Advantages
- Though expensive, monoclonal antibodies are cheaper to develop than conventional drugs because it is based on tested technology.
- Side effects can be treated and reduced by using mice-human hybrid cells or by using fractions of antibodies.
- They are used in different ways.
- They bind to specific diseased or damaged cells needing treatment.
Which monoclonal antibody is best?
- People who are 65 years old or older
- People who are obese or overweight
- Pregnant people
- People with certain underlying medical conditions
Are there side effects of monoclonal antibody treatment?
The most commonly reported side effects were rash (2%) and diarrhea (1%). There was one reported case of anaphylaxis after sotrovimab infusion. Monoclonal antibody therapy is not indicated in severe cases requiring hospitalization.
What to expect from monoclonal antibody treatment?
- Upset stomach (nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea)
- Itching, swelling, rash, or hives
- Dizziness or low blood pressure
- Changes in your heartbeat
- Any new or worsening symptoms
- Difficulty breathing
- Weakness
- Confusion
How effective is the monoclonal treatment?
Throughout the pandemic, monoclonal antibody treatments have proven to be effective against COVID-19. Now, the FDA said they are limited two treatments. LITTLE ROCK, Ark. — "Almost 100% of the circulating viruses here in the U.S. is suspected to Omicron," said Dr. Naveen Patil, deputy state health officer for the Arkansas Department of Health.

What are monoclonal antibodies used for during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-made proteins that mimic the immune system's ability to fight off harmful pathogens such as viruses, like SARS-CoV-2. And like other infectious organisms, SARS-CoV-2 can mutate over time, resulting in certain treatments not working against certain variants such as omicron.
Are antibodies beneficial during the COVID-19 pandemic?
When reinfections or breakthrough infections happen, having antibodies plays an important role in helping prevent severe illness, hospitalization, and death. For many diseases, including COVID-19, antibodies are expected to decrease or “wane” over time.
What is the effectiveness of monoclonal antibody therapy for COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies can be effective at decreasing hospitalization rates and progression to severe disease and death for patients with mild to moderate COVID-19. In addition, mAbs have been shown to improve survival in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who have not mounted their own immune response.
Is there a monoclonal antibody therapy for post COVID-19 exposure?
FDA authorizes bamlanivimab and etesevimab monoclonal antibody therapy for post-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) for COVID-19 | FDA.
Do I need the COVID-19 vaccine if I still have antibodies?
Yes, the COVID-19 vaccines are recommended, even if you had COVID-19.
Why antibody testing Is not currently recommended to assess immunity after COVID-19 vaccination?
Currently authorized SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests have not been evaluated to assess the level of protection provided by an immune response to COVID-19 vaccination. If antibody test results are interpreted incorrectly, there is a potential risk that people may take fewer precautions against SARS-CoV-2 exposure.
How many types of monoclonal antibody COVID-19 treatments are there in the US?
In the United States, there are three anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody treatments with FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of COVID-19: bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab,, and sotrovimab.
How long does it take for immunity to wane after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine?
A study published by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that immunity against severe COVID-19 begins to wane four months after receiving a so-called "booster" third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines.
Does the COVID-19 vaccine reduce the risk of getting "Long COVID"?
Reseach is showing that people who are vaccinated, even with just one dose, tend to have lower rates of long COVID-19 after catching the virus than those who are unvaccinated.
Is it possible to develop immunity to COVID-19 after being exposed?
In addition, the hope is that people who've been exposed to COVID-19 also develop an immunity to it. When you have immunity, your body can recognize and fight off the virus. It's possible that people who've had COVID-19 can get sick again -- and maybe infect other people.
Can you still test positive after recovering from COVID-19?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, some people who contract COVID-19 can have detectable virus for up to three months, but that doesn't mean they are contagious. When it comes to testing, however, the PCR tests are more likely to continue picking up the virus following infection.
How long does it take for symptoms to appear after exposure to COVID-19?
People with COVID-19 have had a wide range of symptoms reported – ranging from mild symptoms to severe illness. Symptoms may appear 2-14 days after exposure to the virus.
Overview
Monoclonal antibodies (also called moAbs or mAbs) are proteins made in laboratories that act like proteins called antibodies in our bodies. Antibodies are parts of your immune system. They seek out the antigens (foreign materials) and stick to them in order to destroy them.
Procedure Details
In most cases, monoclonal antibodies are given mostly as intravenous (IV) solution injected right into your vein (sometimes referred to as an infusion). They’re often given in an infusion center where there are several people getting treatment at one time.
Recovery and Outlook
Infusion times can vary. As an example, though, monoclonal antibody treatment for COVID-19 under Emergency Use Authorization took about an hour for infusion and then another hour or so to watch for any reaction to the infusion.
When to Call the Doctor
If you’ve had a monoclonal antibody treatment, and you’re having an expected reaction, call your healthcare provider or go to an emergency room.
What is the function of antibodies?
Antibodies are proteins that exist in our bodies as part of our immune system to recognize and defend against harmful viruses and bacteria. Monoclonal antibodies are made in a laboratory and designed to target a specific virus or bacteria.
What antibody is used to block the virus?
Monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 attach to the virus to block it from entering human cells. The monoclonal antibody protein also “marks” the virus to be broken down by the immune system and cleared from the body.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause nausea?
