
Additionally, according to Investopedia, a non-qualified employee benefit plan:
- Includes plans known as deferred-compensation, group carve-out plans, split-dollar life insurance and executive bonus plans.
- Has no limit on contributions from the employer.
- Requires minimal reporting and filing on the employer’s part and are usually less money to create than qualified plans.
What are qualified and non qualified plans?
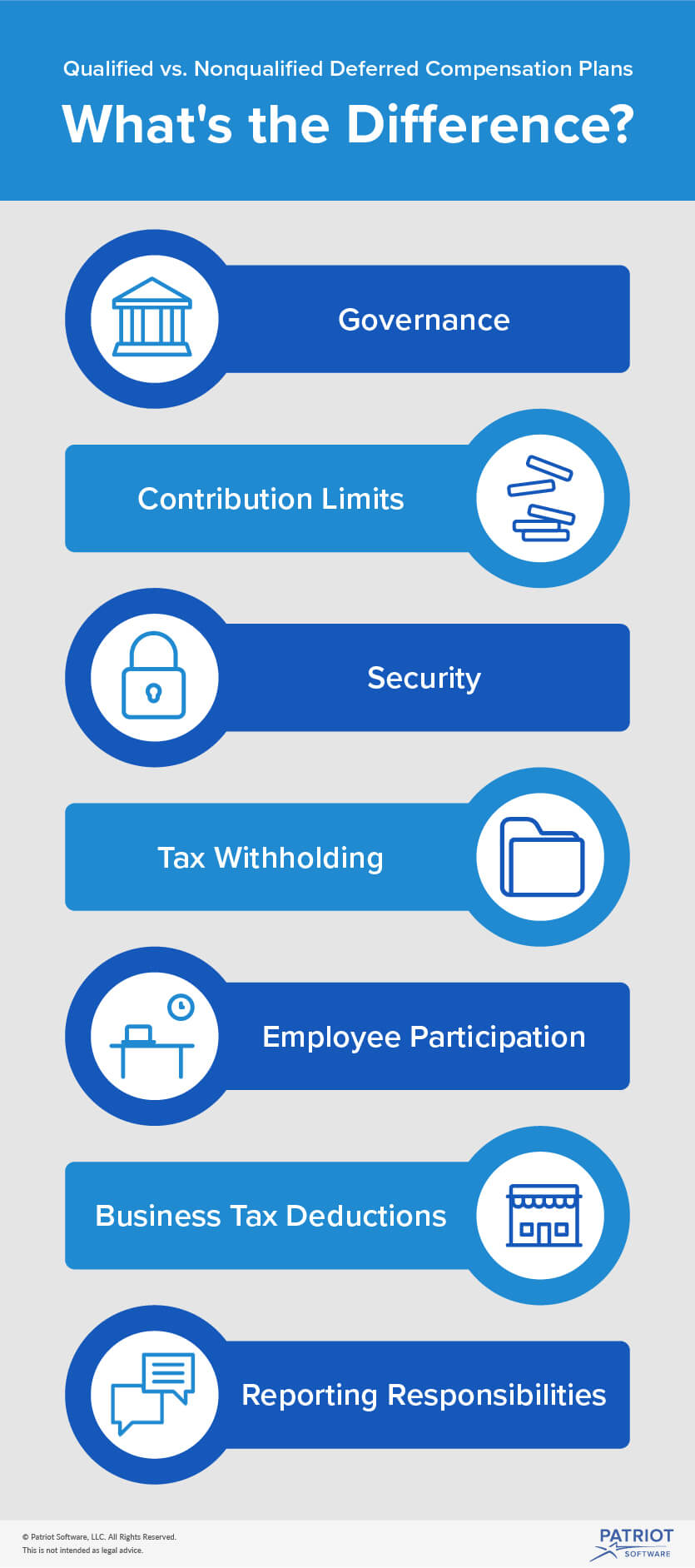
The second difference between qualified plans and nonqualified plans is often not fully appreciated by clients. That difference is cost recovery. In many nonqualified plans, an employer may be able to recover its costs for the entire plan and, as a result, have no long-term cost. Qualified plans have no provision for cost recovery by the employer.
What companies offer defined benefit pension plans?
Who has the best pension plan?
