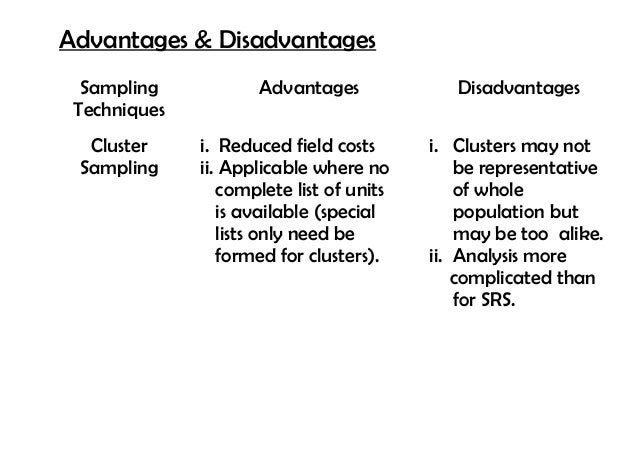
Advantages of Stratified Sampling
- Precise Estimates for subgroups. When members of the subpopulations are relatively homogeneous relative to the entire...
- Efficiency in Conducting the Survey. Stratified sampling can reduce survey costs and simplify data collection. In many...
- Ensures Representation of all Groups of Interest. By explicitly incorporating the strata into...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of stratified sampling?
Advantages and Disadvantages Because it provides greater precision, a stratified sample often requires a smaller sample, which saves money. A stratified sample can guard against an "unrepresentative" sample (e.g., an all-male sample from a mixed-gender population).
Which is an effective use of stratified sampling?
What is your plagiarism score?
- Best plagiarism checker of 2020
- Plagiarism report & percentage
- Largest plagiarism database
When should I use stratified sampling?
Notation
- L = the number of strata
- Nh = number of units in each stratum h
- nh = the number of samples taken from stratum h
- N = the total number of units in the population , i.e., N1 + N2 + ... + NL
What is a disadvantage of using a stratified sampling method?
The method's disadvantage is that several conditions must be met for it to be used properly. As a result, stratified random sampling is disadvantageous when researchers can't confidently classify every member of the population into a subgroup. Find out all about it here.
What are advantages and disadvantages of stratified sampling?
One advantage of stratified random sampling includes minimizing sample selection bias and its disadvantage is that it is unusable when researchers cannot confidently classify every member of the population ...
What are the benefits of sampling?
Advantages of samplingLow cost of sampling. If data were to be collected for the entire population, the cost will be quite high. ... Less time consuming in sampling. ... Scope of sampling is high. ... Accuracy of data is high. ... Organization of convenience. ... Intensive and exhaustive data. ... Suitable in limited resources. ... Better rapport.
What is the point of stratified sampling?
In stratified sampling, researchers divide subjects into subgroups called strata based on characteristics that they share (e.g., race, gender, educational attainment, etc). Once divided, each subgroup is randomly sampled using another probability sampling method.
Why is stratified sampling better than random?
Because it uses specific characteristics, it can provide a more accurate representation of the population based on what's used to divide it into different subsets. This often requires a smaller sample size, which can save resources and time.
Why is stratified sampling better than quota?
Quota sampling is different from stratified sampling, because in a stratified sample individuals within each stratum are selected at random. Quota sampling achieves a representative age distribution, but it isn't a random sample, because the sampling frame is unknown.
Why stratification is important in the field survey?
Efficiency: Stratification may increase efficiency of the estimates by forming strata in such a way that each stratum becomes homogeneous with respect to the characteristic under study. Suitable sampling schemes to the respective strata may increase efficiencies of the estimators.
Why do we use stratified sampling?
Researchers use stratified sampling to ensure specific subgroups are present in their sample. It also helps them obtain precise estimates of each group’s characteristics. Many surveys use this method to understand differences between subpopulations better. Stratified sampling is also known as stratified random sampling.
How does stratified sampling work?
The stratified sampling process starts with researchers dividing a diverse population into relatively homogeneous groups called strata, the plural of stratum. Then, they draw a random sample from each group (stratum) and combine them to form their complete sample.
Why do we need a random sample?
While we want a random sample for unbiased estimates overall, we also want to obtain precise estimates for each income level in our population. Using simple random sampling, income levels with a small number of students and random chance could conspire to provide small sample sizes for some income levels. These smaller sample sizes produce relatively imprecise estimates for them.
