
What are the benefits and risks of using GMOs? The benefits of using GMOs include crops having higher harvest yields which can feed more people in the world, and making food more nutritional. The risks of using GMOs include both the unknown long term risks of eating GMO crops and the negative effects that they can have on an environment.
What are some pros and cons about GMOs?
Pros: Cons: Faster Growth Rate Animals and plants can be genetically modified to promptly mature.For example, crops can be engineered to increase crop yield. There are crops being engineered to survive unfavorable conditions such as high heat or low light.
What are the major benefits of using GMOs?
What are the major benefits of using GMOs? The major benefit of all commercial GMO’s is that they are bred to either tolerate direct application of herbicides and/or have the ability to produce their own pesticides. They have not been bred to increase yield, become drought tolerant, improve nutrition or to have any other benefit to the consumer.
Which companies benefit from GMOs?
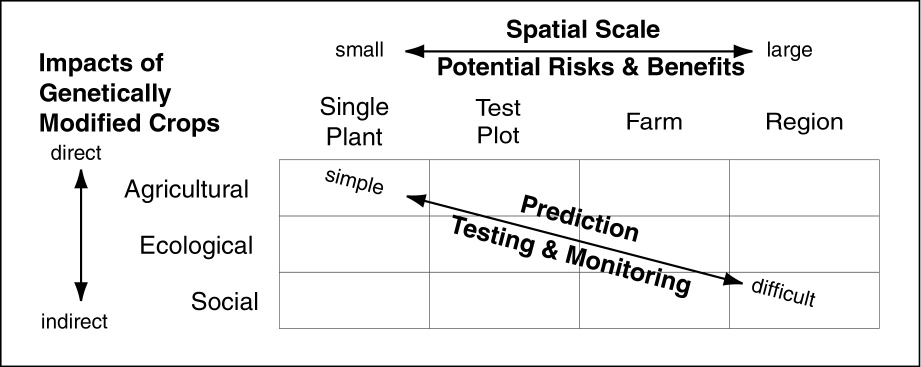
- Enhanced use of integrated pest-management practices with negligible impact on non-target organisms (Mendelsohn et al., 2003; Marvier et al., 2007).
- Reduced exposure to pesticides by farmers using Bt crops (Mannion and Morse, 2012; Shutske, 2005).
- Enhanced safety of foods and animal feed due to lower levels of mycotoxins. ...
- Increased farmer incomes. ...
Do the pros of GMOs outweigh the cons?
Related Documents
- Gmo Labeling Pros And Cons. In this scenario, consumers will have a better choice (Carter and Gruère, 2003). ...
- Pros And Cons Of GMO. Do The Pros of GMO’s outweigh the Cons? ...
- GMO Labeling Affect The Economy. ...
- The Conflict Over Gmo Foods. ...
- Gmo Myth Or Fact
What does Calkins think about GMOs?
What percentage of soybeans are genetically modified?
Who said GMOs take mankind into realms that belong to God and God alone?
Can GMOs cause harm?
Do GMOs harm the environment?
See more
About this website
What are the benefits of GMO?
Some benefits of genetic engineering in agriculture are increased crop yields, reduced costs for food or drug production, reduced need for pesticides, enhanced nutrient composition and food quality, resistance to pests and disease, greater food security, and medical benefits to the world's growing population.
What are some risks of GMOs?
What are the new “unexpected effects” and health risks posed by genetic engineering?Toxicity. Genetically engineered foods are inherently unstable. ... Allergic Reactions. ... Antibiotic Resistance. ... Immuno-suppression. ... Cancer. ... Loss of Nutrition.
What are the advantages and disadvantages risks of GMOs?
The pros of GMO crops are that they may contain more nutrients, are grown with fewer pesticides, and are usually cheaper than their non-GMO counterparts. The cons of GMO foods are that they may cause allergic reactions because of their altered DNA and they may increase antibiotic resistance.
What are 5 Advantages and disadvantages of GMOs?
10 Advantages and Disadvantages of GMOsThey offer more useful knowledge for genetics. ... They allow for more profit. ... They add more value to crops. ... They are known to decrease the prices of food. ... They yield products that are found to be safe.
What are the five disadvantages of GMOs?
What Are the Disadvantages of GMOs?It can be dangerous to other insects that are important to our ecosystem. ... It sparks concerns on changing the field of agriculture. ... It can damage the environment. ... It causes unwanted residual effects. ... It can create more weeds. ... It threatens crop diversity. ... It has trade issues.
10 Benefits of GMOs | Helps Farmers in Developing Countries | Farms.com
Many farmers in North America are fortunate enough to be able to practice agriculture and provide food for their families and beyond. However, in parts of the developing world, the struggle to produce food is difficult, and GMOs (Genetically Modified Organisms) help farmers in those areas.