Most people tolerate monoclonal antibody infusions very well. Some people may experience infusion-related side effects, such as nausea and dizziness, that are short-lived and go away on their own. As with any medication, there is the potential for mild or more severe allergic reactions, which are uncommon.
What is the role of monoclonal antibodies in the immune system?
Monoclonal antibodies are designed to function in different ways. A particular drug may actually function by more than one means. The role of the drug in helping the immune system may include the following: Flagging cancer cells. Some immune system cells depend on antibodies to locate the target of an attack.
Why do some drugs have monoclonal antibodies?
Similarly, some monoclonal antibodies are attached to a chemotherapeutic drug in order to deliver the treatment directly to the cancer cells while avoiding healthy cells. Binding cancer and immune cells. Some drugs combine two monoclonal antibodies, one that attaches to a cancer cell and one that attaches to a specific immune system cell.
How are monoclonal antibodies administered?
Monoclonal antibodies are administered through a vein (intravenously). How often you undergo monoclonal antibody treatment depends on your cancer and the drug you're receiving. Some monoclonal antibody drugs may be used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
Why do immune cells depend on antibodies?
Some immune system cells depend on antibodies to locate the target of an attack. Cancer cells that are coated in monoclonal antibodies may be more easily detected and targeted for destruction. Triggering cell-membrane destruction.
What is the function of an antibody?
An antibody attaches itself to a specific molecule (antigen) on the surface of a problematic cell. When an antibody binds to the antigen, it serves as a flag to attract disease-fighting molecules or as a trigger that promotes cell destruction by other immune system processes.
What is the immune system?
The immune system is composed of a complex team of players that detect and destroy disease-causing agents, such as bacteria and viruses. Similarly, this system may eliminate damaged or abnormal cells, such as cancer cells. One factor in the immune system is the work of antibodies.
Do monoclonal antibodies work?
Monoclonal antibody drugs for cancer: How they work. If you're considering monoclonal antibody therapy as part of your cancer treatment, learn about these drugs and carefully weigh the benefits against the potential side effects. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Monoclonal antibody drugs are cancer treatments that enlist natural immune system functions ...
WHAT IS A MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY?
Your body naturally makes antibodies to fight infection. However, your body may not have antibodies designed to recognize a novel (or new) virus like SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
How Can I Get Monoclonal Antibodies?
To receive a mAb you should be referred for treatment by your healthcare professional and directed to available infusion locations. If you do not have a healthcare provider, call the Combat COVID Monoclonal Antibodies Call Center at 1-877-332-6585 to find out who to talk with about your symptoms and treatment.
WHAT IF I DO NOT QUALIFY FOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT?
Your healthcare professional may decide you do not qualify for mAb treatment. There could be several reasons for this. You may not meet all eligibility criteria or you may have an underlying health condition that disqualifies you for mAb treatment.
WHAT CAN I EXPECT FROM TREATMENT (INFUSION)?
The mAb treatment is usually offered at an infusion center because the treatment is given through an intravenous (IV) infusion or shots. Depending on the mAb treatment you receive, the whole process takes about 1-3 hours, depending on the treatment..
CAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT MAKE ME SICK?
Antibody treatments do not contain any live SARS-CoV-2, so there is no risk you will get COVID-19 from mAb treatment. However, the antibody treatment may have side effects:
What is non specific interaction with the antigen?
Non specific interaction with the antigen- considerable heterogeneity within the antibody pool. Life span of the host animal is limited. Multiple animals had to be immunized against the same antigen. Antibody response depends on the host animal.
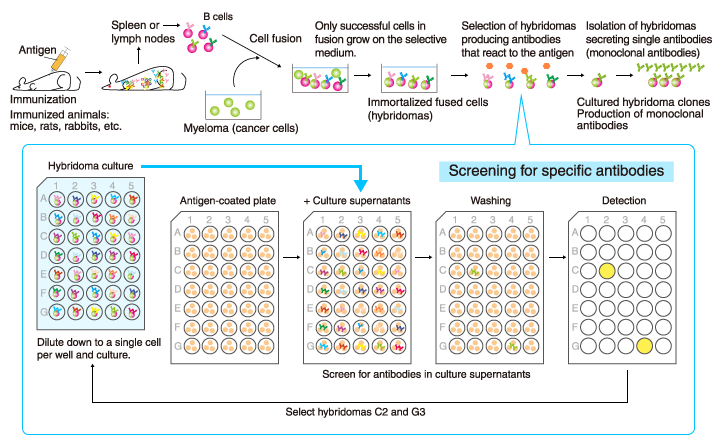
What are the advantages of hybridoma?
Advantages of using Monoclonal Antibodies: 1 Hybridoma serves as an immortal source of monoclonal antibody. 2 Same quality of the antibody is maintained amongst the different production batches. 3 Highly reproducible and scalable, unlimited production source. 4 Speed and sensitivity and specificity of assays. 5 Can produce antibodies when needed. 6 No need to worry about maintaining the animals. 7 Antigen or immunogen need not be pure.
Is a polyclonal antibody system well developed for mice and rats?
System is only well developed for mouse and rat and not for other animals. More than 99% of the cells do not survive during the fusion process – reducing the range of useful antibodies that can be produced against an antigen. Advantages of Using Polyclonal Antibodies: Production is quicker. Less expensive.
Is antibody production faster?
Production is quicker. Less expensive. Have choice of producing antibodies in different animals. Chances of getting a better response to the antigen is increased– can try different animal sources as antibody produced recognizes different epitopes on the same antigen.