What is a benefit-cost ratio in project management?
A benefit-cost ratio is a tool you can use when performing a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate what projects to undertake or what value a project can bring. The benefit-cost ratio (BCR) helps summarize the relationship between a project’s costs and benefits by expressing the ratio as a decimal.
What is benefit cost ratio in cost benefit analysis?
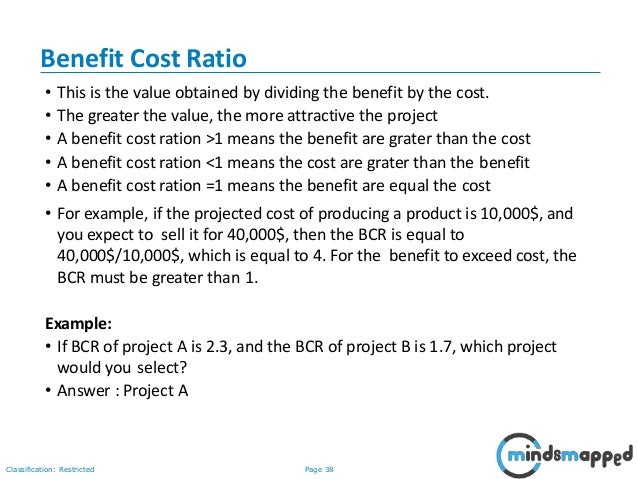
Benefit Cost Ratio - BCR. What is a 'Benefit Cost Ratio - BCR'. A benefit cost ratio (BCR) is an indicator used in cost-benefit analysis, to show the relationship between the costs and benefits of a proposed project, in monetary or qualitative terms. Next Up. Cost-Benefit Analysis. Net Present Value Rule.
What is the benefit cost ratio of present value?
Ratio of Both Present Values The benefit cost ratio (or benefit-to-cost ratio) compares the present value of all benefits with that of the cost and investments of a project or investment. These benefits and costs are treated as monetary cash flows or their equivalents, e.g. for non-monetary benefits or company-internal costs.
How to calculate benefit-to-cost ratio (BCR) of a project?
Fill in the number of periods, the forecasted cost- and benefit-related cash flows, the discount rate and calculate the benefit-to-cost ratio of your project: We hope you have found this BCR calculator useful.
How is benefit-cost ratio calculated?
The benefit cost ratio is calculated by dividing the present value of benefits by that of costs and investments.
What is the ratio of benefits to cost?
A benefit–cost ratio (BCR) is an indicator, used in cost–benefit analysis, that attempts to summarize the overall value for money of a project or proposal. A BCR is the ratio of the benefits of a project or proposal, expressed in monetary terms, relative to its costs, also expressed in monetary terms.
What is PMP benefit/cost ratio?
The benefit-cost ratio (BCR) helps summarize the relationship between a project's costs and benefits by expressing the ratio as a decimal. If the ratio is greater than 1.0, the benefits outweigh the costs. If the ratio is less than 1.0, the costs outweigh the benefits.
What does a benefit-cost ratio of 2.1 mean?
This means: A. The costs are 2.1 times the benefits.
Why is cost benefit ratio important?
Summary. The benefit-cost ratio is used to determine the viability of cash flows from an asset or project. The higher the ratio, the more attractive the project's risk-return profile. Poor cash flow forecasting or an incorrect discount rate would lead to a flawed benefit-cost ratio.
What is benefit ratio answer in one sentence?
Ratio by which remaining partners are benefited on retirement of any partner is known as Gain ratio or benefit ratio.
How is NPV calculated in PMP?
Generally calculated using formula PV = FV / [1+i] ^n, where FV = Future value, i = rate of interest, and n = number of years (^ signifies an exponent). Net Present Value is the cumulative sum of PV. This is an example of when PMI might use a similar question setup, but change the call of the question.
Why is a cost-benefit analysis used in project management?
The Purpose of Cost-Benefit Analysis There are two main purposes in using CBA: To determine if the project business case is sound, justifiable and feasible by figuring out if its benefits outweigh costs. To offer a baseline for comparing projects by determining which project's benefits are greater than its costs.
What is cost-benefit analysis example?
For example: Build a new product will cost 100,000 with expected sales of 100,000 per unit (unit price = 2). The sales of benefits therefore are 200,000. The simple calculation for CBA for this project is 200,000 monetary benefit minus 100,000 cost equals a net benefit of 100,000.
Can benefit to cost ratio be negative?
B/C ratios may be negative; however. A negative value indicates that the project is expected to generate greater disbenefits than actual benefits; meaning that on a net basis, the project would make conditions worse rather than better.)
What does a cost-benefit analysis indicate?
A cost-benefit analysis is the process of comparing the projected or estimated costs and benefits (or opportunities) associated with a project decision to determine whether it makes sense from a business perspective.
How do I calculate BCR in Excel?
The formula for benefit-cost ratio is: Benefit-Cost Ratio = ∑ Present Value of Future Benefits / ∑ Present Value of Future Costs.
What is benefit cost ratio?
The benefit cost ratio (or benefit-to-cost ratio) compares the present value of all benefits with that of the cost and investments of a project or investment. These benefits and costs are treated as monetary cash flows or their equivalents, e.g. for non-monetary benefits or company-internal costs.
What are the components of benefit cost ratio?
The Formula for calculating the benefit cost ratio consists of three components: The present value of all benefits, the present value of all costs and, finally, the division of these present values. We will discuss them in this subsection.
How Is the Benefit Cost Ratio Calculated?
The benefit cost ratio is calculated by dividing the present value of benefits by that of costs and investments.
What is the present value of benefits of a series of cash flows?
The present value of benefits of a series of cash flows equals the likewise discounted costs. This situation is obviously more preferable than options with a BCR lower than 1. However, if there are alternatives with a benefit-to-cost ratio exceeding 1, they are likely to be favored.
How to calculate present value of benefits?
The present value of benefits is calculated as the sum of discounted benefits. To determine this sum, all inflows in a period (i.e. cash flows considered as benefits) need to be discounted with 1 plus the discount rate i to the power of the period. This calculation needs to be performed for every period.
What is BCR in project management?
In project management, the benefit cost ratio can support the cost-benefit analysis of a business case.
Why is the ratio important?
The ratio helps interpret the ‘inherent riskiness’ of forecasted net cash flows and profitability, e.g. in cases where small profit margins are prone to a higher risk while large margins offer a buffer for price adjustments
Why is benefit cost ratio important?
Conclusion. A benefit-cost ratio helps project managers address whether or not a project should be pursued, or in some cases, which project presents the best option. It is a valuable and necessary tool for cost-benefit analysis and project selection.
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost-benefit analysis is a systemic approach to evaluating and comparing the costs and benefits of different project proposals. A benefit-cost ratio is a tool you can use when performing a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate what projects to undertake or what value a project can bring.
What is the BCR in project management?
The benefit-cost ratio (BCR) helps summarize the relationship between a project’s costs and benefits by expressing the ratio as a decimal. If the ratio is greater than 1.0, the benefits outweigh the costs. If the ratio is less than 1.0, the costs outweigh the benefits.
What is the BCR of a project?
An easy way to do it is to divide: Project A has a BCR of 5:2, and 5 / 2 is 2.5 . Do that with all four projects, and you find that project C has the highest BCR. A. BCR stands for benefit-cost ratio and it measures the benefits (revenue) against the cost of implementing the project.
What is the importance of staying aware of opportunity costs?
As an active PMP credential holder, staying aware of opportunity costs can help you counter the limitations of relative profitability.
Which project has the highest BCR?
An easy way to do it is to divide: Project A has a BCR of 5:2, and 5 / 2 is 2.5. Do that with all four projects, and you find that project C has the highest BCR.
What is the next best alternative to Project 3?
If you choose Project 3, the next best alternative is Project 2.
What is benefit cost ratio?
The benefit-cost ratio is used to determine the viability of cash flows from an asset or project.
What is BCR in cost analysis?
The benefit-cost ratio (BCR) is a profitability indicator used in cost-benefit analysis to determine the viability of cash flows generated from an asset or project. The BCR compares the present value of all benefits generated from a project/asset to the present value of all costs. A BCR exceeding one indicates that the asset/project is expected to generate incremental value.
What is discount rate?
The discount rate used refers to the cost of capital, which can be the company’s required rate of return. Required Rate of Return The required rate of return (hurdle rate) is the minimum return that an investor is expecting to receive for their investment. Essentially, the required rate of return is the minimum acceptable compensation for ...
Is benefit cost ratio a determinant of feasibility?
Although the benefit-cost ratio is a simple tool to gauge the attractiveness of a project or asset, it should not be the sole determinant of a project’s feasibility. Other ratios and further analysis are recommended.
Is the ratio easy to calculate?
If the inputs are known (cash flows, discount rate), the ratio is relatively easy to calculate.
What is Benefit-Cost Ratio?
The benefit-Cost ratio is what you gain from the project against the project cost. This financial technique allows you to assess the project’s viability based on the intended expenditure and the benefits you expect to get back.
Why is benefit cost ratio important?
A benefit-cost ratio will help you know the overall value of money for the project you are about to undertake. This is important and makes the BRC a profitability index for you. You will therefore know how to budget and plan your finances appropriately.
Why do we need to calculate BCR?
As mentioned before, BCR helps you to plan your finances and ensure that you get the most benefit from your project. Therefore, we recommend that you calculate the benefit-cost ratio of your project before commencing. It would be best if you did it in the project’s planning stage to give you the go-ahead.
What happens if the benefits outweigh the costs?
Keep in mind that this is a numerical equation. If the benefits outweigh the costs, then that project is a wise investment, and you can proceed. However, if the costs outweigh the benefits, it would be best to take a step back, reconsider and make necessary adjustments.
How to come up with a cost-benefit ratio?
To come up with an accurate benefit—cost ratio that will help you make the best decisions, you need to use cost-benefit analysis. This process allows you to arrive at the correct ratio by weighing the sum of the benefits you will get from a project versus the costs you incur. It is not as complex as it sounds, and you will soon realize that you can execute it in an instant.
Why is it important to have a project manager?
Project managers play an important role in the successful execution of projects. They do not have fixed tasks, given that projects are structured differently. However, all these roles are aimed...
Can you cook up a benefit cost ratio?
You cannot just cook up a benefit-cost ratio. You need to have a comprehensive list that accounts for all specifics of the project. For the costs, you will be able to pinpoint what exactly you are spending. Therefore, this tool allows you to account for all money flowing in and out. Even though it may be challenging to do this for unpredictable costs or emergencies, you will always find that there will be unforeseen benefits at the end of the project. Therefore, they balance out.
What is BCR in cost benefit analysis?
In cost benefit analyses, the BCR is one of the common methods to assess and compare the future profitability of a series of cash flows (see PMI PMBOK®, 6 th ed., part 1, ch. 1.2.6.4, p. 34). It is often used to supplement comparisons based on the net present value. In these cases, the BCR indicates the relation of costs and benefits. It is interpreted as follows:
What is discount rate?
The discount rate is used for discounting the cash flows. Set a rate that is consistent with the requirements of your organization, e.g. capital cost or internal return target, or a risk-adjusted market interest rate. The calculator will apply this discount rate to all cash flows in order to discount them.
What is benefit cost ratio?
Benefit-Cost ratio is the ratio of the benefits of a project compared to the costs calculated in terms of Present Value (PV).
Do you need to calculate BCR in PMP?
Ideally speaking, you will not be required to calculate BCR in the PMP exam. Expect the value of BCR to be given in the question where you can select the highest as being most favorable.
What does it mean when the benefit cost ratio is more than one?
Benefit cost ratio of more than one indicates that the present value of the benefits is better than the present value of the costs. If the benefit cost ratio is significantly greater than one, then you can consider taking up the project.
How to calculate benefit cost ratio?
You calculate the benefit cost ratio by dividing the total discounted value of the benefits by the total discounted value of the costs. To calculate the discounted value of each, you use the present value formula for the each. To know more about calculating present value, refer Economic Model for Project Selection – Present Value.
What is benefit cost ratio?
The benefit cost ratio is yet another economic model of project selection. In this economic model, you calculate the ratio between the cost of the project and benefits form the project. The benefits include all forms of revenue you generate from the project and not just the profits. A benefit cost ratio greater than one indicates that projects generates more benefits than the cost incurred.
Why use the benefit cost ratio method?
You use the benefit cost ratio method to identify relationship between possible benefits and costs of the project. You use this method to measure qualitative as well as the quantitative factors. This is so, because at times you cannot exclusively measure benefits and costs in financial terms.
Why do project managers sacrifice quality?
In order to force a worthwhile project to cross the extra hurdle, project managers might also need to sacrifice quality for short-term gains (for example, by using cheaper, lower-quality equipment) and possibly even inadvertently engineer a situation where the project becomes a financial burden in the long run.
Why is project financing more expensive than conventional financing?
As a result, project financing is more expensive than conventional financing because of the time managers and technical experts spend evaluating and monitoring the project, the charges made by lenders for assuming additional risks, and insurance coverage.
What is cost of capital?
This cost of capital is equivalent to the return that financiers require for investment in the business. It includes three factors: a return for deferred consumption, an allowance for inflation, and a return for the systematic risk or variability inherent with the proposal. 3 Where BCR uses the company cost of capital as the relevant discount factor, and has included contingencies in the cash outflows, then the financial penalties of risk are overstated.
How is uncertainty in project management managed?
Uncertainty in the project management world is managed through risk identification, risk quantification, and risk response development . The latter is concerned with avoidance, mitigation and/or acceptance of the risk consequences. With all responses, a contingency value should be estimated and included in the planned cash outflows. Given that the risk responses are identified, and valued in the cash flows, care must be exercised to ensure that the discount factor reflects interest forgone rather than the business risk already included in the cash flow estimates.
Why are project managers short timetables?
The short timetables for IT projects also cause the project manager to become a negotiator for resources —rather than an owner, as in a functional organization. This results in short-term teams, which are built to achieve a task and then returned to their functional home base—be it the IT department, the customer, or the process environments. Cost allocation for short-term, often part-time, shared resources is a highly complex and inexact area of management accounting. The fixed-cost nature of much of the resource cost means that the project charges often reflect an organization's allocation policies rather than a true measure of resource consumption or opportunity cost.
How do financiers manage project risk?
A common method financiers use to manage their exposure to project risk is to fund a project portfolio. Ideally, the projects in the portfolio should be independent. If they are dependent on each other, risk increases, because when one fails, the others are at more risk of failure.
Should a project be ranked by absolute size?
Given that absolute size matters, and projects with a BCR of 1 or more meet the minimum required rate of return, profitable projects should be ranked by absolute size. To do otherwise could mean rejecting the projects providing the greatest increase in wealth in favor of those that seem to have the greatest rate of return. Most business managers and shareholders would not regard such a practice as good business decision-making.
What Is Cost-Benefit Analysis?
According to the official definition, cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a business process that adds up all the benefits of an initiative (i.e. a project) and then subtracts the associated costs.
What is the most popular method for estimating project time and cost?
One of the most popular techniques for estimating project time and cost is certainly the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
What is the best way to evaluate feasibility of a project?
And as an unbiased method of assessing benefits, costs, and profits, CBA is an excellent way to evaluate the feasibility of your project. When your project is objectively proven as feasible and profitable, you will: Get stakeholder support. Attain the green light from top management.
When was cost benefit analysis invented?
Cost Benefit Analysis dates back to the 18th century , when a French engineer and economist by the name of Jules Dupuit decided to evaluate the feasibility of a construction project by taking a look at how much people were willing to pay for it.
Should you consider long term costs?
You should consider long-term costs, as well, not just immediate costs. For example, if you’re evaluating the feasibility of migrating the entire company to new software, you have to factor in the software’s costs in the long-term, too. Perhaps even training, if necessary.
Is discount rate analysis good?
Similarly, if your discount rate analysis shows that the interest for your project’s product will grow in time, then it’s still beneficial – even if the payback period is longer.
Is guesswork a project management method?
You’ll have to constantly prove that you’re minimizing costs and maximizing benefits. It’s a lot of stress. And guesswork isn’t a project management method. CBA is.

How The Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR) Works
- Benefit-cost ratios (BCRs) are most often used in capital budgetingto analyze the overall value for money of undertaking a new project. However, the cost-benefit analyses for large projects can be hard to get right, because there are so many assumptions and uncertainties that are hard to qua…
What Does The BCR Tell You?
- If a project has a BCR that is greater than 1.0, the project is expected to deliver a positive net present value (NPV) and will have an internal rate of return (IRR) above the discount rate used in the DCF calculations. This suggests that the NPV of the project’s cash flows outweighs the NPV of the costs, and the project should be considered. If the BCR is equal to 1.0, the ratio indicates t…
Example of How to Use The BCR
- As an example, assume company ABC wishes to assess the profitability of a project that involves renovating an apartment building over the next year. The company decides to lease the equipment needed for the project for $50,000 rather than purchasing it. The inflation rate is 2%, and the renovations are expected to increase the company's annual profit by $100,000 for the next three …
Limitations of The BCR
- The primary limitation of the BCR is that it reduces a project to a simple number when the success or failure of an investment or expansion relies on many factors and can be undermined by unforeseen events. Simply following a rule that above 1.0 means success and below 1.0 spells failure is misleading and can provide a false sense of comfort with a project. The BCR must be u…
Definition and Meaning of Benefit Cost Ratio
How Is The Benefit Cost Ratio calculated?
- The BCR Formula
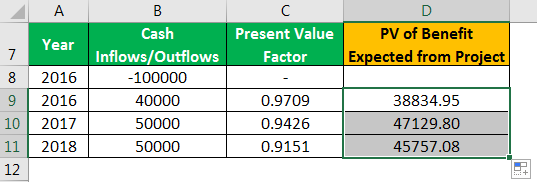
The benefit cost ratio is calculated bydividing the present value of benefits by that of costs and investments. This is the consolidated formula (source): where: BCR = Benefit Cost Ratio PV = Present Value CF = Cash Flow of a period (classified as benefit and cost, respectively) i = Discou… - Components of the BCR Formula
The Formula for calculating the benefitcost ratio consists of three components: The present value of all benefits, thepresent value of all costs and, finally, the division of these present values.We will discuss them in this subsection.
Example
- A project manager is performing the cost-benefitanalysis of 3 different software options. The company expects a return rate of12% which is reflected in a corresponding discount rate.
Conclusion
- The benefit cost ratio is a common indicator of the profitability of a potential investment or project. While it does not cover all aspects of a cost benefit analysis, it indicates whether an option is beneficial. As the BCR compares discounted benefits with discounted costs, it offers a good indication of how big a ‘buffer’ between benefits and costs is. However, like all other indica…
Formula For The Benefit-Cost Ratio
Example of The Benefit-Cost Ratio
Interpreting The Benefit-Cost Ratio
Advantages of The Benefit-Cost Ratio
- Key advantages of the benefit-cost ratio include: 1. It is a useful starting point in determining a project’s feasibility and whether it can generate incremental value. 2. If the inputs are known (cash flows, discount rate), the ratio is relatively easy to calculate. 3. The ratio considers the time value of moneythrough the discount rate. 4. The ra...
Limitations of The Benefit-Cost Ratio
Final Thoughts
More Resources