- The Typical 401 (k) Match. When an employer decides to offer a 401 (k) plan for its workers, there are different types of plans on the market to choose from. ...
- Generous Employer 401 (k) Matches. …
- Amgen.
- Boeing. …
- BOK Financial. …
- Farmers Insurance. …
- Ultimate Software.
What is a qualified and non qualified plan?
The qualified plan may accept tax deductible or non-deductible contributions. If the contributions are tax deductible, then all withdrawals from the plan are taxable. If the plan contributions are non-deductible (as is the case with Roth accounts), the withdrawals are normally tax-free.
What is an example of a non qualified retirement plan?
Non-qualified retirement plans fail to meet IRS guidelines for qualified retirement accounts. These plans accept only non-deductible contributions. Money is taxable to the employee when it is received. All money that grows inside the plan is tax-free, however. An example of this type of plan is an annuity.

What is the difference between a qualified plan and a nonqualified plan?
Qualified plans have tax-deferred contributions from the employee, and employers may deduct amounts they contribute to the plan. Nonqualified plans use after-tax dollars to fund them, and in most cases employers cannot claim their contributions as a tax deduction.
What is an example of a nonqualified plan?
Examples of nonqualified plans are deferred compensation plans, supplemental executive retirement plans, split-dollar arrangements and other similar arrangements. Contributions to a deferred compensation plan will reduce an employee's gross income, but there's no rollover option upon termination of employment.
What is the benefit of a non-qualified retirement plan?
Contributions to a nonqualified plan will lower your current income taxes (you must still pay Social Security and Medicare taxes). You will owe taxes when you receive your plan payouts so it provides a way to manage the timing of your tax payments prior to retirement.
Is a 401 K qualified or nonqualified?
If you have a 401(k), you have a qualified plan. Qualified plans fall under a set of laws that come from the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). Employers like qualified plans because they get a tax break for any contributions they make for their employees.
Is a Roth IRA qualified or nonqualified?
Qualified distributions from a Roth IRA are done when a person is over 59.5 years old or meets some special qualifications. The IRS spells out the rules for Roth IRA qualified distributions. Generally, a distribution or withdrawal is considered to be qualified if it's made at age 59.5 or later.
What type of accounts are non-qualified?
The type of investments that can be held in non-qualified accounts are annuities, mutual funds, equities, etc. If non-qualified accounts are invested in annuities, the growth on those accounts would grow on a tax deferred basis and the earnings are taxable at the time of withdrawal.
What is one of the major negatives of a non-qualified retirement plan?
From the employer's perspective, the biggest disadvantage of NQDC plans is that compensation contributed to the plan isn't deductible until an employee actually receives it. Contributions to qualified plans are deductible when made. From the employee's perspective, NQDC plans can be riskier than qualified plans.
Which of the following would be considered a nonqualified retirement plan?
Which of the following would be considered a nonqualified retirement plan? Examples of nonqualified plans are individual annuities and deferred compensation plans for highly paid executives, split-dollar insurance arrangements, and Section 162 executive bonus plans.
What are the main objectives of non-qualified plans?
Nonqualified plans are designed to meet specialized retirement needs for key executives and other select employees and can act as recruitment or employee retention tools. These plans are also exempt from the discriminatory and top-heavy testing that qualified plans are subject to.
What does nonqualified plans mean on a w2?
The non-qualified plan on a W-2 is a type of retirement savings plan that is employer-sponsored and tax-deferred. They are non-qualified because they fall outside the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) guidelines and are exempt from the testing required with qualified retirement savings plans.
Are pensions qualified or nonqualified?
This is typically advantageous for many taxpayers because their income will be lower during retirement and therefore, the effective tax rate on the money will be lower. For this reason, most retirement plans and pension funds are qualified plans.
Are annuities qualified or nonqualified?
Qualified annuities are purchased with pre-tax funds, while non-qualified annuities are funded with money on which taxes have been paid. According to the IRS, a “qualified plan must satisfy the Internal Revenue Code in both form and operation.” This affects the taxes on withdrawals or payouts from the annuity.
What is a non qualified employee benefit plan?
Additionally, according to Investopedia, a non-qualified employee benefit plan: Includes plans known as deferred-compensation, group carve-out plans, split-dollar life insurance and executive bonus plans. Has no limit on contributions from the employer. Requires minimal reporting and filing on the employer’s part and are usually less money ...
