds of nitrogen, 4.5 to 6.6 pounds of P2O5, and 2 to 3 pounds of sulfur per year.
How can I maintain or improve soil organic matter levels?
Building soil organic matter is a long-term process but can be beneficial. Here are a few ways to do it:
Comments
We were unable to load Disqus. If you are a moderator please see our troubleshooting guide.

What Is Organic Matter?
The Benefits of Organic Materials
- Increasing levels of O.M. improve the physical, chemical, and biological functions of the soil. The benefits of O.M. are summarized into the following five functions: 1. Biological Function There are many benefits to O.M., most of which begin with enhancing the biological diversity and activity in the soil. As O.M. increases, microbial activity ten...
Management Practices to Increase Soil Organic Matter
- Several factors such as climate, soil type, crop grown, and specific management practices can each influence the amount of soil O.M. regionally or in specific fields; therefore, local conditions should be used as benchmarks for comparison when implementing practices to increase soil O.M. (Figure 3, STS). Soils that have greater O.M., such as those originally developed in prairies, …
What Is Soil Organic Matter?
Why Are The Upper Midwest Soils So Rich in Organic Matter?
Classifications of Organic Matter
Organic Matter Cycling
Benefits of Organic Matter
Building Organic Matter
Soil Organic Matter Terminology
Destroying Organic Matter
Summary
- The bottom line is that soil organic matter matters a lot. Soil organic matter is responsible for maintaining a healthy, productive soil by providing food and a house for microbes (which run the show in the world beneath our feet). Soil organic matter also helps protect our soils from erosion losses, which is important because soil is a non-renewab...
References