
Beyond health, the benefits of GMOs are widespread:
- Less cost
- Higher yields
- Fewer chemicals and pesticides
- Less soil erosion than unmodified crops
- Used in medicine to produce life-saving vaccines, insulin, and treatments for diseases
Do GMOs harm health?
In addition, over the two decades that GMOs have been on the market, there have been no occurrences of health issues due to genetically modified organisms. As GMOs stand today, there are no health benefits to eating them over non-GMO foods. However, this may change in the future as technology develops and becomes more sophisticated.
Why are GMOs safe to eat?
Top 10 Reasons Why GMOs Are Good
- Increases Crop Yield. Before now, scientists could modify crop output through artificial selection but can’t control which gene to transfer.
- GMOs Tastes Better. Artificial selection has produced many sweeter fruits and juicy apples. ...
- GMOs Can Help Us Defeat Climate Change. ...
- Helps to Fight Against Nutrition. ...
- Low-Income Farmers Benefit From GMOs. ...
Why should we develop genetically modified organisms?
- Media Credits. The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit.
- Last Updated. For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. ...
- Media. ...
- Text. ...
- Interactives. ...
Are GMOs good or bad?
GMOs are relatively new and, like anything new, there are conflicting viewpoints about many issues surrounding the use of these plants. One area that draws a lot of attention is whether these GMO plants and the foods that contain them are safe to eat. There is no data to indicate that consumption of GMOs is bad for human health.

What are some benefits of genetically modified organisms?
The possible benefits of genetic engineering include:More nutritious food.Tastier food.Disease- and drought-resistant plants that require fewer environmental resources (such as water and fertilizer)Less use of pesticides.Increased supply of food with reduced cost and longer shelf life.Faster growing plants and animals.More items...•
What are 3 benefits of GMOs?
Growing GMO crops leads to environmental benefits such as reduced pesticide use, less water waste, and lower carbon emissions. The two main types of GMO crops in use are bioengineered to either produce their own pesticides or to be…
What are the benefits and risks of genetically modified organisms?
The benefits of using GMOs include crops having higher harvest yields which can feed more people in the world, and making food more nutritional. The risks of using GMOs include both the unknown long term risks of eating GMO crops and the negative effects that they can have on an environment.
What are the 10 advantages of genetically modified organisms?
List of Advantages of Genetically Modified FoodsInsect Resistance. Some GMO foods have been modified to make them more resistant to insects and other pests. ... Stronger Crops. ... Larger Production. ... Environmental Protection. ... Extensive Protection for Crops. ... More Nutritious Foods. ... Decreased Use of Pesticides. ... More Income.More items...•
What are the 10 advantages and disadvantages of GMO products?
10 Advantages and Disadvantages of GMOsThey offer more useful knowledge for genetics. ... They allow for more profit. ... They add more value to crops. ... They are known to decrease the prices of food. ... They yield products that are found to be safe.
How are genetically modified foods beneficial?
In the food industry, GMO crops have had genes added to them for various reasons, such as improving their growth, nutritional content, sustainability, pest resistance, and ease of farming ( 2 ).
What are the advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering?
Genetic engineering made it possible to create crop varieties regarded as “more beneficial”. Unlike selective breeding, modern genetic engineering is more gene-specific. One of the downsides of selective breeding is the possibility of generating traits that are less desirable.
Can the benefits of genetic modification outweigh its risks?
The UQ PhD study found the benefits of GM plants and food outweighed the risks, finding no compelling evidence of harm to humans from GM plants. GM plants have been trialled in most states with South Australia, Tasmania and Western Australia the only states to ban GM plants.
What are the five disadvantages of GMOs?
What Are the Disadvantages of GMOs?It can be dangerous to other insects that are important to our ecosystem. ... It sparks concerns on changing the field of agriculture. ... It can damage the environment. ... It causes unwanted residual effects. ... It can create more weeds. ... It threatens crop diversity. ... It has trade issues.
What are 5 environmental disadvantages of genetically modified foods?
Perceived disadvantages of genetically modified crops may be grouped into five categories: 1) potential impact on non-target species; 2) potential for increased weediness; 3) increase in toxin levels in the soil; 4) exchange of genetic material between the transgenic crop and related plant species; and 5) selection for ...
Which of the following is an advantage of GMOs quizlet?
An advantage of a crop being genetically modified to be resistant to herbicide is that herbicide will kill every other plant apart from that crop so that crop will not have to compete with weeds for water and nutrients from the soil.