The benefits and risks of GMOs | alimentarium
Since genetically modified organisms (GMOs) first appeared at the beginning of the 1990s, they have been widely adopted in agriculture. However, their newness has raised a certain number of societal issues. Whilst their positive or negative impacts on production and on the environment continue to fuel debate, the fact that they are harmless to human health has now garnered consensus with the ...
9. RISK FACTORS OF GMOS - Food and Agriculture Organization
9. RISK FACTORS OF GMOS. There are a number of publications which address this issue. Maclean and Laight (2001) and Dunham (1999) have produced very useful reviews which discuss many of the points raised in this paper.
Benefits and risks associated with genetically modified food products
Scientists employing methods of genetic engineering have developed a new group of living organisms, termed 'modified organisms', which found application in, among others, medicine, the pharmaceutical industry and food distribution. The introduction of transgenic products to the food market resulted …
How do farmers use GMOs?
In most cases, farmers who use GMO technologies do so to increase productivity , either by increasing production yields (minimising pest-related losses), or financial returns (reducing labour or the use of specific phytosanitary products).
When did GMOs first appear?
GMO. Since genetically modified organisms (GMOs) first appeared at the beginning of the 1990s, they have been widely adopted in agriculture. However, their newness has raised a certain number of societal issues.
Is GMP harmful to the environment?
The Swiss National Science Foundation reports the results of the analysis of over a thousand international scientific publications: “Genetically modified plants (GMPs) are not harmful for human health or for the environment.
Is GMO cultivation forbidden?
Meanwhile, cultivation of GMOs remains forbidden in over thirty nations. In 2015, a majority of European Union countries decided to block the cultivation of eight new types of GMO pending new data and approval from regulatory bodies. Nonetheless, the European Union remains the greatest user of GMOs: 30 million tonnes of genetically modified soya ...
What is GMO in agriculture?
Definition. Pros. Cons. Identification. Bottom line. GMOs, short for genetically modified organisms, are subject to a lot of controversy. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), GMO seeds are used to plant over 90% of all maize (corn), cotton, and soy grown in the United States, which means that many of the foods you eat likely ...
What are GMO crops?
GMO crops grown and sold in the United States include corn, soybean, canola, sugar beet, alfalfa, cotton, potatoes, papaya, summer squash, and a few apple varieties ( 29. Trusted Source. ). In the United States, no regulations currently mandate the labeling of GMO foods.
Why do people fear eating foods with added genes?
Because cancers are caused by DNA mutations, some people fear that eating foods with added genes may affect your DNA. This worry may stem partly from an early mice study, which linked GMO intake to a higher risk of tumors and early death. However, this study was later retracted because it was poorly designed ( 18.
How does genetic modification affect plants?
Genetic modification significantly accelerates this process by using scientific techniques that give the plant the specific desired trait. For example, one of the most common GMO crops is Bt corn, which is genetically modified to produce the insecticide Bt toxin.
Is GMO food safe for humans?
Still, a review of multiple studies concluded that the low amounts of glyphosate present on GMO foods are safe for human consumption ( 28. Trusted Source. ). GMO crops also allow for fewer pesticide applications, which is a positive for the environment.
Is it mandatory to label food with GMOs?
In the United States, it’s currently not mandatory to label foods that contain GMOs. However, as of 2022, all foods that contain GMO ingredients must have the term “bioengineered food” somewhere on the packaging or a scannable code to show that it has GMO ingredients. Last medically reviewed on July 2, 2020.
Is corn a GMO?
Trusted Source. ). GMO crops are incredibly common in the United States, with at least 90% of soy, cotton, and corn being grown through genetic techniques ( 4. Trusted Source.
What are the pros and cons of GMOs?
What are the pros and cons of GMO foods? Engineers design plants using genetically modified organisms, or GMOs, to be tougher, more nutritious, or taste better. However, people have concerns over their safety, and there is much debate about the pros and cons of using GMOs. A manufacturer creates GMOs by introducing genetic material, or DNA, ...
Why do engineers use GMOs?
Engineers design plants using genetically modified organisms, or GMOs, to be tougher, more nutritious, or taste better. However, people have concerns over their safety, and there is much debate about the pros and cons of using GMOs. A manufacturer creates GMOs by introducing genetic material, or DNA, from a different organism through ...
How are GMOs created?
A manufacturer creates GMOs by introducing genetic material, or DNA, from a different organism through a process called genetic engineering. Most currently available GMO foods are plants, such as fruit and vegetables. All foods from genetically engineered plants on sale in the United States are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
What are the most common GMO crops?
The most common GMO crops grown in the country are cotton, corn, and soybeans. Herbicide-tolerant crops allow for a more effective use of pesticides. The U.S. Department of Agriculture have reported that 94 percent of soybean and 91 percent of cotton crops were genetically modified by 2014.
