How does being bilingual affect your brain?
Read more extracts from science books:
- Zoology in 30 seconds: conservation and extinction
- Why we need to rethink the way we classify people
- Could a lot of monkeys write Shakespeare?
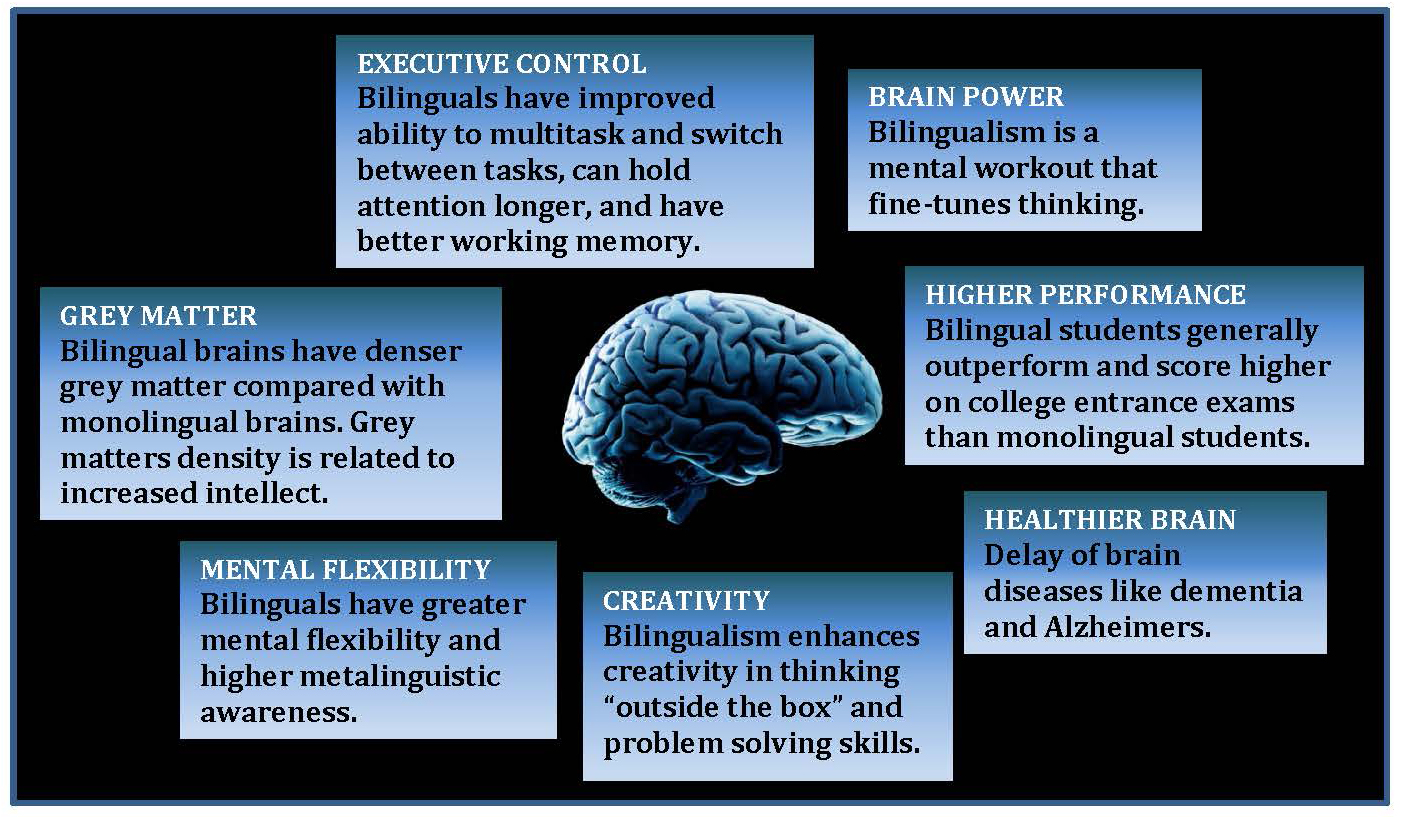
Why bilingualism is good for your brain?
