What exactly is tax amortization benefit?
- A tax credit.
- A tax deduction.
- And a capital loss deduction.
How to calculate amortization expense for tax deductions?
- Whenever possible, make extra payments to reduce the principal amount of your loan faster. ...
- Consider the interest rate on the debts you have outstanding. ...
- You can find loan amortization calculators on the Internet. ...
- Use the $10,000 figure and calculate your amortization over the remaining term of the loan. ...
How to calculate and make estimated tax payments?
How to Calculate Estimated Taxes and Make A Payment. Once you’ve used our estimated tax calculator to figure out how much you owe, making the payment is fairly straightforward and takes less than 15 minutes. You’ll need to make the payments four times per year, according to these due dates: April 15th (payment #1) June 15th (payment #2)
How to calculate the total amount with tax?
- ‘Wearing that armor gave me a sense of power’: Temuera Morrison on playing Boba Fett
- Kerala Lottery 2022: Win Win W-652 draw results to be declared at 3 pm, first prize Rs 75 lakh
- National Girl Child Day 2022: A nation's journey towards achieving equality in India's society

Can goodwill be amortized for tax purposes in Canada?
Goodwill and Intangible Assets cannot be depreciated for tax purposes since they are not tangible assets.
Is amortisation tax deductible in Australia?
Amortisation of intangible assets is not always tax deductible. Its deductibility depends on the corporate income tax legislation of single countries....Further Detail and Source Legislation.Asset typeUseful life (years)Telecommunications site access rightTerm of the right10 more rows
What is a tax amortization benefit factor?
In accounting, tax amortization benefit (or tax amortisation benefit) refers to the present value of income tax savings resulting from the tax deduction generated by the amortization of an intangible asset.
Is amortisation of intangible assets tax deductible?
Amortisation of intangible assets is not always tax deductible. Its deductibility depends on the corporate income tax legislation of single countries. Most countries define maximum amortisation rates or minimum number of years in which the amortisation of intangible assets can be deducted, if at all.
Does amortization affect tax?
You can deduct amortization expenses to reduce your tax liability. Deducting amortization lowers taxable earnings and shrinks your year-end tax bill. You can deduct a portion of the cost of an intangible asset for each year that it's in service until it has no further value.
How do you amortize expenses?
Subtract the residual value of the asset from its original value. Divide that number by the asset's lifespan. The result is the amount you can amortize each year.
Is goodwill tax deductible in India?
In September 2012, the Supreme Court of India declared that Goodwill would fall under the expression “any other business or commercial rights of a similar nature” under clause (b) of Explanation 3 of section 32(i) of the income Tax Act, 1961. Therefore, goodwill is considered to be tax deductible as well.
What is contributory asset charge?
A contributory asset charge is a charge against revenues to reflect a fair return on or return of contributory assets used in the generation of the cash flows associated with the intangible asset being valued. Once determined, contributory asset charges are typically allocated based on revenues.
Is amortisation tax deductible in South Africa?
Intangible assets: as a general rule, amortisation of intangible assets is not tax deductible. Therefore purchase price should be allocated to tangible assets as much as possible. As an exception, amortisation of acquired Patents can be deducted with a 5% p.a. limitation (Article 11 - Section gC-V-aa-A).
Is HMRC amortisation tax deductible?
With effect for acquisition of goodwill and customer-related intangibles on or after 8 July 2015, amortisation, impairment, and certain other charges are not deductible for tax.
How are intangible assets treated for tax purposes?
Intangible fixed assets are taxed and relieved as income, and relief may be given as expenditure is incurred, on an accounting basis or at a fixed annual rate.
What is tax amortization benefit?
Tax amortisation benefit (TAB) refers to the net present value of income tax savings resulting from the amortisation of intangible assets. Amortisation of assets decreases the net taxable income and thereby the corporate income tax to be paid as cash.
What is the present value of the tax savings caused by the amortisation of an asset?
The present value of the tax savings caused by the amortisation of an asset is a mathematical function of its fair value. This creates circularity, because the fair value should include the present value of the tax savings.
When should amortisation benefits be included in fair value?
The inclusion of tax amortisation benefits in fair value is implicit in FASB Accounting Standards Codification 740 Income Taxes (ASC 740), which requires assets acquired and liabilities assumed to be stated at their “gross” fair value, even if the transaction happens to be a non-taxable business combination rather than an asset purchase.
