Who benefited under a mercantile system?
Who benefited under a mercantile system? ... Explain why the European nations wanted to maximize their exports and minimize their imports under a mercantile system. Under a mercantile system, wealth was achieved by gaining gold and silver. Therefore, European nations wanted to increase, not spend, their holdings of gold and silver. ...
How did mercantilism help the British Empire?
The British had an empire to run. The way that they kept their economy healthy was through a system called mercantilism. This pushed the colonists to buy only British goods, instead of goods from other European countries. The distance from Britain and the size of the British Empire was an advantage for the colonies.
How did mercantilism benefit nations that founded colonies?
Under mercantilism, colonies were important because they produced raw materials for the mother country, goods that the country would have to import otherwise (things like grain, sugar, or tobacco). The colonies also gave the mother country an outlet for exports, which increased jobs and industrial development at home.
Why was trade important to mercantilism?
Why was a favorable balance of trade important to mercantilism? Having a favorable balance of trade was essential to mercantilism. A favorable balance of trade meant that there were more goods leaving the country to be sold (exports) than there were goods coming into the country to be bought (imports).
Who benefited under mercantilism?
The mother nations of colonies benefited most from mercantilism. This is because the colonial home nations (such as Spain or Britain) used...
What country relied on mercantilism?
The primary countries that employed mercantilism were of western Europe—France, Spain, Portugal, Italy, and Britain, as well as Germany and the Netherlands.
Which European countries benefited from mercantilism?
European nations — including France and England (later Great Britain) — used this system to their advantage from the 16th century through the mid-19th century. The purpose was to extract as much wealth as possible from the colonies without investing much into them.
How did America benefit from mercantilism?
Under mercantilism, colonies were important because they produced raw materials for the mother country, goods that the country would have to import otherwise (things like grain, sugar, or tobacco). The colonies also gave the mother country an outlet for exports, which increased jobs and industrial development at home.
How did European nations use mercantilism?
First popularized in Europe during the 1500s, mercantilism was based on the idea that a nation's wealth and power were best served by increasing exports, in an effort to collect precious metals like gold and silver. Mercantilism replaced the feudal economic system in Western Europe.
Does Canada use mercantilism today?
Mercantilism is not past and gone. It is alive and the dominant theory of economic reality in both China and Canada today.
How did Britain benefit from mercantilism?
As such, mercantilism became the key economic model of the time. It encouraged the colonists to purchase goods from England rather than rival nations. The colonies sent raw materials to England where they were manufactured into finished products and sold to the colonists.
Who didnt benefit from mercantilism?
This cartoon shows that mercantilism only really benefitted the mother country and did not support or improve the colonies. This is shown in the cartoon in that the mother country is being served all of the raw materials, precious metals and food from the colony “servers” and the colonies receive nothing in return. 9.
How does mercantilism affect Canada?
As a result, Canada developed a tightly governed economy under mercantilism with infrastructure that reflected its needs: docks and harbours, storehouses for furs, and a workforce just large enough to trade furs, fight local wars, and develop a farming sector that could meet subsistence needs.
How did mercantilism benefit the mother country?
How does mercantilism benefit the Mother Country? Colonies supply raw materials at a discounted price to the Mother Country. The Europeans would then make those raw materials into finished products and then sell those finished products back to the colonies for a higher price.
What are some examples of mercantilism?
A mercantilistic example includes the Sugar Act of 1764 that made colonists pay higher tariffs and duties on imports of foreign-made refined sugar products.
Which of the following regions were the most successful colonies within the economic system of mercantilism?
Correct answer: Dominion of New England. Which of the following regions were the most successful colonies within the economic system of mercantilism?
What did mercantilism teach about trade?
Mercantilism taught that trade was a zero-sum game, with one country's gain equivalent to a loss sustained by the trading partner. Overall, however, mercantilist policies had a positive impact on Britain, helping to transform the nation into the world's dominant trading power and a global hegemon.
How did mercantilism help create trade patterns?
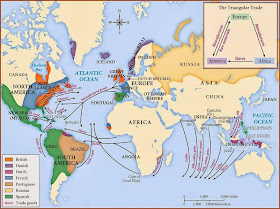
Mercantilism helped create trade patterns such as the triangular trade in the North Atlantic, in which raw materials were imported to the metropolis and then processed and redistributed to other colonies.
