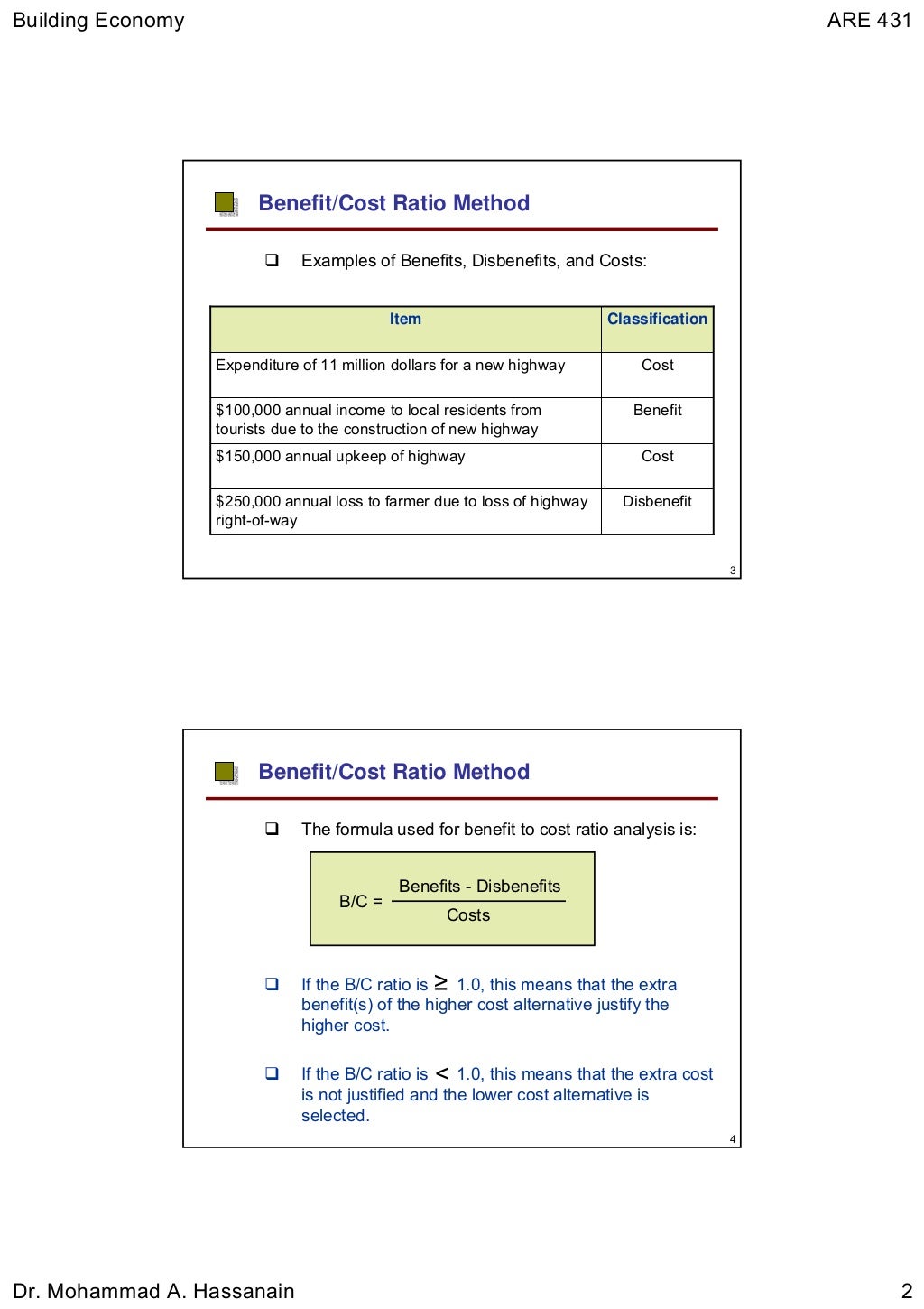
- The BCR Formula. The benefit cost ratio is calculated by dividing the present value of benefits by that of costs and investments.
