What is the average cost of employee benefits?
Wages by themselves account for about 70 percent of compensation costs. The total average cost for insurance benefits, including health, life, and disability insurance, comes to $2.73 per hour, or $5,698 annually per employee. Legally-required benefit contributions such as Social Security and Medicare add up to $2.65 per employee per hour.
How do you calculate employee benefits?
- Gross Earnings – Lets use an example here for our Sample Employee Fred Fredders. ...
- Employer Paid Taxes are also a big expense that must be added in. ...
- Employer Paid Insurance and Other % Based Costs – Insurance is always a large cost to the Employer and plays a large factor in the overall Hourly Costs. ...
What is the actual cost of an employee?
Labor costs have risen dramatically in the senior housing space. That's not just because employees are getting raises; it's more a function of the need to use contract labor. When the contract labor gets replaced with full-time employees, this cost ...
How much is my employee benefits package worth?
Your benefits package would theoretically be worth more than $15,000, so your total compensation would be valued at roughly $65,000. Take a look at how much your benefits package adds to your overall compensation, based on the Department of Labor’s most recent estimates.

How much do employee benefits typically cost?
The national average of employee benefits cost Taken together, the average total compensation is $37.73 per hour. For state and government workers, the average cost for employers paying employee benefits equals $19.82 per hour, in addition to their average salary and wage which was $32.62 per hour.
How much does an employee actually cost a company?
There's a rule of thumb that the cost is typically 1.25 to 1.4 times the salary, depending on certain variables. So, if you pay someone a salary of $35,000, your actual costs likely will range from $43,750 to $49,000.
What percentage of employee cost is benefits?
According to the latest data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the average total compensation for all civilian employees in 2020 is $37.73 per hour. Benefits make up 32 percent of an employee's total compensation.
How much should I budget for employee benefits?
Experts suggest that you should expect to pay a range of 1.25 to 1.4 times each employee's base salary. That extra $10,000 might include things like $120 for life insurance—an average cost for your younger and older workers—$5,760 for family health coverage, $520 for dental insurance, and $200 for long-term disability.
How do you calculate the cost of benefits for an employee?
Calculating the benefit load — the ratio of perks to salary received by an employee — helps a business effectively plan. Find the benefit load by adding the total annual costs of all employees' perks and divide it by all employees' annual salaries to determine a ratio — that ratio is your company's benefits load.
What is fully loaded cost of employee?
The simplest way to derive the average loaded cost of an employee is to count up your total corporate expenses and divide it by the total number of productive hours worked.
How much do employers pay for health insurance?
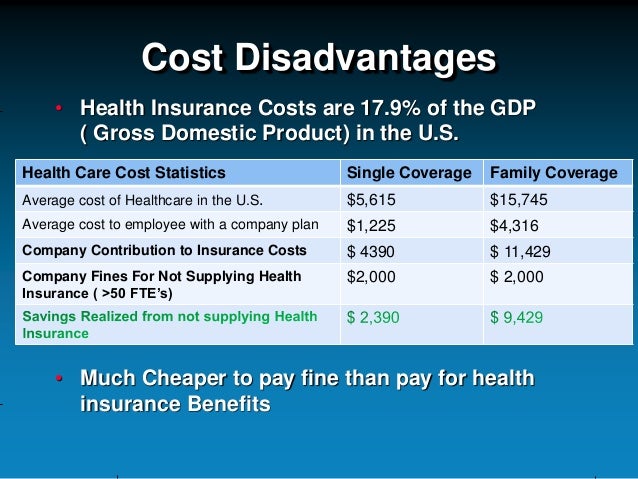
Employers pay 83% of health insurance for single coverage In 2020, the standard company-provided health insurance policy totaled $7,470 a year for single coverage. On average, employers paid 83% of the premium, or $6,200 a year. Employees paid the remaining 17%, or $1,270 a year.
What is the average cost of fringe benefits?
Although rates vary, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average fringe benefit rate (aka benefit costs) is 30%.
What is the most valued employee benefit?
Health insurance is the most expensive benefit to provide, with an average cost of $6,435 per employee for individual coverage, or $18,142 for family coverage. The next most-valued benefits were ones that offer flexibility and improve work-life balance.
How do you budget for salary and benefits?