Why is genetic modification important?
Because genetic modification can make plants resistant to disease and tolerant of herbicides, the process can increase the amount of food that farmers are able to grow. This can reduce prices and contribute to food security.
Why do manufacturers use genetic modification?
Manufacturers use genetic modification to give foods desirable traits. For example, they have designed two new varieties of apple that turn less brown when cut or bruised. The reasoning usually involves making crops more resistant to diseases as they grow.
Why are plants more resistant to diseases?
Plants that are more resistant to diseases spread by insects or viruses result in higher yields for farmers and a more attractive product. Genetically modification can also increase nutritional value or enhance flavor. All of these factors contribute to lower costs for the consumer.
Why are genetically modified foods beneficial?
These include reduced production costs, making foods cheaper; improved availability as fruits maintain freshness in seasons when they would not be normally available; fewer chemicals in plants because of their improved pest resistance and thus also less stress on the environment due to lower need for toxic pesticides; reduced allergens in certain foods like soy, peanuts or wheat that often cause food allergies; and pharmaceutical use of plants for the production of edible vaccines and medications.
What are genetically modified soybeans used for?
Genetically modified soybeans, corn and other crops are used to make the ingredients (e.g., flour, cornmeal, oils) for a variety of processed foods such as breads, cereals, dairy products, hot dogs, snacks and soda.
What are the benefits of genetic engineering?
Initially, genetic engineering focused on increasing crop yields and making plants easier and cheaper to produce. Desirable qualities for these purposes include: 1 Herbicide tolerance. The aim of making plants more resistant to herbicides is to allow farmers to safely kill weeds without harming the crop. Some of the crops that have been altered to be more herbicide tolerant include corn, cotton, soybeans, canola rapeseed, sugar beets, rice, wheat, lettuce and alfalfa. 2 Pest resistance. Some crop plants have been genetically engineered to produce a chemical that is toxic to certain pests such as fungi or insects but harmless to humans or animals. Examples of the plants that have been modified to be pest resistant include soybeans, corn, cotton, canola, wheat and apples. 3 Disease resistance. Genetic modification has also made plants with improved resistance to certain diseases. Some of the crops altered in this way include bananas, corn and papayas. 4 Increased production. Many crops have been genetically modified to produce higher yields under specific environmental conditions.
What is the synonym for genetically modified foods?
Synonyms for genetically modified foods include genetically engineered foods, bioengineered foods and biotech foods. The genetic engineering process involves removing a desired gene or genes from one organism (plant, bacteria or virus) and placing them into the DNA of another in order to introduce new traits to the second organism (plant).
What is the term for the spread of genetically modified plants beyond controlled areas?
Spreading of genetically modified plants beyond controlled areas to become “super weeds”. Pests developing resistance to the toxins produced by genetically modified plants. Toxins produced by genetically modified plants affecting or killing non-target organisms.
What are some examples of pest resistant crops?
Examples of the plants that have been modified to be pest resistant include soybeans, corn, cotton, canola, wheat and apples. Disease resistance.
How does genetic engineering help farmers?
Improved adaptability to environmental conditions. Genetic engineering has allowed farmers to grow crops such as rice, corn, wheat and other cereals in harsh conditions (e.g., salty soil, drought, cold temperatures) that were previously unsuitable for these crops. Pharmaceutical benefits.
What does Calkins think about GMOs?
Calkins thinks that those who want to see further development of GMOs are going to have to establish trust with the other side, but he doesn’t see that happening by simply conducting more laboratory experiments to prove the safety of genetic engineering. With biotech opponents appealing to imagery and folklore, Calkins says, "businesses need to develop counter-images or offsetting cases about their good character."
What percentage of soybeans are genetically modified?
McLean is referring to the fact that GMOs have been on the market for almost a decade without U.S. consumers being alerted to their presence. About 50 percent of soybeans grown in the United States last year were genetically modified, and those soybeans became part of countless processed foods from oils to cereals.
Who said GMOs take mankind into realms that belong to God and God alone?
England’s Prince of Wales , for example, has argued that GMOs take "mankind into realms that belong to God and God alone.". Even for the non-religious, transgenic crops can violate the maxim so memorably stated in the old margarine commercials: "It’s not nice to fool Mother Nature.".
Can GMOs cause harm?
So far, no medical harm to humans has been traced to ingesting GMOs. Of course, the fact that no harm has been established is not the same as proving that GMOs pose no dangers. One concern is the potential for allergic reactions.
Do GMOs harm the environment?
Aside from the danger of super-weeds, GMOs may pose dangers for other creatures in the ecosystem. "Crops that are engineered to be pesticidal may harm insects other than those they were intended to repel," says Rebecca Goldburg, senior scientist at the Environmental Defense Fund.