- Components of the BCR Formula. The Formula for calculating the benefit cost ratio consists of three components: The present value of all benefits, the present value of all costs and, ...
- Input Parameters and Assumptions. The cash flows used for calculating the benefit cost ratio are typically monetary values stemming from a business forecast.
What is the formula for cost benefit analysis?
What is the Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula?
- Example of Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula (With Excel Template) Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Cost-Benefit Analysis in a better manner. ...
- Explanation. ...
- Relevance and Use of Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula. ...
- Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula Calculator
- Recommended Articles. ...
How to estimate benefits in a cost?
How to Calculate Your Backyard Renovation Cost
- Make a list of what you’re after. Depending on the size of your backyard, it’s possible to either make it look like a private resort or an approachable outdoor living ...
- Hold on to what’s good. ...
- You need a design phase. ...
- Spaces should have more than one use. ...
- Don’t be shocked by the cost of nixing rocks. ...
- If you invest in one thing, make it trees. ...
What is the benefit cost ratio (BCR)?
What is the Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR)? The benefit-cost ratio (BCR) is a profitability indicator used in cost-benefit analysis to determine the viability of cash flows generated from an asset or project. The BCR compares the present value of all benefits generated from a project/asset to the present value of all costs.
How is a benefit cost ratio computed?
There are two common summary measures used in a benefit-cost analysis. The first is a benefit-cost ratio. To find this ratio, divide the program’s net benefits by its net costs. The result is a summary measure that states, “for every dollar spent on program X, Y dollars are saved.”
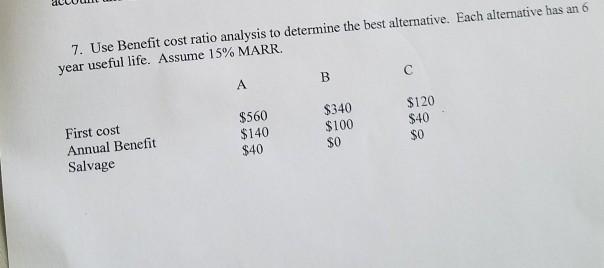
How do you calculate benefit-cost ratio with example?
Use the following data for calculation of the benefit-cost ratio. Since the BCR of Project B is higher, Project B should be undertaken....Example #3.ParticularsAmountPresent Value of Benefit Expected from Project4000000Present Value of Cost of the Project2000000
What is the formula for calculating cost ratio?
How To Calculate Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR): With ExamplesBCR = PV of expected benefits / PV of expected costs.BCR = PV of expected benefits / PV of expected costs to the power of each period.More items...•
How is cost-benefit analysis calculated?
For simple examples, where the same benefits are received each period, you can calculate the payback period by dividing the projected total cost of the project by the projected total revenues: Total cost / total revenue (or benefits) = length of time (payback period).
Why is benefit-cost ratio calculated?
The benefit-cost ratio is used to determine the viability of cash flows from an asset or project. The higher the ratio, the more attractive the project's risk-return profile. Poor cash flow forecasting or an incorrect discount rate would lead to a flawed benefit-cost ratio.
What is cost-benefit analysis example?
For example: Build a new product will cost 100,000 with expected sales of 100,000 per unit (unit price = 2). The sales of benefits therefore are 200,000. The simple calculation for CBA for this project is 200,000 monetary benefit minus 100,000 cost equals a net benefit of 100,000.
What does a benefit-cost ratio of 2.1 mean?
This means: A. The costs are 2.1 times the benefits.
What is a good benefit/cost ratio?
If a project has a BCR greater than 1.0, the project is expected to deliver a positive net present value to a firm and its investors. If a project's BCR is less than 1.0, the project's costs outweigh the benefits, and it should not be considered.
How do I do a cost-benefit analysis in Excel?
