
Why is Meiosis Important in Studying Biology?
- Allows sexual reproduction of diploid organisms As mentioned previously, meiosis allows the reduction of a diploid cell to a haploid gamete, which can then recombine with another haploid gamete ...
- Enables genetic diversity The crossing over or recombination of genes which occurs in meiosis rearranges the alleles present in each chromosome of a homologous pair, allowing the mixing of ...
- Aids the repair of genetic defects
What are the advantages and disadvantages of meiosis?
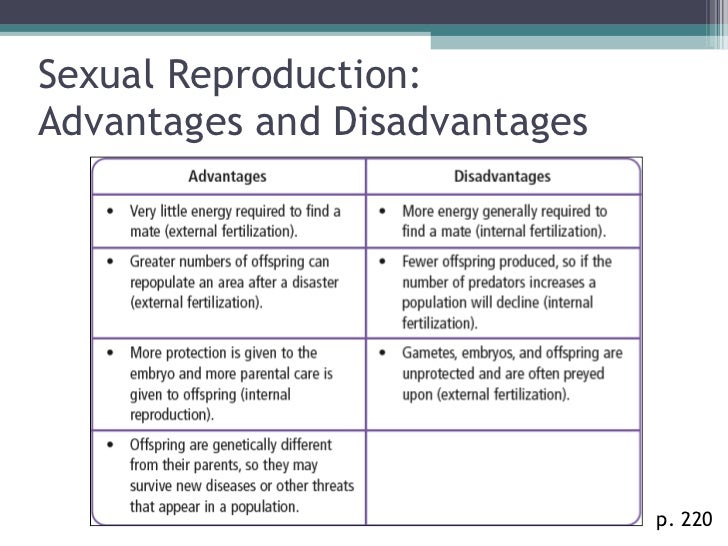
Sexual Reproduction in Animals: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages of sexual reproduction. One of the most important advantages of sexual reproduction is that it results in genetic variation among offsprings.
- Disadvantages of sexual reproduction. However, sexual reproduction is not the perfect reproductive method if it examined in detail there are many disadvantages which are considerable.
- Conclusion. ...
What are the functions of meiosis?
What are 5 functions of the mitochondria?
- Production of ATP. Perhaps the most well-known role of mitochondria is the production of ATP, the energy currency of cells. …
- Calcium Homeostasis. …
- Regulation of Innate Immunity. …
- Programmed Cell Death. …
- Stem Cell Regulation.
Why does meiosis is important for the survival of organisms?
Why is meiosis important for survival? Meiosis is a phase in sexually reproductive organisms, wherein cell-division takes place. It is of great importance, because it creates genetic diversity in the population.
What are five facts about meiosis?
Steps of Mitosis
- Prophase: The cell's nuclear membrane disappears and the chromatin coils into tightly packed structures called chromosomes. ...
- Metaphase: Chromosomes move to the center of the cell and live up along the cell's midline.
- Anaphase: Chromosomes begin to be pulled across to opposite sides of the cell by the the spindle fibers.
What are the benefits of mitosis?
Mitosis is the reason we can grow, heal wounds, and replace damaged cells. Mitosis is also important in organisms which reproduce asexually: this is the only way that these cells can reproduce. This is the one key process that sustains populations of asexual organisms.
What are the pros and cons of meiosis?
Advantage: The crossing over of genes during meiosis brings variation in the individuals and that is good for the survival of the population. Disadvantage: The organisms always have to find a sexual partner for sexual reproduction to occur.
What is the advantages of meiosis and mitosis?
An advantage of meiosis is that it produces genetic variation. A disadvantage or meiosis is that it requires 2 gametes. An advantage of mitosis is that it allows your cells to easily replicate and make sister chromosomes.
What is meiosis Why is it important?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that involves the reduction in the number of the parental chromosome by half and consequently the production of four haploid daughter cells. This process is very essential in the formation of the sperm and egg cells necessary for sexual reproduction.
What are the advantages of cell division?
Significance of Cell divisionRenewing of damaged cells.Production of new cells from older ones.Maintains the total number of chromosomes.Provides more cells for growth and development.Repairs and controls damages caused to the cells.Also helps in survival and growth of living organisms.More items...
What is the function of meiosis in humans?
Meiosis, on the other hand, is used for just one purpose in the human body: the production of gametes—sex cells, or sperm and eggs. Its goal is to make daughter cells with exactly half as many chromosomes as the starting cell.
What is the benefit of meiosis when compared to asexual reproduction?
Meiosis is important to sexual reproduction, because through events like crossing over during prophase 1 (the swapping of genetic material between sister chromatids after a process of pairing called synapsis, the exchange sites are called chiasmus) and independent assortment during metaphase, meiosis creates the ...
Why meiosis is important for the survival of a human?
As sexually-reproducing, diploid, multicellular eukaryotes, humans rely on meiosis to serve a number of important functions, including the promotion of genetic diversity and the creation of proper conditions for reproductive success.
Why is meiosis useful quizlet?
Meiosis is necessary for the reproduction of multicellular organisms, so that the chromosome number can be retained, and each organism does not have double the amount of chromosomes as its parents. It is also important for genetic variation.
