
The income you receive from your 401 (k) or other qualified retirement plan does not affect the amount of Social Security retirement benefits you receive each month. However, you may be required to pay taxes on some or all of your benefits if your annual income exceeds a certain threshold—and your 401 (k) distributions can cause it to do that.
How will my pension affect my social security?
The 10 most tax-friendly states for retirees:
- Wyoming.
- Nevada.
- Delaware.
- Alabama.
- South Carolina.
- Tennessee.
- Mississippi.
- Florida.
Can investment income affect my Social Security benefits?
Thus dividends and capital gains won't negatively affect your Social Security benefits directly, even if you decide to file earlier than your full retirement age. However, dividends and capital gains can still affect your ultimate net Social Security benefits due to taxes.
How will your government pension affect social security?
- The last day you worked at the job providing the pension was before July 1, 2004
- You filed for your spousal or survivor's benefits and were entitled to receive them prior to April 1, 2004
- You paid Social Security taxes on the money you earned during the last 60 months that you worked for the government
How are Social Security benefits affected by your income?
Key Points
- Your marital status could affect Social Security benefits.
- Divorce can sometimes leave you with a reduced Social Security check.
- Eligibility for spousal benefits and survivor benefits can depend how long you were married.
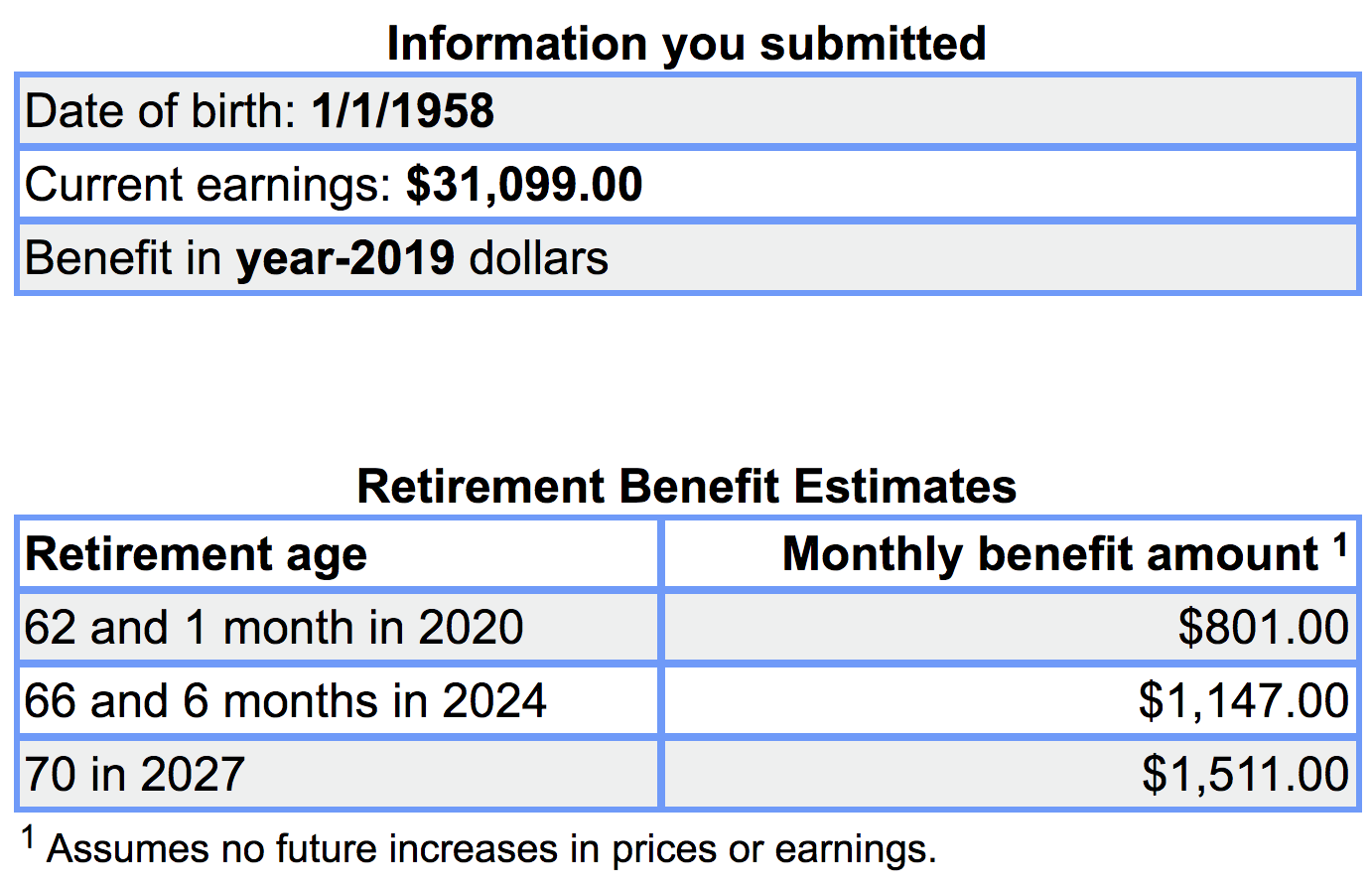
How much is Social Security reduced if you have a pension?