What was the peak of mercantilism in England?
Main article: Economic history of the United Kingdom § The Age of Mercantilism. In England, mercantilism reached its peak during the Long Parliament government (1640–60). Mercantilist policies were also embraced throughout much of the Tudor and Stuart periods, with Robert Walpole being another major proponent.
What was the dominant economic ideology of Europe in the early modern period?
Mercantilist ideas were the dominant economic ideology of all of Europe in the early modern period, and most states embraced it to a certain degree. Mercantilism was centred on England and France, and it was in these states that mercantilist policies were most often enacted.
Why did Adam Smith reject mercantilism?
Adam Smith rejected the mercantilist focus on production , arguing that consumption was paramount to production. He added that mercantilism was popular among merchants because it was what is now called rent seeking. John Maynard Keynes argued that encouraging production was just as important as encouraging consumption, and he favored the "new mercantilism". Keynes also noted that in the early modern period the focus on the bullion supplies was reasonable. In an era before paper money, an increase in bullion was one of the few ways to increase the money supply. Keynes said mercantilist policies generally improved both domestic and foreign investment—domestic because the policies lowered the domestic rate of interest, and investment by foreigners by tending to create a favorable balance of trade. Keynes and other economists of the 20th century also realized that the balance of payments is an important concern. Keynes also supported government intervention in the economy as necessity, as did mercantilism.
What is a mercantilism policy?
Business and economics portal. v. t. e. Mercantilism is an economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports for an economy. It promotes imperialism, tariffs and subsidies on traded goods to achieve that goal.
What is the economic policy that maximizes the exports and minimizes the imports for an economy?
Mercantilism. Mercantilism is an economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports for an economy. It promotes imperialism, tariffs and subsidies on traded goods to achieve that goal.
What was the greatest benefit of mercantilism?
Between 1640-1660, Great Britain enjoyed the greatest benefits of mercantilism. During this period, the prevailing economic wisdom suggested that the empire's colonies could supply raw materials and resources to the mother country and subsequently be used as export markets for the finished products. The resulting favorable balance of trade was ...
What did mercantilism lead to?
Mercantilism did, however, lead to the adoption of enormous trade restrictions, which stunted the growth and freedom of colonial business. In the 1660s, for example, England passed the Acts of Trade and Navigation (aka Navigation Acts), a series of laws designed to make American colonies more dependent on manufactured products from Great Britain. ...
What was the economic position of the colonies during the mercantilist period?
Mercantilism in Great Britain consisted of the economic position that, in order to increase wealth, its colonies would be the supplier of raw materials and exporter of finished products. Mercantilism brought about many acts against humanity, including slavery and an imbalanced system of trade. During Great Britain's mercantilist period, colonies ...
What was the slave trade?
Slave Trade. Trade, during this period, became triangulated between the British Empire, its colonies, and foreign markets. This fostered the development of the slave trade in many colonies, including America. The colonies provided rum, cotton, and other products heavily demanded by imperialists in Africa.
What was the British mercantilism of the 17th century?
Mercantilism, an economic policy designed to increase a nation's wealth through exports, thrived in Great Britain between the 16th and 18th centuries.
What did the British government demand?
Inflation and Taxation. The British government also demanded trade in gold and silver bullion, ever seeking a positive balance of trade. 3 The colonies often had insufficient bullion left over to circulate in their own markets; so, they took to issuing paper currency instead.
What were the protected goods that were only sold to British merchants?
British authorities further enumerated a set of protected goods that could only be sold to British merchants, including sugar, tobacco, cotton, indigo, furs, and iron. 1 . In "Wealth of Nations", father of modern economics Adam Smith argued that free trade -- not mercantilism -- promotes a flourishing economy.
What is mercantilism in the United States?
In general, mercantilism is the belief in the idea that a nation's wealth can be increased by the control of trade: expanding exports and limiting imports. In the context of the European colonization of North America, mercantilism refers to the idea that colonies existed for the benefit of the Mother Country. ...
What was the most important thing for Britain to do under the theory of mercantilism?
The most important thing for Britain to do, under the theory of mercantilism, was keep its money and not trade with other countries to get necessary items. The colonists' role was to provide many of these items to the British.
What was the impact of Smith's work on the founding fathers?