What is a qualified benefit plan?
A qualified benefit plan also: Qualifies for certain tax benefits and government protection, including tax breaks for employers and tax credits for businesses with these plans in place. Allows employee contributions and earnings to be tax-deferred until withdrawal with employers choosing the amounts they may deduct from the plan.
What is an ERISA plan?
ERISA sets the minimum of protection standards for employees. These plans are the most stringent, as they require a number of guidelines to qualify as an ERISA plan — including vesting, benefit accrual and funding restrictions. A few of the most well-known retirement plans, including 401 (k), profit-sharing plans, 403 (b), ...
Why is competitive benefit plan important?
Competitive benefit plans are among the most important factors if you hope to attract and retain employees. Carefully consider and weigh each option to determine the circumstances that will work best for your business model and are in your employees’ best interests.
Why is it important to contribute money to a non-qualified plan?
It is important that the money contributed from employees is seeing growth in the long term. The IRS mandates the following to be in place for contributed assets to grow in a non-qualified plan: Money from these plans must be separated from other employer assets. They are subject to a substantial risk of forfeiture.
Can non qualified plans be seized?
Therefore, in the event of bankruptcy or other unforeseen events, the assets can be seized by creditors. If both of these requirements are met, contributions to non-qualified plans will grow just like they would in any qualified plan.
Can an employer use a non qualified plan?
An employer may decide to use these plans if they want to defer a greater amount of money to a retirement plan than that of a qualified plan, or want to hire or retain an employee by providing added benefits not within the standard qualified benefit plans. A downside of a non-qualified benefit plan is being unable to enjoy the same benefits ...
What is a non qualified plan?
What is a Non-Qualified Plan? A non-qualified plan is an employer-sponsored, tax-deferred retirement savings plan that falls outside the Employment Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). Unlike qualified plans, non-qualified plans are exempt from the regulations and testing that apply to qualified plans. Non-qualified plans are used as ...
What is the difference between non qualified and qualified plans?
Another key difference between the two types of plans is participation. Non-qualified plans are only selectively offered to senior executives, while all employees who meet the eligibility criteria must be allowed to participate in qualified plans.
What are the different types of non qualified plans?
1. Deferred Compensation Plans. Deferred compensation plans include true deferred compensation plans and salary-continuation plans. The goal of both plans is to supplement the retirement income of executives. The difference between the two plans lies in the funding source.
What is the difference between a salary continuation plan and a deferred compensation plan?
A true-deferred compensation plan simply allows an employee to receive a portion of salary earned during retirement (or a later year) to receive tax benefits. In a salary-continuation plan, the employee continues to receive a lower salary from the employer during retirement.
What is salary continuation plan?
In a salary-continuation plan, the employee continues to receive a lower salary from the employer during retirement. 2. Executive Bonus Plans. Executive bonus plans provide supplemental benefits to select executives and employees. Most commonly, employees under such plans receive a life insurance policy.
How do qualified plans prevent excessive contributions?
Finally, qualified plans prevent excessive contributions that would favor higher-paid employees by limiting contributions through various caps, rules, and restrictions set by the IRS. Non-qualified plans are not subject to such restrictions and allow employers and employees to contribute as much as they like.
What is insurance coverage?
Insurance Coverage Insurance coverage is the amount of risk, liability or potential loss that is protected by insurance. It helps individuals recover from financial losses. with employer-paid premiums. The expenses are reported as executive bonus compensation and can be treated as tax-deductible by the employer. 3.
Examples of Non-Qualified Defined Benefit Plan in a sentence
Executive is a participant in the BB&T Corporation Non-Qualified Defined Benefit Plan (the “SERP”).
Related to Non-Qualified Defined Benefit Plan
Canadian Defined Benefit Plan means any Canadian Pension Plan which contains a “defined benefit provision” as defined in subsection 147.1 (1) of the Income Tax Act (Canada).
What is a nonqualified retirement plan?
Nonqualified retirement plans are employer-sponsored retirement plans that aren’t subject to the rules laid out in the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA). This law created minimum standards for plan participation, funding, and reporting, among other things.
Why is a nonqualified retirement plan better than a qualified retirement plan?
For the average person, a qualified retirement plan will be a better fit because it provides better protections and greater flexibility for moving between jobs.