We'll reduce your Social Security benefits by two-thirds of your government pension. In other words, if you get a monthly civil service pension of $600, two-thirds of that, or $400, must be deducted from your Social Security benefits.
Can you collect Social Security and a pension at the same time?
Yes. There is nothing that precludes you from getting both a pension and Social Security benefits. But there are some types of pensions that can reduce Social Security payments.
What income reduces Social Security benefits?
If you are younger than full retirement age and earn more than the yearly earnings limit, we may reduce your benefit amount. If you are under full retirement age for the entire year, we deduct $1 from your benefit payments for every $2 you earn above the annual limit. For 2022, that limit is $19,560.
Do pensions count as earned income?
Earned income does not include amounts such as pensions and annuities, welfare benefits, unemployment compensation, worker's compensation benefits, or social security benefits.
At what age is Social Security no longer taxed?
At 65 to 67, depending on the year of your birth, you are at full retirement age and can get full Social Security retirement benefits tax-free.
What income is counted against Social Security?
People can earn $50,520 before reaching full retirement age without affecting their benefits. And the amount of reduction is also just $1 for every $3 earned over the cap. In addition, income only counts against the cap until the month before full retirement age is reached.
What income is Social Security based on?
Social Security replaces a percentage of your pre-retirement income based on their lifetime earnings. The portion of your pre-retirement wages that Social Security replaces is based on your highest 35 years of earnings and varies depending on how much you earn and when you choose to start benefits.
How much income can you make without affecting your Social Security?
The Social Security earnings limit is $1,630 per month or $19,560 per year in 2022 for someone who has not reached full retirement age. If you earn more than this amount, you can expect to have $1 withheld from your Social Security benefit for every $2 earned above the limit.
How is Social Security calculated?
The standard benefits formula uses an average of your inflation-adjusted earnings in the 35 years during which you made the most money. That average is divided by 12 to get a monthly income figure, called your Average Indexed Monthly Earnings, or AIME.
How much does WEP reduce Social Security?
In certain situations, the WEP reduces your Social Security benefits by up to half of your pension. Simply put, if you qualify for a pension of $900 monthly, the WEP may cut your Social Security benefits by up to $450. Image Source: Getty Images.
How much does 40% Social Security mean?
If you paid Social Security taxes for less than 21 years, you'll see the biggest impact to your Social Security benefits. The normal 90% drops down to 40%. Using the same monthly earnings of $1,500, the 40% equation translates to benefits of $554.08, or 40% of $926 plus 32% of $574.
What is the percentage of your monthly income for 2019?
In 2019, your benefits would be the total of: 90% of the first $926 of your monthly earnings, plus. 32% of any earnings over $926 but less than $5,583, plus. 15% of any earnings over $5,583. You can see that a lower monthly earnings amount gets a higher percentage of benefits. If your monthly earning number is $900, ...
What does WEP mean on Social Security?
The WEP comes into play when you've worked in "covered" jobs where you paid Social Security payroll taxes and "noncovered" jobs where you didn't pay Social Security payroll taxes, earning a pension instead. In certain situations, the WEP reduces your Social Security benefits by up to half of your pension. Simply put, if you qualify for a pension of $900 monthly, the WEP may cut your Social Security benefits by up to $450.