What would happen without meiosis?
Without meiosis, organisms would not be able to reproduce effectively. If organisms did not undergo mitosis, then they would not be able to grow and replace worn-out cells. They are two of the most important cellular process in existence.
Why is meiosis important?
Meiosis is furthermore important for its role in enabling genetic diversity and facilitating the repair of genetic defects through recombination.
How does meiosis affect genetic diversity?
This allows genetic diversity in a population, which is a buffer to genetic defects, susceptibility of the population to disease and changes in the environment. Without this recombination, the gene pool of populations would stagnate, and a single event could wipe out an entire population. Genetic diversity means that there will be certain individuals within any given population that will be better able to survive a loss of habitat, a change in food availability, a change in weather patterns, diseases or other catastrophic events, ensuring species continuity.
What are the phases of meiosis?
The Phases of Meiosis. Meiosis is split into two parts, or divisions, each of which consists of several phases. These are prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I and telophase I in meiosis I; and prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II and telophase II in meiosis II.
Why is chromosomal reduction necessary?
Thus, a chromosomal reduction is necessary for each species’ continued existence. Before meiosis begins, the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell undergo replication. This is because meiosis produces four daughter cells with half the chromosomes of the parent cell; or four haploid cells from a single diploid cell.
How many chromosomes are in a cell after meiosis?
As you can see, the math doesn’t quite work out: the parent cell must first be converted to a 4n ( tetraploid) cell before division begins. So a cell with n = 46 chromosomes will be converted to a cell with n = 92 chromosomes, which, after meiosis, will produce four cells with n = 23 chromosomes.
How do chromosomes separate?
Chromosomes separate further but are still attached through chiasmata of the nonsister chromatids. Separation leads to the chiasmata moving towards the ends of the chromatids, a process known as terminalization. The nuclear envelope and nucleolus deteriorate, and the centromeres of each chromosome attach to spindle fibers, before lining up on the metaphase plate. The chromosomes are still in pairs, which form tetrads.
Why is meiosis important?
Meiosis is important because it reprograms the gametes, which help the fertilized egg develop and grow.
How does meiosis maintain the integrity of the germ line?
During the process, it maintains the integrity of the germ line by removing faulty RNA and protein, and it eliminates the defective meiocytes. Meiosis is a form of cell division that creates new combinations of genetic material in the newly-formed daughter cells.
What is the first step in meiosis?
Prophase is the first step in meiosis and occurs when the chromosomes condense to where they become visible inside the nucleus. Metaphase happens when microtubules come out of each spindle and attach to the kinetochore.
What is the process of pulling two chromosomes toward opposite ends of the cell?
Anaphase is the process in which these microtubules disassemble and contract, pulling two chromosomes toward opposite ends of the cell. During telophase, the cytoplasm divides in two. Once meiosis is completed, the cycle begins again and is known as meiosis II.
Why is meiosis better than parent?
If a disease comes along, there is a good chance that some of the population won't get sick or die because everyone's DNA isn't exactly alike.
What is the process of making identical cells?
MITOSIS and meiosis. Mitosis creates identical copies of the original cells. This allows our skin or our liver to be made of identical cells and allows plants to be able to mass produce leaves with identical properties. Imagine if every one of our skin cells had different DNA!
Do plants reproduce sexually through meiosis?
Imagine if every one of our skin cells had different DNA! Some single cell organisms and some plants do not reproduce sexually through meiosis. Rather, they use mitosis only to make exact copies of their cells.
Does mitosis produce variation?
Mitosis also does not produce any variation. So, a plant that reproduces through mitosis won't have the chance to produce offspring that might be better than the parent. Meiosis continually reshuffles the genes resulting in a great variety of offspring. Without meiosis we would all look exactly alike.
Why is meiosis beneficial?
The diversity afforded by meiosis is beneficial for the population as a whole. Thus, meiosis helps to create a population that is not only physically and genetically different but also one, which is perfectly fit to survive. « Previous Post. Next Post ».
Why is meiosis important?
It is of great importance, because it creates genetic diversity in the population.
How many haploid cells are produced in meiosis?
Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions, which produce four haploid cells. The meiosis I is the reduction division, meiosis II separates the chromatids, which are the daughter strands of a duplicated chromosome joined together by a centromere. In mitotic cell division, new cells genetically identical to the parent cell are produced.
What happens to the chromosomes in meiosis?
In meiosis, during the formation of gametes in animals and spores in plants, the chromosome number is reduced to half. These chromosomes contain the basic DNA chain.
Why does variation occur in meiosis?
In meiosis, variation occurs, because each gamete (either sperm or egg) contains a mixture of genes from two different parent chromosomes in sexual reproduction. In other words, the genetic coupling of non-identical DNA takes place in meiosis. It results in an offspring, which has the genetic material of two different individuals.
How does meiosis affect the population?
In this way, a population contains fit individuals and the process continues for generations together. The diversity afforded by meiosis is beneficial for the population as a whole.
What are the two stages of meiosis?
Let's Work Together! Meiosis takes place in two stages – Meiosis I , where DNA replication takes place and crossing-over occurs; and Meiosis II , which lacks DNA replication, but is similar to Mitotic cell division.