- Biliguists are faster and more accurate at performing cognitive tasks
- But they have less insight into their own performance than monolinguals
- Bilingualism may bring cognitive disadvantages as well as benefits
Why does being bilingual help keep your brain fit?
It means that as parts of the brain succumb to damage, bilinguals can compensate more because they have extra grey matter and alternative neural pathways. Bilingualism can also offer protection after brain injury.
What are some of the pros to being bilingual?
- You will always be more fluent on one language than the other — I personally struggle with this one, when. ...
- You are the first person to come to your parent/friend mind when they need to translate something, for example; My parents have various meetings due to their jobs, so guess ...
- Jokes don’t translate the same!!! ...

What happens to your brain when you're bilingual?
A bilingual brain can compensate for brain deterioration by using alternative brain networks and connections when original pathways have been destroyed. Researchers call this theory “cognitive compensation” and conclude that it occurs because bilingualism promotes the health of both gray and white matter.
What are the benefits of bilingual?
There is growing evidence to suggest that bilingualism can delay the onset of dementia and Alzheimer's disease for example. Other benefits of being bilingual include things such as a faster stroke recovery, lower stress levels, and delay many effects of old to name a few.
How are bilingual brains different?
The brain uses a shared mechanism for combining words from a single language and for combining words from two different languages, indicating that language switching is natural for those who are bilingual.
What is the research based benefit of bilingual brain?
Researchers have shown that the bilingual brain can have better attention and task-switching capacities than the monolingual brain, thanks to its developed ability to inhibit one language while using another.
How does being bilingual improve memory?
Bilingualism enhances working memory in sequential bilingual children from low SES backgrounds. Bilingual benefits are found in language-independent working memory tasks that involve both storage and processing. Higher bilingual proficiency is associated with better verbal working memory performance.
What are the cognitive and social benefits of being bilingual?
Being bilingual can have tangible practical benefits. The improvements in cognitive and sensory processing driven by bilingual experience may help a bilingual person to better process information in the environment, leading to a clearer signal for learning.
Are bilingual brains smarter?
Western News - Study: Bilingualism does not make you 'smarter' Despite numerous social, employment, and lifestyle benefits, speaking more than one language does not improve your general mental ability, according to a new study conducted by Western's Brain and Mind Institute.
Do bilinguals have higher IQ?
Bilingual children who regularly use their native language at home while growing up in a different country have higher intelligence, a study has found. In a study, bilingual children proved to be more intelligent than those who speak just one language.
How does bilingualism affect brain structure?
Abstract. Bilingualism affects the structure of the brain in adults, as evidenced by experience-dependent grey and white matter changes in brain structures implicated in language learning, processing, and control. However, limited evidence exists on how bilingualism may influence brain development.
What are the benefits of dual language learning for children?
Benefits to Young Children from Multiple Language ExposureIncreased analytics language orientation.Perform higher on standardized tests.Easier for children to learn a third language or additional languages.Higher self-esteem.Increased social-emotional skills.Increased creativity and problem-solving skills.
Who benefits from bilingual education?
Those who learn a second or third language from a young age are able to develop communication skills and a higher degree of literacy. Children who grow up in bilingual environments develop a keen awareness of how language works and have a stronger foundation for learning additional languages in the future.
What are the cognitive benefits of learning or speaking two languages?
Cognitive performance Learning a new language through an immersive process does appear to improve functions like attention and mental alertness. It has been shown that people who speak other languages often exhibit more empathy and a global mindset.
Why are bilingual people better at their job?
In addition to the obvious advantages when travelling to other countries or looking for a job, bilingual people have better skills such as memory or attention . Recent research has also shown that their brains delay the symptoms of dementia and that they recover better after suffering a stroke. In terms of our memory, mental calculations ...
How does bilingualism help with stroke?
Improve the recovery from a stroke. Bilingualism also seems to be beneficial when a person suffers a stroke. People who speak several languages are twice as likely to recover their normal cognitive functions after an attack of this type compared to those who speak only one.
