Stage 2 benefits the cell because the smaller molecules react when they touch oxygen molecules which creates energy, water, and carbon dioxide. The cell then uses the energy to do all its functions, the water helps keep the cell hydrated, and the carbon dioxide is released so there will not be a too much CO₂.
What are the 3 steps in order of cellular respiration?
what are the three steps of aerobic cellular respiration
- Cellular Respiration (UPDATED)
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis, Prep Steps
- Stages of cellular respiration
- Cellular Respiration Steps and Pathways
What are the three phases of cellular respiration?
What are the main stages of cellular respiration and where do they take place quizlet?
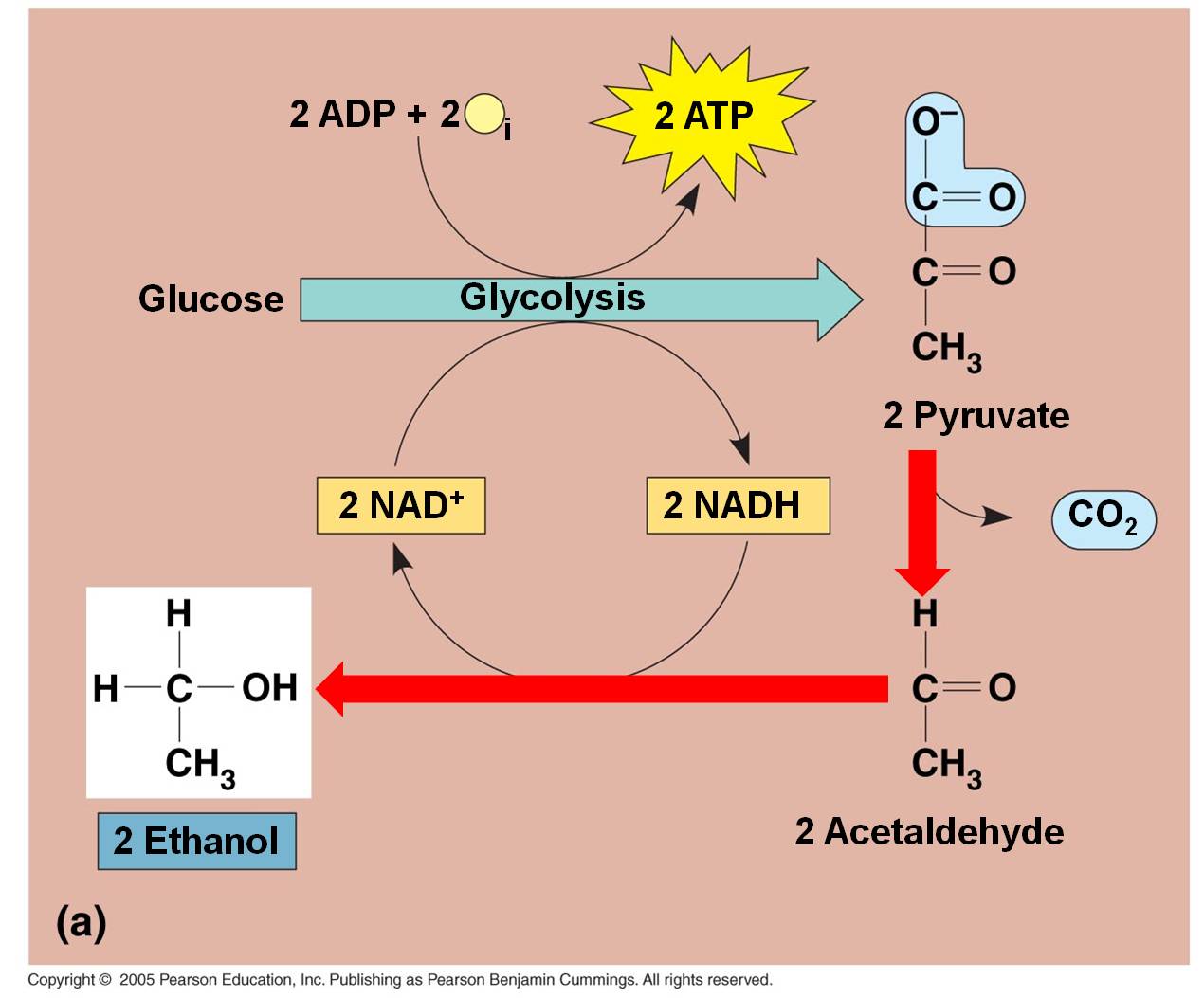
- st- Glycolosis. Splitting sugars in cytoplasm, energy investment phase -> 2 ATP molecules combine with glucose molecule.
- nd- Oxidation. Pyruvates moving into mitochondria, through oxidation pyruvates broken into water.
- rd- Krebs Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle. …
- th- Electron Transport Chain.
What is the final step in cellular respiration?
What are the 7 steps of cellular respiration in order?
- Glycolysis.
- Pyruvate oxidation.
- Citric acid cycle.
- Oxidative phosphorylation.
Where does the final stage of cellular respiration occur?
mitochondria. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. If oxygen is available, aerobic respiration will go forward. In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria, which are the sites of cellular respiration.

How does cellular respiration benefit cells?
Cellular respiration releases stored energy in glucose molecules and converts it into a form of energy that can be used by cells.
What happens during Stage 2 of cellular respiration?
Cellular Respiration Stage II: The Krebs Cycle. Recall that glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate (pyruvic acid), which are then converted to acetyl CoA during the short transition reaction.
Does cellular respiration have 2 stages?
Cellular respiration occurs in three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process. The other two stages are aerobic processes. The products of cellular respiration are needed for photosynthesis, and vice versa.
What are the 2 stages of respiration?
The reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages: glycolysis (stage 1), the Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle (stage 2), and electron transport (stage 3). Figure below gives an overview of these three stages, which are further discussed in the concepts that follow.
What happens in the second stage of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration second stage occurs in in the inner compartment of the mitochondria. During the reactions, pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA which enters the Krebs Cycle. For two pyruvates, the two ATP and ten coenzymes form.
What are the reactants of Stage 2 cellular respiration?
Oxygen and glucose are both reactants in the process of cellular respiration. The main product of cellular respiration is ATP; waste products include carbon dioxide and water.
What happens in each stage of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration uses energy in glucose to make ATP. Aerobic (“oxygen-using”) respiration occurs in three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport. In glycolysis, glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvate. This results in a net gain of two ATP molecules.