When the purchaser of an intangible asset is allowed to amortise the price of the asset as an?
When the purchaser of an intangible asset is allowed to amortise the price of the asset as an expense for tax purposes , the value of the asset is enhanced by the present value of the future tax savings allowed by the amortisation. This idea is analogous to the treatment commonly afforded to depreciation expense in net present value calculations.
What is the TAB in tax?
The TAB is added to the value of the intangible asset on the premise that a potential purchaser will be willing to pay an amount that reflects the present value of the tax amortisation benefit.
What is tax amortization benefit?
In accounting, tax amortization benefit (or tax amortisation benefit) refers to the present value of income tax savings resulting from the tax deduction generated by the amortization of an intangible asset .
When an intangible asset is amortized as an expense for tax purposes, the value of the asset is enhanced?
When the purchaser of an intangible asset is allowed to amortize the price of the asset as an expense for tax purposes, the value of the asset is enhanced by this tax amortization benefit. Specifically, the fair market value of the asset is increased by the present value of the future tax savings derived from the tax amortization of the asset.
How long is the amortization period for a trademark?
For example, while trademarks can have an indefinite useful life for accounting purposes, the tax legislation of the United States establishes a mandatory 15-year amortization period for trademarks.
What is the present value of future tax savings?
This circularity can be handled using a two-step procedure consisting in estimating the value of the intangible asset in the absence of the tax amortization benefit first and then grossing up the previous value by a tax amortization benefit factor.
How to calculate amortization?
Accountants typically use the straight-line method to calculate amortization. First, you start with the total cost of the asset. Next, you determine its useful life. Determining the asset value can be tricky in some instances.
What is amortization in finance?
Amortization has two perfectly acceptable uses in finance terms. One describes a type of loan, and the other describes a way to calculate deductible expenses.
What are intangible assets?
Intangible Assets. Intangible assets include anything that is not physical in nature, including patents, business licenses, copyrights, and trademarks. These types of assets usually have no value at the end of their useful lives. Businesses can either acquire or create intangible assets.
What happens if you don't claim amortization expense?
If you’re not claiming an amortization expense on your intangible assets, you’re missing out on an easy write-off. In most cases, you want to claim every applicable deduction so you can minimize your tax liability, so you should take advantage of this deduction if you can.
How long does a mortgage amortize?
However, this eventually inverts and the principal begins to comprise most of your payment over time. Most mortgages have an amortization schedule of 30 years. However, shorter-term mortgages allow borrowers to amortize their loans more quickly.
Is amortization a deduction?
There are tons of deductions that can help you minimize your taxable income, and amortization is only one of them. If you’re not a tax pro, you might not even be aware of all the deductions that you can claim. You should consult with a tax advisor to ensure you’re taking advantage of every available write-off. A tax pro can also help you develop a tax planning strategy that can help you save even more money.
Can you deduct amortization expenses?
You can deduct amortization expenses to reduce your tax liability. Deducting amortization lowers taxable earnings and shrinks your year-end tax bill. You can deduct a portion of the cost of an intangible asset for each year that it’s in service until it has no further value.
What is tax amortization benefit?
3 Tax amortization benefit is defined as: “…the cash flow generated from an asset as a result of being able to write off the full fair value of the asset for tax purposes.” bizfluent.com, (2017, September 27). How to Calculate Tax Amortization Benefit
How long is intangible asset amortization?
Under U.S. tax law, both intangible assets and goodwill in a taxable asset purchase are amortized over fifteen years.
How long is goodwill amortized?
This is different from U.S. tax amortization benefit rules where all identifiable intangible assets and goodwill are amortized over a 15-year period for tax purposes, in a taxable asset acquisition or in a stock acquisition where the buyer makes a §338 election.
When valuing a foreign company, valuation professionals can encounter challenges in calculating the tax amortization benefits applicable to?
Often, when valuing a foreign company, valuation professionals can encounter challenges in calculating the tax amortization benefits applicable to the intangible assets recognized in a given acquisition.
When valuing a foreign target company in the context of a purchase price allocation, should the local tax rules?
When valuing a foreign target company in the context of a purchase price allocation, the local tax rules within the company’s jurisdiction should be considered and applied pursuant to the acquisition structure. Acquisition transactions can be structured as a taxable asset acquisition or a stock acquisition.