What is proportionate stratified sampling?
In proportionate stratified sampling, the sample size of each stratum is proportional to its share in the population. For example, if the rural subgroup comprises 40 percent of the population you’re studying, your sampling process will ensure it makes up 40% of the sample.
How to stratify a population?
Stratified sampling involves multiple steps. First, break down the population into strata. From each stratum, use simple random sampling to draw a sample. This process ensures that you obtain observations for all strata.
What is strata in statistics?
Strata are subpopulations whose members are relatively similar to each other compared to the broader population. Researchers can create strata based on income, gender, and race, among many other possibilities. For example, if your research question requires you to compare outcomes between income levels, you might base the strata on income. All members of the population should be in only one stratum.
How many students are selected for stratified sampling?
To avoid this problem, we’ll use stratified sampling. Our sampling plan might dictate that we select 100 students from each income level using simple random sampling. Of course, this plan presupposes that we know the household income level for each student, which might be problematic.
Why do researchers use stratified sampling?
Researchers and statisticians use stratified sampling to analyze relationships between two or more strata. As this sampling involves multiple layers or strata, it is crucial to calculate the strata before calculating the sample value. Stratified sampling advantages and disadvantages.
How does stratified sampling work?
The procedure used to carry out stratified sampling has several stages . We describe the most relevant below:
What is the difference between a disproportionate and proportional stratified sample?
The sampling fraction is the main differentiating factor between proportional and disproportionate stratified sampling. In a disproportionate sampling, each stratum has a different sampling fraction.
How to stratify a sample?
The procedure used to carry out stratified sampling has several stages. We describe the most relevant below: 1 Define the target (total) population 2 Choose the stratification variables and how many strata will exist. 3 Identify each item in the population and assign a unique identifier. Each element of the population must belong to a single stratum. 4 Determine the size of each stratum (explained in the next section) 5 The elements of each stratum are randomly selected until the specific number defined for each stratum is obtained. Stratified sampling advantages and disadvantages
Why is more information required than studying the general population?
More information is required than studying the general population, either to stratify or to determine the weight of each stratum in the population.
What is better use?
Better use is made of the knowledge that the researcher has about the population under study.
Is stratum sample size proportional to population size?
In this approach, each stratum sample size is directly proportional to the size of the total population. That means that each sample of strata has the same sampling fraction.
Which is more robust, simple random sampling or stratified random sampling?
Overall, simple random sampling is more robust than stratified random sampling, especially when a population has too many differences to be categorized.
Why is sampling preferred in heterogeneous populations?
The sampling technique is preferred in heterogeneous populations because it minimizes selection bias and ensures that the entire population group is represented. It is not suitable for population groups with few characteristics that can be used to divide ...
What is the best way to select a small sample?
One of the ways researchers use to select a small sample is called stratified random sampling. Estimates generated within strata are more precise than those from random sampling because dividing the population into homogenous groups often reduces sampling error and increases precision. When seeking a potential stratum, ...
What is sample selection bias?
Sample Selection Bias Sample selection bias is the bias that results from the failure to ensure the proper randomization of a population sample. The flaws of the sample selection
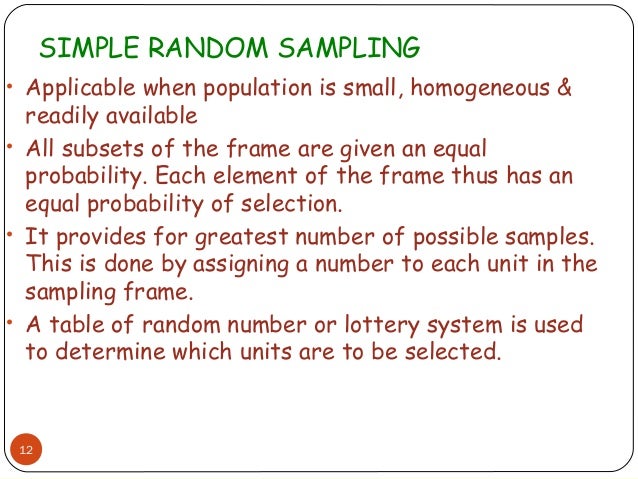
What is a simple random sample?