What is the purpose of Social Security?
The Social Security Administration (SSA) keeps a record of your earned income from year to year, and the portion of your income that is subject to Social Security taxes is used to calculate your benefits in retirement. The more you earned while working (and the more you paid into the Social Security system through tax withholding), ...
How much will Social Security be in 2022?
3 For 2022, that maximum is $4,194 a month (up from $3,895 a month in 2021). 4 5
Will Social Security be reduced after FRA?
Starting with the month when you attain FRA, your benefits will no longer be reduced. Note that these dollars are not lost forever; instead, your Social Security benefit will be increased to account for them after you reach your FRA. 12
Is Social Security considered earned income?
Your Social Security benefits are determined by a number of factors , but your earned income over the course of your working life is probably the most important—so the more the better. Is Social Security considered earned income? Unfortunately, the answer is “no.” 1
Is Social Security Taxable?
Your income from Social Security can be partially taxable if your combined income exceeds a certain amount. “Combined income” is defined as your gross income plus any nontaxable interest that you earned during the year, plus half of your Social Security benefits. For example, if you’re married, file a joint tax return with your spouse, and your combined income ranges from $32,000 to $44,000, then you may have to pay tax on up to 50% of your Social Security benefits. If your combined income is greater than $44,000, then up to 85% of your benefits may be taxable. For single filers, those income numbers are $25,000 to $34,000 and greater than $34,000. 13
How much Social Security income is taxed?
Between $25,000 and $34,000, you may have to pay income tax on up to 50% of your Social Security benefits. More than $34,000, up to 85% of your Social Security benefits may be taxable. If you file as married filing jointly, and you and your spouse have a combined income of:
When will Social Security be reduced?
Modified date: November 11, 2020. If you receive a government pension, your Social Security benefits may be reduced. Usually, it's a fair trade. But things get complicated if you job hop between the public and private sectors. Here's what you need to know. If you work for the federal, state, or local government, ...
What if you’re not covered by Social Security?
In many situations, the benefits that you will receive under a government pension will be equal—or even superior—to Social Security benefits with an equivalent employment and earnings record. But if you are concerned by the absence of Social Security benefits, you should consider the following to help secure your retirement:
How much do you have to contribute to your pension?
Often, if this is the case, your employer (for instance, The Ohio State University) will require that employees contribute at least 10% of every paycheck to the pension fund. Unlike 401 (k)s, where employees choose their own level of involvement (and often underfund their own retirement) this allows the pension program to plan and provide for its beneficiaries. (When you consider that public employees are not paying their half of the payroll tax—6.2%—the 10% requirement works out to roughly a 3.8% contribution toward their retirement.)
Is Social Security taxable if you have a minimum income?
First, your Social Security benefits will not be taxable if your combined income is below the minimum numbers above. And second, the maximum amount of your Social Security benefits that will be taxable under the worst case scenario is 85%.
Is pension income taxable?
Since pension income will represent part of your adjusted gross income, it will have an impact on how much of your Social Security benefits are taxable.
When did the federal government start a second retirement system?
In 1984, the federal government introduced a second retirement system, known as the Federal Employees Retirement System, or FERS. If you began working for the federal government from 1984 on, you’re automatically part of the FERS system, and not CSRS. Employment under the FERS system is covered by Social Security, ...
What happens to Social Security after you reach full retirement age?
After you reach full retirement age, Social Security will recalculate your benefit and increase it to account for the benefits that it withheld earlier. 7 .
What happens if you start collecting Social Security benefits earlier?
However, once you reach full retirement age, Social Security will recalculate your benefit to make up for the money it withheld earlier.
What Is Full Retirement Age?
For Social Security purposes, your full or "normal" retirement age is between age 65 and 67, depending on the year you were born. If, for example, your full retirement age is 67, you can start taking benefits as early as age 62, but your benefit will permanently be 30% less than if you wait until age 67. 3
How Does Social Security Know?
You might wonder how the Social Security Administration keeps track of your work and your earnings. The answer: It doesn't. It's your responsibility to report how much you've made.
How much will Social Security deduct if you don't retire?