What is the role of acquisition structures in tax?
Acquisition structures play a crucial role in determining how certain tax rules are applied.
Can a 338 be a taxable asset?
However, in certain circumstances, the buyer can make a Section 338 election 2 whereby the transaction can be treated as a taxable asset purchase for tax purposes. Once the acquisition structure and its tax implications have been established, the business valuation professional must consider the appropriate tax rules that apply to ...
What is tax amortization benefit?
In Valuation (finance), tax amortization benefit (or tax amortisation benefit) refers to the present value of income tax savings resulting from the tax deduction generated by the amortization of an intangible asset.
What is the present value of future tax savings?
The present value of the future tax savings is a mathematical function of the fair market value. This creates circularity, because the fair market value includes the present value of the tax savings.
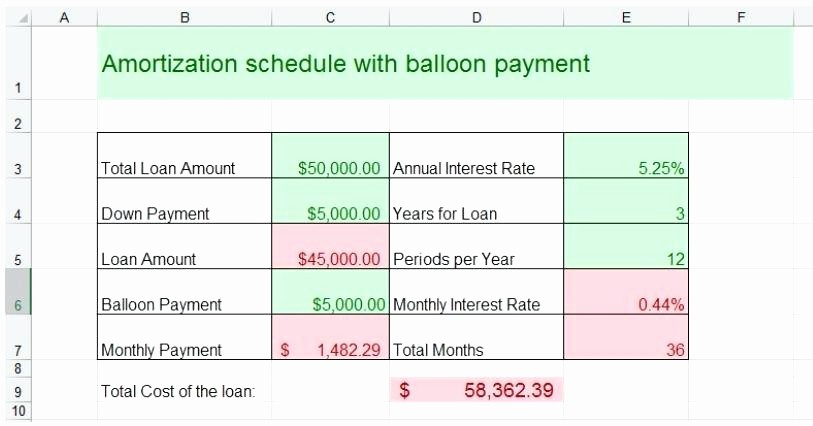
How does amortization schedule help?
Amortization schedule helps one to know when he has to pay EMI against his loan and what is the EMI which he needs to pay, how much interest he has to pay on his loan, what is the principal outstanding of the loan. It is a very systematic and easy way to track repayment of the loan.
What is amortization of a loan?
Amortization refers to paying off debt amount on periodically over time till loan principle reduces to zero. Amount paid monthly is known as EMI which is equated monthly installment. EMI has both principal and interest component in it which is calculated by amortization formula. Amortization calculation depends on the principle, the rate of interest and time period of the loan. Amortization can be done manually or by excel formula for both are different.
What happens if a borrower does part payment?
If any borrower does part payment his amortization schedule changes and effect of same is visible on EMI or tenure that means borrower can request for tenure change where EMI tenure will reduce and his EMI amount will be same or he can request for the change in EMI where EMI amount will reduce and tenure will be the same.

Overview
Tax amortization benefit factor
The tax amortization benefit factor (or TAB factor) is the result of a mathematical function of a corporate tax rate, a discount rate and a tax amortization period:
where
1. TAB factor is the value assuming end-year discounting
2. t is the corporate tax rate applicable to the future amortization of the asset
Intangible asset valuation
When the purchaser of an intangible asset is allowed to amortize the price of the asset as an expense for tax purposes, the value of the asset is enhanced by this tax amortization benefit. Specifically, the fair market value of the asset is increased by the present value of the future tax savings derived from the tax amortization of the asset. The present value of these savings is to be estimated and included as a part of the fair market value when valuing an intangible asset.
Circularity of the tax amortization benefit
The present value of the future tax savings is a mathematical function of the fair market value. This creates circularity, because the fair market value includes the present value of the tax savings. This circularity can be handled using a two-step procedure consisting in estimating the value of the intangible asset in the absence of the tax amortization benefit first and then grossing up the previous value by a tax amortization benefit factor.
See also
• Business valuation
• Business valuation standard
• Intellectual property valuation
• Market-based valuation
Sources
• The Canadian Institute of Chartered Business Valuators. Illustrative Example of Intangible Asset Valuation. 2009.
External links
• Online tax amortization benefit calculator and a list of legal tax amortization periods per country
• Tax amortization benefit calculator