How does genetic engineering affect crops?
Genetic engineering of crops can enhance crop yields and nutritional quality, increase resistance to pests, improve tolerance to drought and reduce insecticide use. Biofortified crops in particular can have a significant impact, especially for people in the developing world who obtain most of their calories from one or a small number of subsistence crops that may be deficient in essential vitamins or minerals. One example is "Golden Rice," fortified with beta-carotene, the precursor of vitamin A, whose consumption can prevent vitamin A deficiency. (Vitamin A deficiency is common in places where people obtain most of their calories from rice, which does not contain the compound.)
Why are GMOs controversial?
The issue of so-called "genetically modified organisms," or GMOs, is frequently in the news and the subject of controversy. Perhaps pseudo-controversy is a better term, because much of the criticism is gratuitous and ill-informed. Genetic modification is by no means new; in fact, over the course of human history we have continuously genetically modified animals and plants through selection and breeding to enhance their desirable characteristics. Humans have invented increasingly sophisticated techniques, particularly since the discovery that all higher organisms have the same carrier of genetic information, the double-stranded helix of DNA.
Why is CRISPR important?
CRISPR-Cas9 presages a revolution in agriculture and human medicine because it is so much more precise and predictable than earlier techniques. Precision and predictability are important to ensure that the results are safe and achieve their desired ends. There are notable historical examples of older, pre-molecular techniques of genetic modification in agriculture that turned out to be missteps. Examples include the Lenape potato, which contained elevated, harmful levels of a plant alkaloid; the creation of hyper-aggressive Africanized honeybees by crossbreeding African and European species in the 1950s; and inadvertently making some varieties of corn in the United States more susceptible to the Southern Corn Leaf Blight fungus, which resulted in significant crop losses in 1970.
What Is a GMO?
Genetically Modified Organisms are plants and animals that aren’t found naturally but can be created through genetic engineering. Their genetic structure can be altered in a way to enhance their characteristics and ramp up the production process.
What are the advantages of Genetically Modified Organisms?
Scientists are convinced that the genetic engineering of plants represents a technology with enormous potential for sustainably increasing food production. Also, developing countries are expected to have many advantages of genetically modified organisms in economic terms.
What are the Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Organisms?
Although combining genes from different organisms is considered beneficial for crops, this latest incarnation of biotechnology is condemned by many. People firmly believe that GM crops pose a threat to human health and biodiversity. The following disadvantages of genetically modified organisms still add too many controversies.
Frequently Asked Questions
The advantages of genetic engineering include more nutritious meals, better food, disease- and drought-resistant plants that require less environmental upkeep, Less usage of pesticides, increased food supplies with lower costs, and longer shelf life.
What is genetically modified organism?
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) are changing the world, but is it for the better or is it for the worse? GMOs are genetically modified organisms: This means that the DNA of an organism, such as a plant, has been genetically altered to have specific traits. Unflattening, by Nick Sousanis, illustrates that in order to gain a deeper ...
How does genetic modification work?
According to Monsanto, the genetic modification process begins with identifying desired traits such as: high nutritional content, draught resistance, or high harvest yields. Next, the desired trait is introduced into the DNA of the seed of a crop that they are trying to improve.
What are the risks of using GMOs?
The risks of using GMOs include both the unknown long term risks of eating GMO crops and the negative effects that they can have on an environment. There are many benefits to using GMOs. They benefit our world in important ways such as modifying crops to have higher nutritional content, to be drought resistant, and have higher harvest yield.
What is Jane Goodall's concern about GMOs?
Goodall is very concerned about GMOs and even calls their use a crime against plants. One of her concerns is regarding superweeds and superbugs.
What is the gene that Monsanto uses to make crops?
Goodall explains that Monsanto inserts a gene from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) into the DNA of crop seeds. This causes pests to die when they eat the GMO crop. After a time, pests adapt and become immune to the Bt and then the manufacture must make it stronger, or develop another strain.
How can GMOs help?
They can help to solve hunger issues in developing countries by increasing yields and nutritional values. However the risks are just as real. GMOs are so new that scientists are unaware of the effects that they could have on humans in the long run.
Why is it important to use GMOs?
Using GMOs is an issue in which it is important to consider both the risks and the benefits. The benefits of using GMOs include crops having higher harvest yields which can feed more people in the world, and making food more nutritional. The risks of using GMOs include both the unknown long term risks of eating GMO crops and ...