What is the significance of meiosis?
Meiosis is the process in which the parent cell divides twice into four daughter cells containing half the original amount of genetic information, i .e., the daughter cells are haploid. The gametes are produced by meiosis.
How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
It results in the formation of four daughter cells in each cycle of cell division. The daughter cells are identical to the mother cell in shape and size but different in chromosome number. The daughter cells are haploid. Recombination and segregation take place in meiosis.
Why is it important to keep the number of chromosomes constant?
It maintains the constant number of chromosomes by halving the same. This is important because the chromosome number doubles after fertilization. In this process independent assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes takes place.
How long does meiosis last?
All mammalian oocytes arrest meiosis at birth until ovulation. This means that in human oocytes, arrest lasts up to 40 years.
Which division reduces the ploidy of cells in meiosis?
In contrast, in meiosis I, sister kinetochores must attach to the same pole and homologous kinetochores must attach to the opposite poles. This is the key division that reduces the ploidy of cells in meiosis. In meiosis II, like mitosis, sister kinetochores must attach to the opposite poles.
What happens to aneuploidy during meiosis?
Missegregation during meiosis results in aneuploidy in progeny or fertilized eggs. In the case of humans, it is reported that 20% of all eggs are aneuploids, most of which are results of chromosome missegregation in oocytes (Hassold and Hunt 2001).
Why is Prdm9 fast evolving?
Prdm9 is a fast-evolving protein in many animals, including humans (Oliver et al. 2010), and this rapid change is thought to counteract a loss of individual hot spots because of biased gene conversion during the recombination process (Nicolas et al. 1989).
What is the process that reduces chromosome numbers from diploid to haploid?
This consists of two opposite processes: meiosis, which reduces chromosome numbers from diploid to haploid, and conjugation (fertilization), which restores the diploid state by fusion of two haploid cells. Meiosis generates diversity through two events: recombination and chromosome segregation.
Why is sexual reproduction important?
It is essential for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes and diploid organisms and produces gametes, such as eggs and sperm. Sexual reproduction is thought to be essential for long-term survival of species, as it generates diversity and mixes the genetic materials within the species.
Is meiosis the same as mitosis?
In contrast to mitosis, molecular mechanisms and regulation of meiosis are much less understood. Meiosis shares mechanisms and regulation with mitosis in many aspects, but also has critical differences from mitosis. This review highlights these differences between meiosis and mitosis. Recent studies using various model systems revealed differences ...
What is the final result of meiosis?
Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images. The final result of meiosis is the production of four daughter cells. These cells have one half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Only sex cells are produced by meiosis. Other cell types are produced by mitosis.
What happens to chromosomes in meiosis?
Chromosomes thicken and detach from the nuclear envelope. Similar to mitosis, the centrioles migrate away from one another and both the nuclear envelope and nucleoli break down. Likewise, the chromosomes begin their migration to the metaphase plate. At the end of prophase I of meiosis, the cell enters into metaphase I.
What is the function of microtubules in meiosis?
Similar to mitosis, microtubules such as the kinetochore fibers interact to pull the chromosomes to the cell poles. Unlike in mitosis, sister chromatids remain together after the homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles. At the end of anaphase I of meiosis, the cell enters into telophase I.
What happens at the end of metaphase I of meiosis?
At the end of metaphase I of meiosis, the cell enters into anaphase I.
What phase of meiosis is the nucleus bounded by?
At the end of interphase, the cell enters the next phase of meiosis: Prophase I.
What stage of meiosis do the two cell poles move further apart?
In preparation for the next stage of meiosis, the two cell poles also move further apart during the course of anaphase II. At the end of anaphase II, each pole contains a complete compilation of chromosomes. Following anaphase II of meiosis, the cell enters into telophase II.
What happens at the end of telophase?
At the end of telophase I and cytokinesis, two daughter cells are produced, each with one-half the number of chromosomes of the original parent cell. Depending on the kind of cell, various processes occur in preparation for meiosis II. There is, however, a constant: The genetic material does not replicate again.

Why?
The Phases of Meiosis
- Meiosis is split into two parts, or divisions, each of which consists of several phases. These are prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I and telophase I in meiosis I; and prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II and telophase II in meiosis II. You will need some terminology to understand these phases: 1. Bivalent– a pair of homologous chromosomes held together by a chiasma. 2. Chiasm…
Why Is Meiosis Important in Studying Biology?
- Meiosis is important for three main reasons: it allows sexual reproduction of diploid organisms, it enables genetic diversity, and it aids the repair of genetic defects. 1. Allows sexual reproduction of diploid organisms As mentioned previously, meiosis allows the reduction of a diploid cell to a haploid gamete, which can then recombine with anothe...
How Is Meiosis Different from mitosis?
- Mitosisis the production of two genetically identical diploid daughter cells from one diploid parent cell. Meiosis produces four genetically distinct haploid daughter cells from a single diploid parent cell. These germ cells can then combine in sexual reproduction to form a diploid zygote. Meiosis only occurs in eukaryotic organisms which reproduce sexually, whereas mitosis occurs in all euk…