What is a nonqualified deferred compensation plan?
A nonqualified deferred compensation plan, such as a Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (SERP), is an employer-provided plan that gives the employee supplemental retirement income. The employee does not have to pay taxes on the income until they retire. Executive bonus plans. An employer takes out a life insurance policy in their employee's ...
What is executive bonus plan?
Executive bonus plans. An employer takes out a life insurance policy in their employee's name and pays the premiums, allowing executives to access the cash value of the policy when they retire. Split-dollar life insurance plans. The employer pays for a permanent life insurance policy on behalf of the employee, and the employee ...
Do nonqualified retirees pay taxes?
Nonqualified retirement plans also enable participants to defer income taxes on part of their earnings until retirement when they will presumably be in a lower tax bracket and lose a smaller percentage of their income to the government. However, they still must pay Social Security and Medicare taxes in the year they earn the money.
Do nonqualified plans have age restrictions?
Finally, nonqualified plans don't have age restrictions on when participants can take penalty-free withdrawals. Some don't have required minimum distributions (RMDs) either. Employees and employers can work together to decide upon a distribution schedule that works for both of them.
Why is a nonqualified plan important?
A nonqualified plan can be an important benefit and may help you recruit and retain top talent. As the business owner, you are probably among the highest paid employees at your company and therefore you might benefit from nonqualified deferrals.
What to do before adding retirement plan to employee benefits?
Before you add any type of retirement or savings plan to your employee benefits package, talk to your tax professional and financial advisor. They can help you determine which type of plan – qualified, nonqualified, or both – is best for your business.
What is a nonqualified plan?
Nonqualified plans include deferred-compensation plans, executive bonus plans, and split-dollar life insurance plans. The tax implications for the two plan types are also different. With the exception of a simplified employee pension (SEP), individual retirement accounts (IRAs) are not created by an employer and thus are not qualified plans. 2 .
What happens if an employee quits a nonqualified plan?
If the employee quits, they will likely lose the benefits of the nonqualified plan. The advantages are no contribution limits and more flexibility. Executive Bonus Plan is an example.
What are the requirements for a pension plan?
A plan must meet several criteria to be considered qualified, including: 3 1 Disclosure— Documents about the plan’s framework and investments must be available to participants upon request. 2 Coverage— A specified portion of employees, but not all, must be covered. 3 Participation— Employees who meet eligibility requirements must be permitted to participate. 4 Vesting— After a specified duration of employment, a participant’s right to a pension is a nonforfeitable benefit. 5 Nondiscrimination— Benefits must be proportionately equal in assignment to all participants to prevent excessive weighting in favor of higher-paid employees.
What is defined benefit plan?
With a defined-benefit plan, there is a guaranteed payout amount and the risk of investing is borne by the employer. Plan sponsors must meet a number of guidelines regarding participation, vesting, benefit accrual, funding, and plan information to qualify their plans under ERISA.
Is vesting a nonforfeitable benefit?
Vesting— After a specified duration of employment, a participant’s right to a pension is a nonforfeitable benefit.
Is a qualified plan defined contribution or defined benefit?
The contributions and earnings then grow tax deferred until withdrawal. A qualified plan may have either a defined-contribution or defined-benefit structure. In a defined-contribution plan, employees select investments, and the retirement amount will depend on the decisions they made.
Do you have to be allowed to participate in a qualified retirement plan?
All employees who meet the eligibility requirements of a qualified retirement plan must be allowed to participate in it, and benefits must be proportionately equal for all plan participants. Disclosure— Documents about the plan’s framework and investments must be available to participants upon request.
Why are non qualified plans considered executive?
This is because non-qualified plans are designed to meet their specific needs as high earners—and to provide extra incentive to keep them at a particular company. One exception to the executive rule involves deferred-compensation plans which teachers or other specific seasonal workers may also fall under.
How are taxes calculated for non qualified plans?
How Are Taxes Calculated on Non-Qualified Plans? Taxes for non-qualified plans are actually split between when the money is earned and when it is paid out. FICA taxes, which are comprised of Medicare and Social Security tax payments, are taken out of the employee’s paycheck when they earn it, as most taxes are.
Why are non qualified plans better than ERISA?