Why are GMOs dangerous?
GMOs can be dangerous to some insects that are important to our ecosystem because the new genes of crops can be deadly to some insects such as the butterflies which are not actually dangerous to the crops , The critics claim that GMOs can cause particular disease or illnesses .
Why are GMOs better for the environment?
GMOs increase the resistance to the pests, the weeds and the disease, The crops are more capable of thriving in the regions with poor soil or adverse climates, they require less herbicides & pesticides, So, They will be more environment friendly.
How do GMOs affect the ecosystem?
GMOs threaten the crop diversity, GM genes can spread to the other organic farm crops and threaten the crop diversity in the agriculture, And if the crop diversity decreases, it will have the direct impact on our entire ecosystem .
How does GMO affect crops?
GMO crops increases the genetic alterations knowledge and it makes the genes in the crops more advantageous for the human consumption and production, The plants will be temperature resistant or produce higher yields, It offers greater genetic diversity in different regions where the climate limits the productivity .
Why are GMOs important?
GMO crops planted add the nutritional value to the crops that lack necessary vitamins and nutrients, GMOs offers increased flavor and nutrition, Along with the resistances to the insects and the disease , They will help the malnourished populations receive more nutrients from their diet .
Why are GMOs beneficial?
Genetically Modified organisms ( GMOs ) are the effective ways to provide the farmers a larger profit, while making them spend less time on the resources, They are economically beneficial because they are used to repel the pests that prevents the need for the pesticides to be used that means more savings . GMOs are known to decrease the food prices ...
What is genetically modified organism?
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are the form of scientific farming where the chemicals are pumped to the crops to increase the product sizes and yield , Although this method is highly debated and it has become increasingly common in everyday foods .
Why are genetically modified foods easier to transport?
Genetically modified foods are easier to transport. Because GMO crops have a prolonged shelf life, it is easier to transport them greater distances. This improvement makes it possible to take excess food products from one community and deliver it to another that may be experiencing a food shortage.
How can genetic modification improve GMO crops?
2. Nutritional content can be improved. Genetic modifications do more than add pest resistance or weather resistance to GMO crops. The nutritional content of the crops can be altered as well, providing a denser nutritional profile than what previous generations were able to enjoy.
How many companies control the GMO market?
6 companies control most of the genetically modified foods market at the core level. Because most GMO foods are made from corn, wheat, or soybeans, even food manufacturers that use these crops are at the mercy of the manufacturer’s preferences.
Why are genetically modified foods good for you?
Instead of relying on preservatives to maintain food freshness while it sits on a shelf, genetically modified foods make it possible to extend food life by enhancing the natural qualities of the food itself. According to Environmental Nutrition, certain preservatives are associated with a higher carcinogen, heart disease, and allergy risk.
What are the advantages of genetically modified foods?
The primary advantage of genetically modified foods is that crop yields become more consistent and productive, allowing more people to be fed.
How have genetically modified foods changed the way people view their food?
Although genetic modifications have occurred throughout history with selective breeding and growing methods, scientific advances have allowed this practice to advance to the genetic level. In the modern GMO, plants can be resistant to specific pesticides and herbicides while becoming adaptive to changing environmental conditions.
Why are herbicides bad for crops?
Herbicides and pesticides create certain hazards on croplands that can eventually make the soil unusable. Farmers growing genetically modified foods do not need to use these products as often as farmers using traditional growing methods, allowing the soil to recover its nutrient base over time.
What are GMO crops?
GMO crops grown and sold in the United States include corn, soybean, canola, sugar beet, alfalfa, cotton, potatoes, papaya, summer squash, and a few apple varieties ( 29. Trusted Source. ). In the United States, no regulations currently mandate the labeling of GMO foods.
What is GMO in agriculture?
Definition. Pros. Cons. Identification. Bottom line. GMOs, short for genetically modified organisms, are subject to a lot of controversy. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), GMO seeds are used to plant over 90% of all maize (corn), cotton, and soy grown in the United States, which means that many of the foods you eat likely ...
What is the Bt gene?
For example, the Bt gene is commonly genetically engineered into crops like corn, cotton, and soybeans. It comes from a naturally occurring bacteria known as Bacillus thuringiensis. This gene produces a protein that is toxic to several pests and insects, which gives the GMO plants a natural resistance.
Why do people fear eating foods with added genes?