What areas of the brain respond to sounds in Spanish and English?
The prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortices (two areas of the frontal lobe) had more intense responses in bilingual babies compared to those who only heard and spoke one language.
How long does it take for dementia to develop from bilingualism?
According to some studies, bilingualism can delay the onset of symptoms in people suffering from dementia by just over four years. “These are activities we can engage in to keep our brains and minds healthy (music, social groups, exercise, etc.). Bilingualism is one such experience,” says Bialystok.
How many bilinguals recover from stroke?
After the attack, 40.5% of bilinguals recovered normal cognition, compared to 19.6% of monolinguals. In view of these results, the authors suggest that having mastered two languages improves brain recovery after a stroke and that this advantage could be related to better cognitive reserve.
How old are bilingual children?
According to research from the universities of York (Canada) and Granada (Spain), bilingual children between five and seven years old who participated in the study performed better than the monolingual ones on those tasks that involved using the working memory.
Which lobe of the brain is most related to bilingualism?
All these extra abilities are reflected in the brain. The frontal lobes, responsible for the executive functions, are the regions most related to bilingualism. A study from the University of Washington (USA) conducted in eleven-month-old babies from bilingual families (Spanish and English) and monolingual (only English) revealed differences in these areas.
Why is bilingualism important?
But perhaps the most exciting benefit of bilingualism occurs in ageing, when executive function typically declines: bilingualism seems to protect against dementia.
What does it mean when a bilingual person speaks in one language?
Brain-imaging studiesshow that when a bilingual person is speaking in one language, their ACC is continually suppressing the urge to use words and grammar from their other language. Not only that, but their mind is always making a judgement about when and how to use the target language.
How many languages do people speak in Johannesburg?
In Johannesburg, where they are from, most people speak at least five languages, says one of them, Theo Morris. For example, Theo’s mother’s language is Sotho, his father’s is Zulu, he learned Xhosa and Ndebele from his friends and neighbours, and English and Afrikaans at school.
Do people speak more than one language?
Most people in the world speak more than one language, suggesting the human brain evolved to work in multiple tongues. If so, are those of us who speak only one language missing out? Most people in the world speak more than one language, suggesting the human brain evolved to work in multiple tongues. If so, are those of us who speak only one ...
Why is bilingualism important?
In addition to staving off the decline that often comes with aging, bilingualism can also protect against illnesses that hasten this decline, like Alzheimer’s disease.
What are the cognitive consequences of bilingualism?
Research has overwhelmingly shown that when a bilingual person uses one language, the other is active at the same time. When a person hears a word, he or she doesn’t hear the entire word all at once: the sounds arrive in sequential order.
What is bilingualism in cognitive terms?
Bilingualism appears to provide a means of fending off a natural decline of cognitive function and maintaining what is called “cognitive reserve.”9, 25Cognitive reserve refers to the efficient utilization of brain networks to enhance brain function during aging.
How does bilingualism affect the elderly?
In addition, bilingualism has positive effects at both ends of the age spectrum: Bilingual children as young as seven months can better adjust to environmental changes, while bilingual seniors can experience less cognitive decline . We are surrounded by language during nearly every waking moment of our lives.
Why do bilingual people use control mechanisms?
Because both of a bilingual person’s language systems are always active and competing, that person uses these control mechanisms every time she or he speaks or listens. This constant practice strengthens the control mechanisms and changes the associated brain regions.9–12.
How does the brain guess what a word is?
Long before the word is finished, the brain’s language system begins to guess what that word might be by activating lots of words that match the signal. If you hear “can,” you will likely activate words like “candy” and “candle” as well, at least during the earlier stages of word recognition.
Does bilingualism help with mileage?
If the brain is an engine, bilingualism may help to improve its mileage, allowing it to go farther on the same amount of fuel. Conclusion. The cognitive and neurological benefits of bilingualism extend from early childhood to old age as the brain more efficiently processes information and staves off cognitive decline.