Non-qualified plans benefit employers in a number of ways: They offer a greater amount of flexibility than plans covered under ERISA because employers can choose to offer them only to the executives and employees who will benefit most from them.
What is the federal withholding rate for supplemental wages?
Employers are required to apply federal tax withholding rules on up to $1 million worth of supplemental wages, at a rate of 25% . For supplemental wages exceeding $1 million, the rate is 35% . On an employee’s W-2 form, reported distributions from a non-qualified plan are reported in box 11.
What is a non qualified W-2?
What Are Non-Qualified Plans (W-2)? The non-qualified plan on a W-2 is a type of retirement savings plan that is employer-sponsored and tax-deferred. They are non-qualified because they fall outside the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) guidelines and are exempt from the testing required with qualified retirement savings plans.
Is a 403b qualified?
To be clear, the popular 401 (k) and 403 (b) plans are both qualified. They aren’t considered non-qualified plans, so the information on this page won’t apply to those plans. A non-qualified plan is meant to meet specialized needs for certain employees, mainly key executives, and act as a tool for their recruitment and retention.
What is a non qualified plan?
Non-qualified plans, however, are typically an unfunded agreement between the company and employee that deferred compensation will be paid out at a later date . If the company goes bust, employees might not receive the promised compensation. Oftentimes, employers form trusts to hold non-qualified plan assets, which affords employees protection ...
What is a qualified retirement plan?
Most of us are familiar with qualified retirement plans -- they are employer-sponsored 401 (k), 403 (b), and profit-sharing plans that meet guidelines set forth in the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) of 1974. Qualified plans enjoy attractive tax benefits that make them appealing for millions of American workers.
What is the biggest drawback for employees who contribute to non-qualified retirement plans?
Risk is perhaps the biggest drawback for employees who contribute to non-qualified retirement plans. Contributions to qualified retirement plans are held in segregated trust accounts that enjoy full protection from bankruptcy and creditors.
What is the maximum contribution to a 403b plan in 2021?
One of the main differences between the two is contribution limits. Contributions to qualified 401 (k) and 403 (b) plans are capped at $19,500 in 2021, the same as 2020. Employees ages 50 and older also can contribute an additional $6,500 in “catch-up” contributions.
Why are 401(k) plans inadequate?
For many high earners, 401 (k) plans are inadequate because contribution limits are well below their ability and desire to create a comfortable financial cushion for use in retirement. Companies use non-qualified retirement plans as a recruitment and retention tool for these employees because they allow them to defer compensation ...
Is deferred compensation tax free?
Their deferred compensation has the ability to grow tax-free until it is dispersed. If it’s taken out in retirement, these highly compensated employees might be in lower tax brackets than when they were working. These plans also aren’t subject to mandatory distribution requirements like 401 ...
How Does A Non-Qualified Plan Work?
- The contributions made to non-qualified plans are not deductible for the employer. It means that employers must fund non-qualified plans using after-tax dollars. The contributions are also taxable for employees. However, employees can defer taxes until retirement to benefit from a lower tax bracket. Since employers must use after-tax dollars to fund non-qualified plans, non-q…
Major Types of Non-Qualified Plans
- 1. Deferred Compensation Plans
Deferred compensation plans include true deferred compensation plans and salary-continuation plans. The goal of both plans is to supplement the retirement income of executives. The difference between the two plans lies in the funding source. A true-deferred compensation plan … - 2. Executive Bonus Plans
Executive bonus plans provide supplemental benefits to select executives and employees. Most commonly, employees under such plans receive a life insurance policywith employer-paid premiums. The expenses are reported as executive bonus compensation and can be treated as t…
Non-Qualified Plans vs. Qualified Plans
- Tax Treatment
The main difference between the two types of plans is the tax treatment of contributions. As mentioned earlier, non-qualified plan contributions are not tax-deductible for the employer and must be funded using after-tax dollars. Qualified plans allow employers to treat contributions as … - Participation
Another key difference between the two types of plans is participation. Non-qualified plans are only selectively offered to senior executives, while all employees who meet the eligibility criteria must be allowed to participate in qualified plans.
Learn More
- CFI is the official provider of the global Capital Markets & Securities Analyst (CMSA)®certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful: 1. Deferred Compensation 2. Employee Stock Purchase Plan 3. Employment Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) 4. Vesti…