If you haven't reached full retirement age, Social Security will deduct $1 from your benefits for every $2 or $3 you earn above a certain amount. After you reach full retirement age, Social Security will increase your benefits to account for the money it withheld earlier.
How does Social Security calculate your benefits?
Social Security calculates your benefit amount based on your earnings over the years, whether you were self-employed or worked for another employer. The more money you earned, the more you paid into Social Security—and the higher your future benefits—up to certain limits.
How many people will collect Social Security in 2022?
About 70 million people are expected to collect some type of Social Security benefit in 2022. The Social Security Administration reported in October 2021 the estimated average monthly retirement benefit will be $1,657. 5 While that regular monthly income helps, it's usually not enough to cover living expenses. That's one reason many people are working longer.
How much of your Social Security benefits are taxed?
If your "combined income" -- a Social Security Administration figure that I'll explain below -- is above a certain threshold, then up to 85% of your Social Security benefits could be taxed as income.
How to avoid taxes on Social Security?
The simplest way to avoid Social Security benefit taxation is to be mindful of how much you're withdrawing from your retirement accounts each year. If you're close to one of the taxation thresholds, you could try to withdraw a little less than you planned to avoid the tax.
What happens if my retirement account withdrawals are too high?
If your retirement account withdrawals are too high, you could be putting some of your Social Security benefits at risk. Kailey has been writing about personal finance since 2013. She does her best to keep it interesting and jumps at any opportunity to learn something new. Social Security is a government-created program designed to provide ...
What is adjusted gross income?
Your adjusted gross income is the total amount of taxable income you earn in a year, minus certain adjustments, such as half of any self-employment taxes, alimony payments, or contributions to retirement accounts.
What is Social Security?
Social Security is a government-created program designed to provide a source of continuous income to retirees, but what most people don't know is that if you earn more than a certain amount, the government will take some of that money back in the form ...
How to calculate combined income?
So how do you figure out if you fall into one of these ranges? Your combined income is calculated based on three figures: your adjusted gross income, any nontaxable interest you've earned and half of your Social Security benefits. Your adjusted gross income is the total amount of taxable income you earn in a year, minus certain adjustments, such as half of any self-employment taxes, alimony payments, or contributions to retirement accounts. Your AGI does include withdrawals from traditional retirement accounts -- including traditional 401 (k)s and IRAs -- but it doesn't include withdrawals from Roth accounts, because contributions to these accounts are taxed up front. You may have nontaxable interest if you have tax-exempt bond funds in your investment portfolio.
What If I Receive a Pension?
When you apply for SSDI, the Social Security Administration calculates the amount of your possible monthly disability benefits based on your work history. The SSA may reduce the amount you receive in some cases if you have other sources of income. Specifically, Social Security may lower your disability payments if you receive certain types of pension payments.
What is SSDI payment?
Navigating the multitude of programs offered by the Social Security Administration (SSA) can be a daunting task. Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) makes monthly payments to you if your medical condition qualifies.
What is WEP in Social Security?
There’s also the Windfall Elimination Provision (WEP) to consider. This program can impact how the Social Security Administration calculates your retirement or disability benefits.
How do I qualify for SSDI?
To receive SSDI benefits, you must have a record of working in jobs covered by Social Security. Benefits Planner|Disability-How You Qualify. Retrieved from https://www.ssa.gov/planners/disability/qualify. html. You also must meet Social Security’s definition of disability. Partial or short-term disabilities are not covered by SSDI.
Can a pension change your Social Security benefits?
The short answer is, “yes.” It isn’t a common occurrence but it can happen. Whether or not your pension payment alters Social Security Disability benefits depends on the kind of pension you have and on the type of Social Security benefits you’re receiving.
Does a pension affect SSDI?
This means most government and private pensions will not have an impact on the monthly SSDI benefits you’ll receive once you qualify for disability. As with just about everything in life, there are occasional exceptions to the rule. Some types of disability pensions and long-term disability plans impact SSDI benefits.
Does Social Security reduce your monthly award?
If you’re receiving other types of public benefits, there may or may not a reduction in your Social Security disability benefits. The following public benefits programs, in conjunction with SSDI payments, will not reduce your monthly award:
