What are the negative side effects of fluoride?
This could be considered one of the most overlooked dangers of fluoride. Studies have shown that fluoride can adversely affect your blood glucose and insulin levels. Evidence shows that those with higher levels of fluoride in their body had higher glucose levels in the blood and also diminished levels of insulin.
What are the advantages of fluoride?
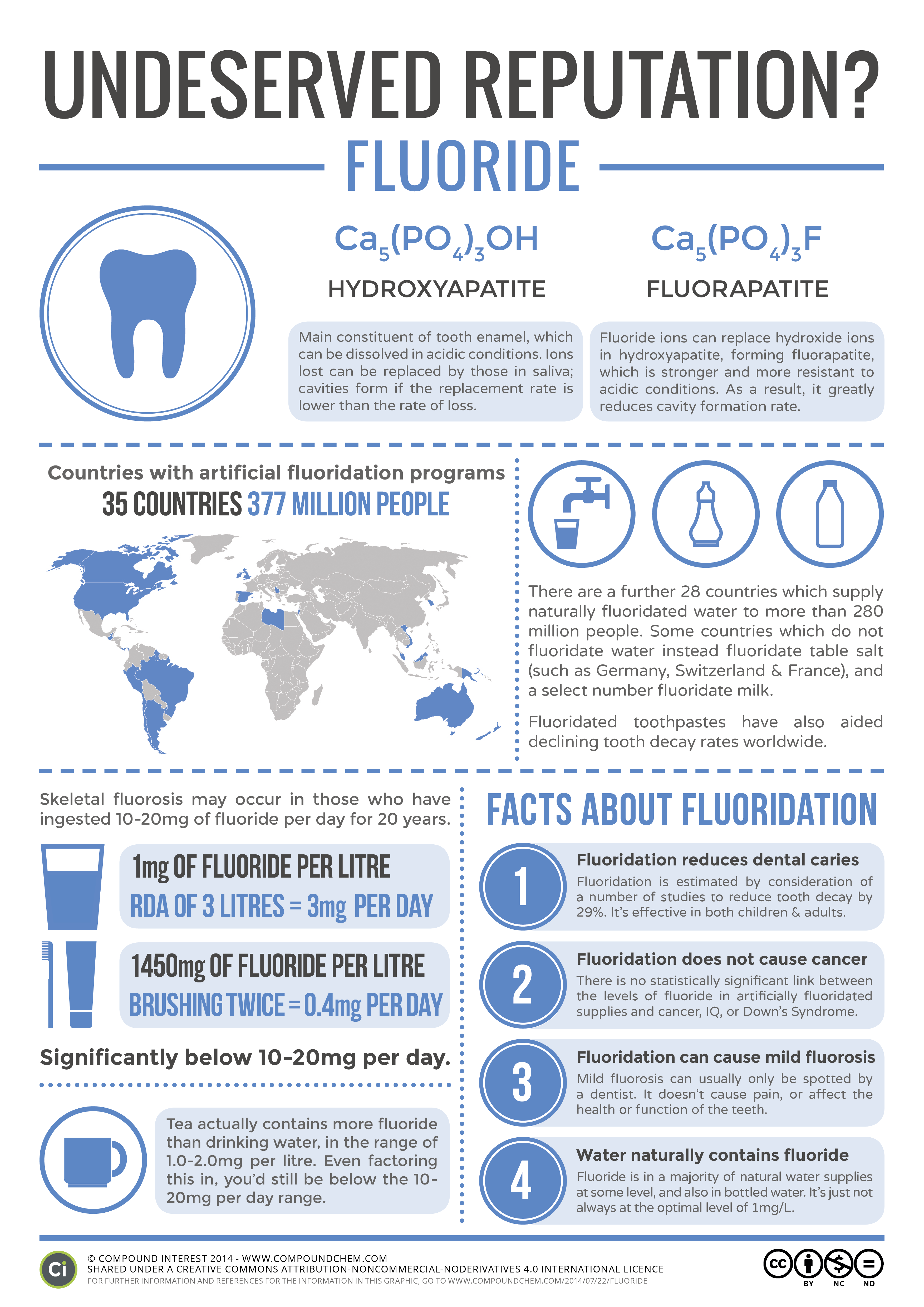
Typically, fluoride is used in the prevention of dental caries, but due to the decreased acceptance among the public and the risk of fluorosis in children, there is the need for effective alternatives. Hydroxyapatite is the main mineral of human tooth enamel and can be used in toothpastes as a biomimetic active ingredient.
Does fluoride actually help teeth?
Fluoride supports healthy tooth enamel and fights the bacteria that harm teeth and gums. Tooth enamel is the outer protective layer of each tooth. Fluoride is especially helpful if you’re at high risk of developing dental caries, or cavities.
What effect does fluoride have on teeth?
Through a chemical process, a mineral compound known as fluorapatite forms, which is especially resistant to acids. In simple terms, fluoride can help make teeth stronger, allowing them to fight off the effects of harmful bacteria that can cause cavities.
See more

What are the health benefits of fluoride?
What are the benefits of fluoride?rebuild (remineralize) weakened tooth enamel.slow down the loss of minerals from tooth enamel.reverse early signs of tooth decay.prevent the growth of harmful oral bacteria.
What does fluoride cure?
Fluoride helps prevent tooth decay by making the tooth more resistant to acid attacks from plaque bacteria and sugars in the mouth. It also reverses early decay.
Is the fluoride treatment worth it?
Yes! Not only does fluoride prevent decay, it can also reduce root hypersensitivity such as cold sensitivity and sensitivity during dental cleanings, which can be common with gum recession.
What are the effects of fluoride on your body?
Fluoride not only affects bone and teeth, but it also impacts young children in the development of the brain. Exposure to fluoride before birth could lead to poorer cognitive outcomes in the future. Higher levels of fluoride lead to low scores in IQ tests.
Can I drink water after fluoride treatment?
In general, patients are advised to wait 30 minutes after a fluoride treatment before eating or drinking. This 30-minutes allows time for the fluoride treatment to seal to the teeth.
Does fluoride whiten teeth?
Fluoride is a safe, effective way to protect your teeth from advancing tooth decay, cavities, and acts as a whitener.
Does fluoride darken teeth?
Excessive fluoride: In small doses, fluoride is an important tooth protector, but in high doses, it can cause your teeth to discolor. Elevated exposure may come from high fluoride content in the local water supply or excessive use of fluoride toothpaste, rinses, and supplements.
How long does fluoride last on teeth?
The fluoride treatment comes mostly in the form of varnish that is applied to the teeth and sticks to the teeth for a period of four to six hours before been washed away by brushing. However, during this time, the fluoride will have been absorbed into the teeth enamel and offer permanent protection for the meantime.
How often should you get fluoride?
Fluoride treatments are important for adults as well. They are an effective way to prevent cavities and other oral health issues, especially as teeth naturally weaken over time. Adults should receive 2–4 fluoride treatments per year, depending on their overall oral health.
Is fluoride in drinking water harmful?
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set a maximum amount of fluoride allowable in drinking water of 4.0 mg/L. Long-term exposure to levels higher than this can cause a condition called skeletal fluorosis, in which fluoride builds up in the bones.
How much fluoride can you consume?
How much fluoride do I need?Life StageRecommended AmountAdult men 19+ years4 mgAdult women 19+ years3 mgPregnant teens and women3 mgBreastfeeding teens and women3 mg6 more rows•Mar 22, 2021
Does fluoride cause thyroid problems?
Background: Fluoride exposure has the potential to disrupt thyroid functioning, though adequate iodine intake may mitigate this effect. This is the first population-based study to examine the impact of chronic low-level fluoride exposure on thyroid function, while considering iodine status.
What are the side effects of fluoride?
There have long been concerns that the side effects of chronic fluoride exposure include the possibility of fluoride-induced thyroid disease, learning disabilities, autism, blood disorders, and osteoporosis. These concerns, however, have not been validated by scientific studies.
Why is fluoride added to toothpaste?
Fluoride is added to public supplies of drinking water as well as to toothpaste and mouthwash because of its capacity for protecting against tooth decay. Tooth decay is also described as dental caries or cavities. Fluoride supplementation has been found to prevent the process of tooth decay in infants, children, and adults.
What is the recommended fluoride concentration?
Updated recommendations from the U.S. Public Health Service now call for a fluoride concentration of 0.7 milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the public water supply , which is a change from the previously recommended concentration of 0.7 to 1.2 mg/L.
How to avoid fluorosis?
To avoid fluorosis, do not expose your teeth to excess fluoride, either with supplements or through excessive exposure to toothpaste or mouthwash.
What foods contain fluoride?
In addition to supplemented sources of fluoride, the mineral is also found in food. Foods that contain fluoride include seafood, raisins, and potatoes. It is also present in drinks such as tea, wine, and grape juice.
Can fluoride affect bones?
Chronically high levels of fluoride intake can affect teeth and bones, while acute ingestion of large amounts of fluoride can cause more dangerous side effects, and may even be life-threatening.
Is fluoride a trace element?
In terms of human health and nutrition, fluoride is a trace element, which comprises a relatively small percentage of the body’s composition . It is believed that fluoride, while beneficial for improving community health and quality of life, may not be necessary for survival.
Why is fluoride important for teeth?
The largest health benefit of fluoride is its ability to protect our teeth and fight the key cause that leads to tooth decay and cavity formation. This has been proven through research conducted by several credible health organizations and institutions. Fluorides form an active component of teeth enamel, especially during teeth formation, making it impermeable and resistant to attack by harmful acids that form in the mouth from the foods we eat. Due to this, the bacteria that survive on the leftover food particles in the mouth (between the teeth) are not allowed to flourish. The harmful acids that damage tooth enamel are formed when oral bacteria digest the food particles lodged in our mouth.
Where do we get fluoride?
We get most of the fluoride from the foodand water that we consume. Pickles, cucumber, dill herb, unsweetened juice of grapes, orange, apple, and grapefruit, vegetables, such as spinach, tomato, asparagus, beans, and peas, and seedless raisins are some of the foods that are rich in dietary fluorides.
Is fluoride a cost effective solution?
Fluoridation of the water supply is a regular and cost-effective practice in many countries; though, currently the practice of adding fluoride in water is being questioned. Also, fluoride forms an active ingredient of toothpastes and mouthwashes (as sodium fluoride), the use of which is strongly recommended by dentists.
Is fluoride a mineral?
Fluoride is an important and essential mineral that forms a main constituent of the bones and teeth. Learn about the health benefits of fluoride. Please Remove Adblock. Adverts are the main source of Revenue for DoveMed. Please remove adblock to help us create the best medical content found on the Internet.
Is fluoride a component of enamel?
This has been proven through research conducted by several credible health organizations and institutions. Fluorides form an active component of teeth enamel, especially during teeth formation, making it impermeable and resistant to attack by harmful acids that form in the mouth from the foods we eat.
Can fluoride cause mottling of teeth?
In such cases, they may have higher than required concentrations of fluoride, which may result in the mottling of teeth, leading to a condition called dental fluor osis (a tooth enamel defect caused by fluor ide).
Is fluoride good for bone loss?
Fluorides are also helpful in treating conditions that cause bone loss, particularly in women after menopause. However, significant reports of detrimental health effects caused by fluoride overexposureis also reported by several major global scientific and research organizations.
Why is fluoride used in dental care?
According to the American Dental Association (ADA), the increased use of fluoride is one of the main reasons for that happening. This mineral fights against the things that attack the enamel on your teeth and cause tooth decay, like sugar and plaque.
What is the purpose of fluoride in teeth?
In your teeth, Fluoride is one of the several minerals that make up the outer enamel layer, helping to keep your teeth strong and protect them from cavities and decay. So, isolated forms of fluoride can be used to further strengthen the enamel and supplement what may have been lost from the teeth over time (demineralization).
How does fluoride help teeth?
By working fluoride into your dental hygiene routine, you’ll be able to keep your teeth and gums much healthier and reduce the number of dentist visits you’ll need. This will also reduce the extent of cleanings and other dental treatments you’ll need. For example, usually, people who utilize fluoride rarely have to have intensive deep teeth cleanings done. Less dental visits will also mean less money spent on treatments.
Why is it important to maintain a good oral hygiene routine?
One powerful weapon in the fight against bacteria and plaque is fluoride.
Does fluoride help with gums?
Fluoride, which can come in many forms of oral hygiene products, will help keep your teeth and gums healthy and protected. Thus, helping you avoid unnecessary trips to the dentist’s office for problems that can be prevented.
Can you get fluoride toothpaste over the counter?
Over-the-counter dental products with fluoride: You can also get over-the-counter fluoride mouthwashes and toothpaste at many of your local stores. Remember, these products will not have as high a concentration of fluoride as the prescription products from your dentist. For over-the-counter fluoride products, make sure to check for the American Dental Association’s (ADA) seal of approval. This indicates that the product has met the ADA’s criteria for effectiveness and safety and has been carefully examined.
Does fluoride help with tooth decay?
Not only does fluoride help remineralize your teeth but it inhibits further demineralization and decalcification that lead to tooth decay. It builds up a stronger outer surface on your teeth, which prevents the occurrence of cavities and can stop early decay from penetrating deeper into the tooth. As Fluoride works to strengthen your teeth, it can even reverse the early stages of tooth decay.
What are the two conditions in which fluoride might play a role?
Fluoride and Health. This section focuses on two conditions in which fluoride might play a role: dental caries and bone fractures. Dental cari es. Dental caries occurs when cariogenic bacteria in the mouth ferment foods and produce acids that dissolve tooth mineral [ 22 ].
How much fluoride is retained in the body?
In adults, about 50% of absorbed fluoride is retained, and bones and teeth store about 99% of fluoride in the body [ 1, 3 ]. The other 50% is excreted in urine [ 1 ]. In young children, up to 80% of absorbed fluoride is retained because more is taken up by bones and teeth than in adults [ 1 ].
How much fluoride is in toothpaste?
Most toothpaste sold in the United States contains fluoride in the form of sodium fluoride or monofluorophosphate, most commonly at a level of 1,000 to 1,100 mg/L (about 1.3 mg in a quarter teaspoon, a typical amount of toothpaste used for one brushing) [ 3 ].
How much fluoride is in milk?
Fluoride concentrations in cow’s milk are also very low, ranging from 0.007 to 0.086 mg/L [ 3 ]. Fluoride levels in infant formulas in the United States vary, depending on the type of formula and the fluoride content of the water used to prepare the formula [ 3 ].
What is the ionic form of fluoride?
Fluoride is the ionic form of the element fluorine, and it inhibits or reverses the initiation and progression of dental caries (tooth decay) and stimulates new bone formation [ 1 ]. Soil, water, plants, and foods contain trace amounts of fluoride.
Why are fortified foods important?
The federal government’s 2020–2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans notes that “Because foods provide an array of nutrients and other components that have benefits for health, nutritional needs should be met primarily through foods. … In some cases, fortified foods and dietary supplements are useful when it is not possible otherwise to meet needs for one or more nutrients (e.g., during specific life stages such as pregnancy).”
Where does fluoride come from?
Most of the fluoride that people consume comes from fluoridated water, foods and beverages prepared with fluoridated water, and toothpaste and other dental products containing fluoride [ 2, 3 ]. Approximately 80% or more of orally ingested fluoride is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract [ 1 ]. In adults, about 50% of absorbed fluoride is ...
What Does Fluoride Do Once In The Body?
Adding fluoride to water does not affect the appearance , taste, or smell. Making it a hard thing to blame and pinpoint as the cause of anything bad. However, it’s detrimental presence in the human body is a lot more obvious.
Why is fluoride added to water?
With water fluoridation, the one and only reason fluoride is added to water is the claim it helps prevent dental cavities. However, in minutes, you’ll learn that this lone pro to water fluoridation is at best, partially true. But the cons we have listed further down, pack a much stronger punch.
Where Does Fluoride Come From?
You won’t see this subtitle in many articles about fluoride, especially on pro-fluoride websites.
What Are The Main Sources Of Fluoride?
As you can tell, fluoride has come a long way from being an unwanted industrial byproduct.
Does My Water Have Fluoride?
For people that live in the United States of America, the CDC has an excellent tool that allows you to check your local water supply. However, some states provide their information, while others don’t. If they do, you’ll be able to see if your city fluoridates its water and how much they add.
What is sodium fluorosilicate?
Sodium Fluorosilicate (Na2SiF6): the sodium salt of fluorosilicic acid. It comes in powder or crystal form. It is also known as sodium silicofluoride⁶. In addition, the fluoride added to drinking water is not pharmaceutically graded.
How much fluoride is excreted daily?
The worst part is that your body only excretes 50% of the fluoride you ingest daily (dependent on other factors, usually less). Which means 50% sticks around, everyday. Building up in your body as a cumulative toxin²⁹. Once circulating inside your body, uptake by bone removes excess fluoride.
What are the downsides of fluoride?
Potential downsides of fluoride include fluorosis, an increased risk of osteosarcoma, and impaired brain development in infants and children.
Why is fluoride added to toothpaste?
Fluoride is a chemical commonly added to toothpaste. It has a unique ability to prevent tooth decay. For this reason, fluoride has been widely added to water supplies to improve dental health. However, many people are concerned about the potential harm from excess intake.
Why is skeletal fluorosis not an issue?
Skeletal fluorosis only happens when people are exposed to very large amounts of fluoride for long periods of time. It’s typically not an issue in countries with fluoridated water, as the fluoride content of water is tightly regulated in these countries.
How much fluoride is in water?
In the United States, fluoridated water should ideally contain approximately 0.7 mg per liter. Some countries may fluoridate salt or milk as well ( 2, 4, 5 ).
What is the term for a tooth that is affected by fluoride?
Fluorosis occurs after prolonged exposure to excessive amounts of fluoride. There are two types: dental (affecting the teeth) and skeletal (affecting the bones).
What is the ionized form of fluorine?
Fluoride is the ionized form of the element fluorine. It’s widely distributed in nature and supports the mineralization of bones and teeth. Fluoride may also help prevent cavities.
When did fluoride start in water?
Water fluoridation started in the US in the 1940s, and about 70% of the US population currently receives fluoridated water. Fluoridation is rare in Europe. Many countries have decided to stop adding fluoride to public drinking water due to safety and efficacy concerns ( 36. Trusted Source.
What is the purpose of fluoride?
Fluoride is a natural mineral that prevents cavities. It restores minerals to tooth enamel and prevents harmful bacteria from building up in the mouth. Overdosing on fluoride can cause negative complications.
Why is fluoride important for teeth?
Tooth enamel is the outer protective layer of each tooth. Fluoride is especially helpful if you’re at high risk of developing dental caries, or cavities.
How does fluoride work?
Fluoride works by restoring minerals to tooth surfaces where bacteria may have eroded the enamel. It can also inhibit the growth of harmful oral bacteria and further prevent cavities.
How old do you have to be to use fluoride toothpaste?
Fluoride toothpaste the size of a pea is recommended for children ages 3 to 6 years old. You should watch children to ensure they spit toothpaste out while brushing.
How much does insurance cover for fluoride?
Insurance usually covers fluoride treatments at the dentist for children. Adults, however, may pay $10 to $30 out of pocket, or more. Always ask your dentist about costs before treatment.
What is the best source of fluoride?
dry mouth, or decreased saliva. weak enamel. Common sources of dietary fluoride include: tea. water. food cooked in water. fish eaten with their bones. infant formula. Optimal fluoride intake comes from food, water, and supplements.
Is fluoride good for children?
Fluoride benefits both children and adults. The earlier children are exposed to fluoride, the less likely they are to develop cavities. A large study found that children and adolescents who received fluoride treatments for one year were 43 percent. less likely to have tooth decay and cavities.
What is fluoride in dentistry?
INTRODUCTION. Fluoride is the ionic form of fluorine, the thirteenth most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is released into the environment naturally in both water and air. Its concentration in water is variable (1).
How does fluoride help with dental caries?
Fluoride works to control early dental caries in several ways. Due to its anticariogenic and antimicrobial properties, the fluoride ion (F−) has been widely used in the treatment of dental caries. The antibacterial action of fluoride is due to the acidification of the bacterial cytoplasm through the formation of hydrogen ion (H+) and F−from hydrogen fluoride and the disruption of the bacterial metabolism by inhibiting vital bacterial enzymes such as proton releasing adenosine triphosphatase and enolase.
How much fluoride reduces caries?
The degree of caries reduction depends on the concentration of fluoride in salt. A domestic salt with 200 mg of fluoride/kg has a lower caries reduction than that with 250 mg of fluoride/kg. The best results are observed when domestic salt contains 350 mg of fluoride/kg.
What is the minimum amount of fluoride in saliva?
In order to achieve a meaningful effect on caries control, the minimal acceptable level of fluoride is 200 mg/kg salt.
How much fluoride should a child drink a day?
The daily dosage of fluoride per child varies from 0.50 mg to 0.85 mg (14). Children are advised to drink around 200 mL of fluoridated milk per day for about 200 days per year (22). Given that the dose is constant and related to age and background fluoride exposure, the risk of adverse effects is very low (22). However, milk fluoridation is a less efficient method for delivery of fluoride when compared to water fluoridation. The fluoride added to milk forms insoluble complexes that make fluoride absorption difficult (14).
What is the source of fluoride?
Water is the major dietary source of fluoride. The variability in water content explains much of the variability in total fluoride intake. Other important sources of fluoride are tea, seafood that contains edible bones or shells, medicinal supplements, and fluoridated toothpastes (2).
When was fluoride added to table salt?
In 1980~82, adding fluoride to table salt was authorized for human consumption (12). Fluoridated salt reaches the consumer through several channels including domestic salt, meals at schools, large kitchens and in bread, and exerts both systemic and topical effects (14). Effectiveness in caries prevention.