Budgeting for salaried employees is pretty easy—just take their gross wages and divide by 12 months if you're doing a monthly budget. However, if you pay on a two-week schedule, some months will have three paychecks. Be sure to consider how often you pay your employees here. Hourly workers can get more complex.
What are the 4 major types of employee benefits?
There are four major types of employee benefits many employers offer: medical insurance, life insurance, disability insurance, and retirement plans. Below, we've loosely categorized these types of employee benefits and given a basic definition of each.
What are the benefits of an employer?
Though salary numbers are more frequently discussed, the health insurance, retirement, time off and legally required benefits, like Social Security contributions, offered by a company are equally , if not more, important. Many employees might not realize how costly these benefits are for an employer to provide.
How much does an employer spend per hour?
That equates to $5,698 per worker, per year. Employers spend an average of $2.65 per employer, per hour, for payments required by law, like Social Security and Medicare. Retirement plans and investment benefits cost employers an average of $0.55 an hour for defined benefits and $0.78 per hour for defined contributions, per employee.
How much does paid leave cost?
Paid leave benefits vary by employer, but cost on average about $5,000 per employee . This, of course, varies by industry and from company to company, and changes depending on whether a worker is entry-level, management, hourly or in an exempt position.
How much has health care increased since 2005?
Benefits Pro noted an increase of 368 percent since 2005 in the cost of employee benefits. During that time, health care alone has increased by 28 percent. This could be due in part to a spike in cases of chronic illness or to higher costs from health care providers.
How much has unemployment increased since 2004?
Since 2004, unemployment insurance costs have risen by 106.8 percent .
Which cities have lower benefits?
Some cities, like Miami, enjoy lower benefit costs. Others, like the greater Phoenix area, have seen an increase in the recent past due to the influx of Fortune 500 companies that have set up shop there.
An Employee Benefits Program: What Is It?
First, let’s define what an employee benefits program is before diving further into how much it will cost and how to get the most out of your budget. There are two types of benefits that go into a plan; mandatory and voluntary benefits.
What Affects the Cost of Your Employee Benefits Program?
It’s difficult to determine what your benefits program could cost without sitting down with an expert and discussing your unique needs. However, in general terms, the cost of your health and employee benefits program will depend on two prominent factors; the size of your business and the breadth of your plan.
How Much Do Employee Benefits Cost on Average?
We can use statistics gathered by the U.S. Bureau of Labor to get a good idea of what various employee benefits cost on average.
Why Offering Employee Benefits Is Worth It
Obviously, benefits packages cost a lot of money and take serious time and effort to put together. However, in today’s competitive job market, an employer cannot afford to not offer employee benefits coverage.
How to Reduce the Cost Of Employee Benefits Programs Without Sacrificing Quality
The first thing to consider when trying to keep costs down is what coverage you’ll want to include in your program. Be sure to analyze your program regularly and ask for employee feedback, because often, there are expensive perks that your employees don’t really want or use.
Why is it important to offer employee benefits?
You either have to do it because the law requires it, or you are highly encouraged to do so because 97% of workers say their benefits are important to how they feel about their job and workplace.
What is Supplemental Pay?
Supplemental pay. Supplemental pay includes any compensation awarded to workers outside of their normal wages, and is defined as a benefit by the BLS. This includes overtime pay, shift differential pay (compensation offered to employees that work outside of normal business hours), and any bonuses.
What is paid leave?
Paid leave comprises any time you’re paying an employee to not work. That includes allotted days for vacation or if someone gets sick, but also holidays. Check out this guide to find out if you live in a state that requires paid leave.
How much overtime do you have to pay for 40 hours a week?
Throwing a wrench in overtime pay budgeting is a new law passed in September of this year which raised the threshold under which salaried employees must be paid overtime for hours worked beyond 40/week from $23,660 to $35,568.
Do companies with 50 employees have to offer health insurance?
The employer mandate of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) says that companies with 50 or more FTE (full-time equivalent) employees must offer health insurance, but about one-third of businesses smaller than this offered health insurance last year anyway to attract job seekers and retain employees.
Is offering employee benefits expensive?