A typical cost benefit analysis involves these steps:Gather all the necessary data.Calculate costs. Fixed or one time costs. Variable costs.Calculate the benefits.Compare costs & benefits over a period of time.Decide which option is best for chosen time period.Optional: Provide what-if analysis.
How do you calculate NPV in cost-benefit analysis?
NPV is calculated by subtracting the discounted costs from the discounted benefits. All projects with a positive NPV provide a net economic benefit. NPV should be used when comparing mutually exclusive project options.
How do you calculate cost benefit ratio in agriculture?
BCR = PV of benefits stream / PV of Costs. Up to my knowledge for agriculture related production oriented produce the best way to calculate B:C ratio by dividing gross returns with total expenditure incurred.
What are the two ways of defining the benefit-cost ratio?
The Benefit Cost Ratio (BCR), also referred to as Benefit-to-Cost Ratio is an indicator that is typically used within a cost benefit analysis....Definition and Meaning of Benefit Cost Ratio.Value Range of Benefit Cost RatioGeneric InterpretationBCR = 1Investment option is neither profitable nor lossy.2 more rows
What is a benefit ratio in insurance?
The benefit-expense ratio is a metric used by the insurance industry to describe the cost of providing underwriting insurance to the revenues it receives from those policies. The ratio is calculated by dividing a company's costs of insurance coverage by the revenues from premiums charged for that coverage.
What is the benefit cost ratio?
What is the benefit-cost ratio formula? The benefit-cost ratio formula, or BCR, is a financial metric that professionals use to assess the costs and benefits of a project to determine its viability. Companies analyze a proposed project with the BCR to see the relationship between the costs to complete the project and the expected benefits over time.
How to find the present value of expected benefits?
You can find the present value (PV) of expected benefits in a period by determining all the cash inflows and monetary benefits you expect from the project, such as incremental revenue, sales, cost savings, increased value of assets or received interest payments. 2.
How to write BCR?
When writing the benefit-cost ratio formula mathematically, it looks like this: BCR = PV of expected benefits / PV of expected costs. Where:
Why is BCR important?
While it's advisable to use multiple indicators and measures when assessing project viability, the BCR is special because of its ability to show absolute amounts of cost and benefits. The BCR formula helps compare project alternatives or difference investments. It can help investors to determine the risk involved in a project by forecasting whether there is a small profit margin with a higher risk or a larger profit margin with a lower risk. Since you can calculate time periods as part of the BCR, you can also use the formula to identify cash flow in relation to time.
When to use BCR?
The most common use for the BCR is when analyzing the overall fiscal value of a new project in capital budgeting. Since capital budgeting often includes projects where you assumptions and where quantitative data may be uncertain, there is often a large variety of potential BCR outcomes.
Is a project a good financial consideration?
This means that the cash flow from the project is more than the cost of the project, so the project is a good financial consideration. When a project has a BCR value lower than one, the cash flow benefits are less than the cost, meaning the project costs more than it will return financially. You can write the BCR formula as the present value ...
Can BCR be qualitative?
You can express BCR values either as monetary or qualitativ e. When a project has a BCR value higher than one, a firm and its investors can expect the project to deliver a positive net present value and an internal rate of return above the discount rate.
What is the benefit cost ratio?
The benefit-cost ratio indicates the relationship between the cost and benefit of project or investment for analysis as it is shown by the present value of benefit expected divided by present value of cost which helps to determine the viability and value that can be derived from investment or project.
What is the benefit of using the benefit cost ratio?
The benefit of using the benefit-cost ratio (BCR) is that it helps to compare various projects in a single term and helps to decide faster which projects should be preferred and which projects should be rejected.
What does BCR mean in investment?
If the Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR) is equal to one, the ratio will indicate that the NPV of investment inflows will equal investment’s outflows. Lastly, if the investment’s BCR is not more than one, the investment’s outflow shall outweigh the inflows or the benefits, and the project should not be taken into consideration.
How to calculate BCR?