Smith and the Founding Fathers. Smith's work had a profound effect on the American founding fathers and the nascent nation's economic system. Instead of founding America on the idea of mercantilism and creating a culture of high tariffs to protect local interests, many key leaders including James Madison (1751–1836) and Alexander Hamilton ...
Who wrote the Wealth of Nations?
The Fife, Scotland site where Adam Smith wrote "The Wealth of Nations". Martin Kelly, M.A., is a history teacher and curriculum developer. He is the author of "The Everything American Presidents Book" and "Colonial Life: Government.". In general, mercantilism is the belief in the idea that a nation's wealth can be increased by the control ...
Who was the first to argue that the wealth of a nation is not determined by how much money it holds?
The idea of a fixed amount of wealth existing in the world was the target of Scottish philosopher Adam Smith (1723–1790), in his 1776 treatise, The Wealth of Nations. Smith argued that the wealth of a nation is not determined by how much money it holds, and he argued that the use of tariffs to halt international trade resulted in less—not ...
What are the advantages of mercantilism?
List of Advantages of Mercantilism. 1. A Prosperous Country. Mercantilism leads to profits and that paves the way for a country to become prosperous. A world that is driven by money and economics trumps everything else, it is only befitting to focus on trade, commerce and business which will get the people better and more secured lives, ...
How does mercantilism help entrepreneurship?
Mercantilism will also boost entrepreneurship. With more trade and higher profits, more aspiring entrepreneurs will get the funds and have the ability to take risks to run their own businesses, also to expand and venture into new territories. 4. A Stronger and More Influential Nation.
What is a mercantilism?
Mercantilism is an ideology and practice that believes in the benefits of profitable trading, puts commerce or trade and business as the foremost priority of a nation and propagates the concept that only such a practice is the best way ahead for a nation, to its prosperity and better future . Mercantilism has many variants. There are economic and social offshoots. There are free market aftermaths and protectionism along with several other schools of thought that have resulted as a direct impact of mercantilism that was born in Europe.
How does mercantilism affect the economy?
Mercantilism leads to more trade, which will lead to economic growth. The increasing trade will certainly spike demand and hence industrial growth will follow. It is not confined to any one industry. Export of foods will lead to growth in agriculture.
Was colonialism a fallout of mercantilism?
Colonialism was a direct fallout of mercantilism and everyone knows how that panned out from the United States to India. The focus being entirely on money, everything else takes a backseat, from human rights to will of people. Trade and commerce cannot be the only benchmarks for a country’s well being.
How did the mercantilism system create stronger economies?
Defenders of mercantilism argued that the economic system created stronger economies by marrying the concerns of colonies with those of their founding countries. In theory, when colonists create their own products and obtain others in the trade from their founding nation , they remain independent from the influence of hostile nations. Meanwhile, founding countries benefit from receiving large amounts of raw material from the colonists, necessary for a productive manufacturing sector.
What is a mercantilism?
Mercantilism was an economic system of trade that spanned from the 16th century to the 18th century. Mercantilism is based on the principle that the world's wealth was static, and consequently, many European nations attempted to accumulate the largest possible share of that wealth by maximizing their exports and by limiting their imports via ...
How does imperialism vs mercantilism work?
Where mercantilist governments manipulate a nation's economy to create favorable trade balances, imperialism uses a combination of military force and mass immigration to foist mercantilism on less-developed regions, in campaigns to make inhabitants follow the dominant countries' laws.
Why did the colonies issue paper currency?
The colonies often had insufficient bullion left over to circulate in their markets, so they issued paper currency instead. Mismanagement of printed currency resulted in inflationary periods. Additionally, since Great Britain was in a near-constant state of war, heavy taxation was needed to prop up its army and navy.
What was the economic system of trade that spanned from the 16th century to the 18th century?
Key Takeaways. Mercantilism was an economic system of trade that spanned from the 16th century to the 18th century. Mercantilism was based on the idea that a nation's wealth and power were best served by increasing exports and so involved increasing trade.
Why did mercantilism involve military?
Under mercantilism, nations frequently engaged their military might to ensure local markets and supply sources were protected, to support the idea that a nation's economic health heavily relied on its supply of capital.
When was mercantilism first popularized?
First popularized in Europe during the 1500s, mercantilism was based on the idea that a nation's wealth and power were best served by increasing exports, in an effort to collect precious metals like gold and silver .
Which country has the most innovation mercantilists?