Because cancers are caused by DNA mutations, some people fear that eating foods with added genes may affect your DNA. This worry may stem partly from an early mice study, which linked GMO intake to a higher risk of tumors and early death. However, this study was later retracted because it was poorly designed ( 18.
How does genetic modification affect plants?
Genetic modification significantly accelerates this process by using scientific techniques that give the plant the specific desired trait. For example, one of the most common GMO crops is Bt corn, which is genetically modified to produce the insecticide Bt toxin.
Does organic food contain GMOs?
However, if a product is simply labeled “ organic ,” it may contain some GMOs ( 30. Trusted Source. ). In the European Union (EU), foods with more than 0.9% GMO ingredients must list “genetically modified” or “produced from genetically modified [name of food].”.
Is GMO food safe for humans?
Still, a review of multiple studies concluded that the low amounts of glyphosate present on GMO foods are safe for human consumption ( 28. Trusted Source. ). GMO crops also allow for fewer pesticide applications, which is a positive for the environment.
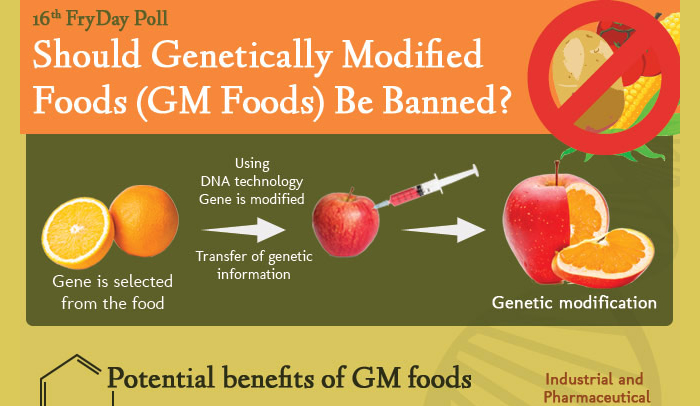
Genetic Revolution
Germline Correction
- More controversial is germline gene editing, changing genes within eggs, sperm or embryo cells, since those changes would be passed on to future generations. Nevertheless, preclinical research using CRISPR-Cas9 to make germline modifications is advancing rapidly. A major advance came in August 2017, when a team led by Shoukhrat Mitalipov of Oregon Health & Science University i…
Overregulation
- Another potentially revolutionary genetic engineering innovation almost ready for the clinic is xenotransplantation, the transplanting of animal organs into humans. Improved immunosuppressant drug regimens and increasing numbers of pig lines that have been gene-edited to eliminate antigens that would cause rejection by the human recipient are a potential ga…
Moral Imperative
- Genetic engineering of crops can enhance crop yieldsand nutritional quality, increase resistance to pests, improve tolerance to drought and reduce insecticide use. Biofortified crops in particular can have a significant impact, especially for people in the developing world who obtain most of their calories from one or a small number of subsistence ...
What’s A GMO?
- Simply put, a genetically modified organism refers to a living thing—from bacteria to fungi to crops—that’s had its genetic code altered in some way. Most of the time, only a small section of the genetic code is changed and the rest is left alone, but these small changes can produce a wide range of results, like increasing the yield of corn, making potatoes resistant to insects, and …
Are They Safe to consume?
- Since GMOs are relatively new, having been introduced only a few decades ago, there have been valid questions about whether they’re safe to eat. Many brands advertise themselves as “non-GMO,” which implies that the alternative is not desirable or healthy. Fortunately, multiple studies have shown that GMOs pose no health risks to the consumer, and are in fact as healthy as conv…
What Are Their Benefits?
- Beyond health, the benefits of GMOs are widespread: 1. Less cost 2. Higher yields 3. Fewer chemicals and pesticides 4. Less soil erosion than unmodified crops 5. Used in medicine to produce life-saving vaccines, insulin, and treatments for diseases
Future of GMOs
- Beginning in 2022, food companies will be required to label products containing GMOs. Since approximately 75% of processed foods contain GMOs, buyers need not be intimidated by the new messaging and should remember that genetically modified products are just as healthy as regular ones. While it is always important to be aware of what is in your food and to advocate for transp…
Sources
- Oselinsky, K., Johnson, A., Lundeberg, P., Johnson Holm, A., Mueller, M., & Graham, D. J., 2021, GMO Food Labels Do Not Affect College Student Food Selection, Despite Negative Attitudes towards GMOs.
- Tufts University health & nutrition letter. New York: Tufts Media LLC., 2016, Study: GMO Foods as Safe as Conventional Choices.