To calculate the BCR formula, use the following steps: Step 1: Calculate the present value of the benefit expected from the project. The procedure to determine the present value is: Aggregate the amounts for all the years. Step 2: Calculate the present value of costs.
What are the limitations of BCR?
The major limitation of the BCR is that since it reduces the project to mere a number when the failure or success of the projector of expansion or investment etc. relies upon various variables and other factors, and those can be weakened by events which are unforeseen.
What are the advantages of benefit cost ratio?
Key advantages of the benefit-cost ratio include: It is a useful starting point in determining a project’s feasibility and whether it can generate incremental value. If the inputs are known (cash flows, discount rate), the ratio is relatively easy to calculate. The ratio considers the time value of money. Time Value of Money The time value of money ...
What is discount rate?
The discount rate used refers to the cost of capital, which can be the company’s required rate of return. Required Rate of Return The required rate of return (hurdle rate) is the minimum return that an investor is expecting to receive for their investment. Essentially, the required rate of return is the minimum acceptable compensation for ...
What is the time value of money?
Time Value of Money The time value of money is a basic financial concept that holds that money in the present is worth more than the same sum of money to be received in the future. This is true because money that you have right now can be invested and earn a return, thus creating a larger amount of money in the future.
Is benefit cost ratio a determinant of feasibility?
Although the benefit-cost ratio is a simple tool to gauge the attractiveness of a project or asset, it should not be the sole determinant of a project’s feasibility. Other ratios and further analysis are recommended.
What is discount rate?
The discount rate is used for discounting the cash flows. Set a rate that is consistent with the requirements of your organization, e.g. capital cost or internal return target, or a risk-adjusted market interest rate. The calculator will apply this discount rate to all cash flows in order to discount them.
What does a BCR of 1 mean?
A BCR of 1 is the result of a present value of the benefits equal to the present value of the costs of a project or investment. A BCR greater than 1 stands for a profitable option. Its value increases as the relative excess ...
What is BCR analysis?
In cost benefit analyses, the BCR is one of the common methods to assess and compare the future profitability of a series of cash flows (see PMI PMBOK®, 6 th ed., part 1, ch. 1.2.6.4, p. 34). It is often used to supplement comparisons based on the net present value. In these cases, the BCR indicates the relation of costs and benefits. It is interpreted as follows: 1 A BCR lower than 1 indicates that the series of cash flows is not profitable. 2 A BCR of 1 is the result of a present value of the benefits equal to the present value of the costs of a project or investment. 3 A BCR greater than 1 stands for a profitable option. Its value increases as the relative excess of the discounted benefits over the discounted costs increases.
What to do if costs are not cash flows?
If some of your costs or benefits are not cash flows, e.g. use of internal resources, convert them into cash flow equivalents for comparison purposes. The same advice is applicable to non-monetary costs and benefits – they need to be converted into a consistent (currency) unit to ensure quantitative comparability.
What is BCR in economics?
The BCR also does not provide any sense of how much economic value will be created, and so the BCR is usually used to get a rough idea about the viability of a project and how much the internal rate of return (IRR) exceeds the discount rate, which is the company’s weighted-average cost of capital (WACC) – the opportunity cost of that capital. ...
What does BCR mean in NPV?
If the BCR is equal to 1.0, the ratio indicates that the NPV of expected profits equals the costs. If a project's BCR is less than 1.0, the project's costs outweigh the benefits, and it should not be considered.
What is BCR in project?
A benefit-cost ratio (BCR) is an indicator showing the relationship between the relative costs and benefits of a proposed project, expressed in monetary or qualitative terms. If a project has a BCR greater than 1.0, the project is expected to deliver a positive net present value to a firm and its investors.
What is the limitation of BCR?
The primary limitation of the BCR is that it reduces a project to a simple number when the success or failure of an investment or expansion relies on many factors and can be undermined by unforeseen events. Simply following a rule that above 1.0 means success and below 1.0 spells failure is misleading and can provide a false sense of comfort with a project. The BCR must be used as a tool in conjunction with other types of analysis to make a well-informed decision.