Offering employee benefits is an increasingly expensive proposition for businesses (benefits costs to employers have increased 368% over the last 14 years), and a complicated one. You can’t predict with absolute certainty who’s going to opt in and pay for voluntary benefits, or how much allotted PTO workers will actually use.
How much does an employer pay per hour?
In the public sector, the average employer-paid portion of all insurance types is $3.14 per hour per employee, which is about 8.7 percent of compensation. Of course, this varies across industries. For example:
How much do covered workers contribute to insurance?
On average, covered workers contribute approximately 18% of the premium for single coverage, and 30% of the premium for family coverage. For workers in smaller firms, the average contribution percentage for family coverage is closer to 39%.
What are the different types of insurance?
According to the BLS report, the term “insurance” encompasses four different types of coverage: health, life, short-term, and long-term disability. How much employers spend on each varies widely across sectors and industries.
Which sector pays the smallest amount of health insurance?
There is more data for the private sector, and the data is broken out for all the available industries and categories. The private sector pays the smallest share of health insurance, coming in at an average of just $2.70 per hour per employee, making up about 8% of total compensation.
Is BLS a good benchmark?
When you’re trying to figure out how much your business should spend on employee benefits, BLS data can be a good place to start, but cost is just one of many facets of your employee benefits package which can and should be benchmarked. While your entire benefits package doesn’t need to be benchmarked, there is an essential list you should measure. ...
How much does it cost to pay someone a salary of $35,000?
So, if you pay someone a salary of $35,000, your actual costs likely will range from $43,750 to $49,000.
Why add up costs?
Add up the costs to see whether your business can afford to add an employee to your staff. If your business is growing and you need more help, you can’t afford to NOT hire more workers. But knowing the cost will help you budget accordingly.
What is mandatory added cost?
Mandatory added costs of an employee. Hiring an employee means considerable payroll tax costs, including: Employer share of FICA (7.65% on compensation up to the annual wage base, which is $132,900 in 2019, plus 1.45% on compensation over the annual wage base). Federal unemployment tax (FUTA) of $42 per employee.
What are fringe benefits?
In addition to fringe benefits, there is a slew of other employment-related costs that may be difficult to quantify. These include: 1 The cost of recruitment, including background checks and drug testing where applicable. 2 The cost of initial and ongoing training. 3 Miscellaneous items, such as uniforms and protective gear where needed.
Do employers have to offer health insurance?
Think about employee benefits you may want or need to offer an employee. Under federal law, only large employers (those with 50 or more full-time and full-time equivalent employees) must offer health insurance or pay a penalty. However, there is a federal tax credit for small employers that choose to provide at least 50% of the cost of health coverage.
What percentage of compensation is health insurance?
Benefits account for approximately 29 percent of an employer’s compensation costs, the study finds. Health insurance made up 7.5 percent of compensation costs on average. Social Security and Medicare contributions, mandated by federal laws, came to 5.8 percent of employer contributions. The study notes that many industries are now adding benefits ...
Where are higher benefit costs found?
Higher benefit costs are found in companies that are centered in big, coastal cities such as San Francisco and New York . This finding isn’t too surprising, given the higher living costs in those cities. But there are some exceptions: parts of Florida such as Miami have relatively lower benefit costs for employers.
How much have benefits increased over time?
Benefits costs increase over time—but in different ways. The analysis finds that total costs of benefits to employers have increased 368 percent over 14 years. During that time, health benefits cost has increased by 28 percent, which the study attributes to chronic illness and rising costs from health care providers.
How much does health insurance cost per hour?
The total average cost for insurance benefits, including health, life, and disability insurance, comes to $2.73 per hour, or $5,698 annually per employee. Legally-required benefit contributions such as Social Security and Medicare add up to $2.65 per employee per hour.
How much has unemployment increased since 2004?
Despite the recent improvements in the U.S. economy, unemployment costs to employers have risen 106.8 percent since 2004—which the study attributes in part to the 2008 recession.
Why is Arizona's minimum wage higher?
Another reason may be a new law in the state that increased the minimum wage and required employers to offer sick time benefits to workers.
Do small companies have fewer workers?
The report notes that, “Ultimately, small companies have fewer workers to provide benefits for, while the largest companies may benefit from an economy of scale that many small or midsized companies lack.”. A more interesting finding may be the difference that location makes when it comes to benefits.