The Global Mercantilist Index, ranking 60 nations on 18 variables ranging from market access and forced localization to currency manipulation and intellectual property protections, finds that China is the world’s most innovation-mercantilist nation.
Which countries have the lowest mercantilism?
In contrast, New Zealand, the Netherlands, Portugal, Sweden, and Singapore, in that order, engage in the lowest levels of innovation mercantilism. The countries are not evenly distributed across the four tiers, with most nations receiving a rank of “Low” (only China receives a “High”).
Which country has the worst mercantilist practices?
While China ranks the worst, a number of other nations, including India, Brazil, Indonesia, and Argentina, also systemically engage in innovation mercantilist practices, placing in the category of “Moderate-high.”. In contrast, New Zealand, the Netherlands, Portugal, Sweden, and Singapore, in that order, engage in the lowest levels ...

Overview
Policies
Mercantilist ideas were the dominant economic ideology of all of Europe in the early modern period, and most states embraced it to a certain degree. Mercantilism was centred on England and France, and it was in these states that mercantilist policies were most often enacted.
The policies have included:
History
Mercantilism became the dominant school of economic thought in Europe throughout the late Renaissance and the early-modern period (from the 15th to the 18th centuries). Evidence of mercantilistic practices appeared in early-modern Venice, Genoa, and Pisa regarding control of the Mediterranean trade in bullion. However, the empiricism of the Renaissance, which first began to quantify large-scale trade accurately, marked mercantilism's birth as a codified school of econo…
Theory
Most of the European economists who wrote between 1500 and 1750 are today generally considered mercantilists; this term was initially used solely by critics, such as Mirabeau and Smith, but historians proved quick to adopt it. Originally the standard English term was "mercantile system". The word "mercantilism" came into English from German in the early-19th century.
The bulk of what is commonly called "mercantilist literature" appeared in the 1620s in Great Brita…
Wars and imperialism
Mercantilism was the economic version of warfare using economics as a tool for warfare by other means backed up by the state apparatus and was well suited to an era of military warfare. Since the level of world trade was viewed as fixed, it followed that the only way to increase a nation's trade was to take it from another. A number of wars, most notably the Anglo-Dutch Wars and the Franco-Dutch Wars, can be linked directly to mercantilist theories. Most wars had other causes …
Origins
The term "mercantile system" was used by its foremost critic, Adam Smith, but Mirabeau (1715–1789) had used "mercantilism" earlier.
Mercantilism functioned as the economic counterpart of the older version of political power: divine right of kings and absolute monarchy.
Scholars debate over why mercantilism dominated economic ideology for 250 years. One group…
End of mercantilism
Adam Smith, David Hume, Edward Gibbon, Voltaire and Jean-Jacques Rousseau were the founding fathers of anti-mercantilist thought. A number of scholars found important flaws with mercantilism long before Smith developed an ideology that could fully replace it. Critics like Hume, Dudley North and John Locke undermined much of mercantilism and it steadily lost favor during the …
Legacy
Adam Smith criticized the mercantile doctrine that majored on the production in the economy, he maintained that consumption was of prime significance to consumption. Additionally, the mercantile system was well liked by the traders as it was now what is referred to as rent seeking. John Maynard Keynes affirmed that motivating the production process was as significant as encouraging the consumption, which benefited the new mercantilism. Keynes also affirmed tha…
British Mercantilism's Control of Production and Trade
The Slave Trade
- Slaverywas a common practice throughout the history of human civilization. The earliest records date back thousands of years to Mesopotamia. The Spanish, French, and Dutch used it to take advantage of the resources in parts of the New World. When local Indigenous populations started to decline, Blacks were transported from parts of Europe and Africa to the West Indies and Sout…
Inflation and Taxation
- The British government demanded the trade of gold and silver bullion and was always seeking a positive balance of trade.4 As such, the colonies often had insufficient bullion left over to circulate in their own markets so they took to issuing paper currency instead. The mismanagement of printed currency resulted in periods of inflation. Great Britain was also in a near-constant state o…
The Bottom Line
- British mercantilism flourished during the middle of the 17th century at a time when England was flexing its muscle in the New World. The idea behind this economic policy was that the colonies existed for the benefit of the Empire, providing a stream of revenue and much-needed resources. But all this came at a cost. England's need to enforce its trade regulations and place in the worl…