What is benefit cost ratio?
The benefit cost ratio (or benefit-to-cost ratio) compares the present value of all benefits with that of the cost and investments of a project or investment. These benefits and costs are treated as monetary cash flows or their equivalents, e.g. for non-monetary benefits or company-internal costs.
What are the components of benefit cost ratio?
The Formula for calculating the benefit cost ratio consists of three components: The present value of all benefits, the present value of all costs and, finally, the division of these present values. We will discuss them in this subsection.
What is BCR in financial accounting?
The BCR can be used to supplement this missing piece of information. Representing the ratio of discounted benefits to discounted costs, it is a relative measure of whether and to which extent the present value of the benefits exceeds that of the investments and cost.
What is BCR in project management?
In project management, the benefit cost ratio can support the cost-benefit analysis of a business case.
What are some examples of cost cash flows?
Examples of cost cash flows are the initial investments, expenses for the creation of products or results, administrative costs, disposal costs, etc.
Does BCR cover cost benefit analysis?
While it does not cover all aspects of a cost benefit analysis, it indicates whether an option is beneficial. As the BCR compares discounted benefits with discounted costs, it offers a good indication of how big a ‘buffer’ between benefits and costs is.
How to calculate cost-benefit ratio?
For calculating the cost-benefit ratio, follow the given steps: Step 1: Calculate the future benefits. Step 2: Calculate the present and future costs. Step 3: Calculate the present value of future costs and benefits. Step 4: Calculate the benefit-cost ratio using the formula.
How is cost benefit analysis used?
Cost-benefit analysis is useful in making decisions on whether to carry out a project or not. Decisions like whether to shift to a new office, which sales strategy to implement are taken by carrying out a cost-benefit analysis. Generally, it is used for carrying out long term decisions that have an impact over several years. This method can be used by organizations, government as well as individuals. Labor costs, other direct and indirect costs, social benefits, etc. are considered while carrying out a cost-benefit analysis. The costs and benefits need to be objectively defined to the extent possible.
Why is cost benefit analysis important?
Cost-benefit analysis is useful in making decisions on whether to carry out a project or not. Decisions like whether to shift to a new office, which sales strategy to implement are taken by carrying out a cost-benefit analysis.
What is labor cost?
Labor costs. Labor Costs Cost of labor is the remuneration paid in the form of wages and salaries to the employees.
What are allowances in manufacturing?
The allowances are sub-divided broadly into two categories- direct labor involved in the manufacturing process and indirect labor pertaining to all other processes. read more. , other direct and indirect costs, social benefits, etc. are considered while carrying out a cost-benefit analysis.
What is a cost-benefit ratio?
A cost-benefit ratio greater than 1 is generally treated as a good indicator. It means that the benefits derived from the investment are more than its costs. It states the benefit earned by the company on spending every dollar. In the example above, the benefit-cost ratio is 1.52 which means the company will earn $1.52 on every $1 investment.
What are the costs incurred at zero?
These costs may include additional working capital requirement or additional equipment, etc. The management discount these costs on their present value.
Why is benefit cost ratio important?
Conclusion. A benefit-cost ratio helps project managers address whether or not a project should be pursued, or in some cases, which project presents the best option. It is a valuable and necessary tool for cost-benefit analysis and project selection.
What is Opportunity Cost?
Opportunity cost is a concept describing the cost of pursuing one project and rejecting other options.
What is the BCR of a project?
An easy way to do it is to divide: Project A has a BCR of 5:2, and 5 / 2 is 2.5 . Do that with all four projects, and you find that project C has the highest BCR. A. BCR stands for benefit-cost ratio and it measures the benefits (revenue) against the cost of implementing the project.
What is indirect cost?
Indirect costs are typically shared between multiple projects, such as software that benefits more than one project. As you study for the PMP exam, remember sunk cost shouldn’t influence whether or not you pursue a project. Those decisions should be made based on the NPV, BCR, and other similar factors.