Simple Random Sample A simple random sample is selecting a subgroup of a population where the prospect of getting selected is equal for all the members of the population.
Why is repeated selection replaced?
To ensure the number of customers falls within the required range, the repeated selection is replaced. The retail store may then apply the estimated characteristics to the rest of the customers.
What is statistical significance?
Statistical Significance Statistical significance is the claim that the results or observations from an experiment are due to an underlying cause, rather than chance.
Why is stratified random sampling more advantageous?
As a result, stratified random sampling is more advantageous when the population varies widely since it helps to better organize the samples for study.
What is stratified random sampling?
Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling, which is when a researcher selects a small group as a sample size for study. ...
Why is a simple random sample better than a subgroup?
However, a simple random sample is more advantageous when the population can't be organized into subgroups because there are too many differences within the population. Also, simple random samples are best when there's little-to-no information about the population, which prevents the population from being broken into subsets based on characteristics or traits.
What is a simple random sample?
A simple random sample is a sample of individuals that exist in a population whereby the individuals are randomly selected from the population and placed into the sample. This method of randomly selecting individuals seeks to select a sample size that is an unbiased representation of the population. However, a simple random sample is not advantageous when the samples of the population vary widely.
Why is stratified sampling important?
The stratified sampling provides better representation to the subgroups (called strata) of the population. The stratification helps in reducing the standard error of the estimate obtained using the stratified sampling.
When is stratified sampling used?
Stratified sampling is used when the population consists of various kinds of sampling units. The sampling units are grouped such that the within-group variation is negligible, and between-group variation is high. These groups are called strata. This is a type of probability sampling.
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling methods are frequently used by researchers to randomly select the subjects for participation in experiments. Learn about multistage, multiphase, and cluster sampling methods.
Why do researchers use stratified sampling?
Researchers rely on stratified sampling when a population’s characteristics are diverse and they want to ensure that every characteristic is properly represented in the sample.
How to use stratified sampling?
To use stratified sampling, you need to be able to divide your population into mutually exclusive and exhaustive subgroups. That means every member of the population can be clearly classified into exactly one subgroup.
What is proportionate sampling?
In proportionate sampling, the sample size of each stratum is equal to the subgroup’s proportion in the population as a whole.
How to stratify by multiple characteristics?
In this case, to get the total number of subgroups, you multiply the numbers of strata for each characteristic.
What is stratified sample?
A stratified sample includes subjects from every subgroup, ensuring that it reflects the diversity of your population. It is theoretically possible (albeit unlikely) that this would not happen when using other sampling methods such as simple random sampling.
Why do you need a similar sample size for each subgroup?
With other methods of sampling, you might end up with a low sample size for certain subgroups because they’re less common in the overall population.
How many groups are there in a stratified race?
For instance, if you were stratifying by both race and gender identity, using four groups for the former and three for the latter, you would have 4 x 3 = 12 groups in total.
Why is stratified sampling important?
Stratified sampling helps you to save cost and time because you'd be working with a small and precise sample.
What is Stratified Sampling?
Stratified sampling is a selection method where the researcher splits the population of interest into homogeneous subgroups or strata before choosing the research sample. This method often comes to play when you're dealing with a large population, and it's impossible to collect data from every member.
What is cluster sampling?
Cluster sampling involves choosing the research sample from naturally occurring groups known as clusters. In stratified sampling, the researcher selects the sample population from non-overlapping, homogeneous strata.
What is the difference between stratified and cluster sampling?
The major difference between stratified sampling and cluster sampling is how subsets are drawn from the research population. In cluster sampling, the researcher depends on naturally-occurring divisors like geographical location, school districts, and the like.
What is a disproportionate stratified sampling?
Disproportionate stratified sampling is a stratified sampling method where the sample population is not proportional to the distribution within the population of interest. The implication is that the members of different subgroups do not have an equal opportunity to be a part of the research sample.
What is the purpose of sampling fraction?
Typically, the researcher derives a sampling fraction and uses this fraction to determine how the variables are selected for the sample. This sampling fraction is always the same across all strata, regardless of their sizes. With disproportionate stratified sampling, every unit in a stratum stands the same chance of getting selected for the systematic investigation.
What are the advantages of disproportionate sampling?
A key advantage of disproportionate sampling is it allows you to collect responses from minority subsets whose sample size would otherwise be too low to allow you to draw any statistical conclusions.