Do you have to calculate PV for PMP?
More than likely , you will not have to calculate PV for the PMP exam. However, you should understand the benefit-cost ratio is the PV of the benefits divided by the PV of the costs. As mentioned previously, the benefit-cost ratio is expressed as a decimal.

Formula
Steps to Calculate Benefit-Cost Ratio
Examples
Advantages
Disadvantages
- To calculate the BCR formula, use the following steps: 1. Step 1: Calculate the present value of the benefit expected from the project. The procedure to determine the present value is: 1. The amount for each year = Cash Inflows*PV factor 2. Aggregate the amounts for all the years. 1. Step 2: Calculate the present value of costs. If the costs are in...
Conclusion
- Example #1
EFG ltd is working upon the renovation of its factory in the upcoming year, and for they expect an outflow of $50,000 immediately, and they expect the benefits out of the same for $25,000 for the next three years. The inflation rate that is currently prevailing is 3%. You are required to assess … - Example #2
Sunshine private limited has recently received an order where they will sell 50 tv sets of 32 inches for $200 each in the first year of the contract, 100 air condition of 1 tonne each for $320 each in the second year of the contract, and the third year they will sell 1,000 smartphones valuing at $5…
Recommended Articles
- The benefit of using the benefit-cost ratio (BCR) is that it helps to compare various projects in a single term and helps to decide faster which projects should be preferred and which projects shou...
- It compares benefit and cost at the same level that is it considers the time value of money before giving any outcome based on absolute figures as there could be a scenario that the pr…
- The benefit of using the benefit-cost ratio (BCR) is that it helps to compare various projects in a single term and helps to decide faster which projects should be preferred and which projects shou...
- It compares benefit and cost at the same level that is it considers the time value of money before giving any outcome based on absolute figures as there could be a scenario that the project appears...
Formula For The Benefit-Cost Ratio
- The major limitation of the BCR is that since it reduces the project to mere a number when the failure or success of the projector of expansion or investment etc. relies upon various variables and...
Example of The Benefit-Cost Ratio
- We can conclude that if the investment has a BCR which is greater than one, the investment proposal will deliver a positive NPV and on the other hand, it shall have an IRR that would be above the discount rate or the cost of project rate, which will suggest that the Net Present Value of the investment’s cash flows will outweigh the Net Present Value of the investment’s outflows …
Interpreting The Benefit-Cost Ratio
- This article has been a guide to Benefit-Cost Ratio and its definition. Here we discuss the formula to calculate Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR) along with examples. Advantages and limitations. You can learn more about excel modeling from the following articles – 1. Advantages of Net Present Value 2. Cost-Benefit Analysis Examples 3. Mutual Fund Expense Ratio 4. Calculate Benefit-Cost Ratio
Advantages of The Benefit-Cost Ratio
Limitations of The Benefit-Cost Ratio
- Cash flow projections for a project are provided below. The relevant discount rateDiscount RateA discount rate is the rate of return used to discount future cash flows back to their present value. It is often a company’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC),is 10%. Question: What is the benefit-cost ratio of the project? Answer: The benefit-cost ratio would be calculated as $97,670.…
Final Thoughts
- The higher the BCR, the more attractive the risk-return profile of the project/asset. The value generated by the BCR indicates the dollar value generated per dollar cost. For example, the BCR of 2.90 in the preceding example can be interpreted as “For each $1 of cost in the project, the expected dollar benefits generated is $2.90.” The following shows the value range of the BCR an…
More Resources
- Key advantages of the benefit-cost ratio include: 1. It is a useful starting point in determining a project’s feasibility and whether it can generate incremental value. 2. If the inputs are known (cash flows, discount rate), the ratio is relatively easy to calculate. 3. The ratio considers the time value of moneyTime Value of MoneyThe time value of money is a basic financial concept that holds th…