
Benefit Principle - Definition
- Benefit Principle Definition. In taxation, the benefit principle is a principle based on the notion that those who benefit more from government expenditure or spending should pay more taxes that ...
- A Little More on What is the Benefit Principle. ...
- References for Benefit Principle
- Academic Research on Benefit Principle. ...
What are the benefits principle?
- A person is at risk of a substantial and preventable harm or loss of a benefit.
- The paternalistic action has a strong likelihood of preventing the harm or obtaining the benefit.
- The projected benefits of the paternalistic action outweigh its risks.
What are the basic principles of taxation?
principles of taxation
- PRINCIPLES OF TAXATION
- TAXATION- Is the inherent power of the sovereign, exercised through the legislature, to impose burdens upon subjects and objects within its jurisdiction for the purpose of raising revenues to ...
- Essential elements of a tax 1. ...
- 5. ...
- Purposes of taxation 1. ...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of taxation?
- Direct taxes are progressive taxes. ...
- Direct taxes are easy to collect. ...
- Tax evasion is very difficult here. ...
- Direct taxes make it easier for tax authorities to predict how much revenue they will be able to make and this is very important when it comes to proper planning. ...
What is benefit principle?
Some of the key points to remember relating to this concept are:
- An individual/firm should act only if the benefits are more than the costs.
- Critics of the cost benefit principle object that people do not really compute the costs and decisions when taking a decision.
- Some costs and benefits might not be easily quantifiable. In this case, the decision taker should use estimations.
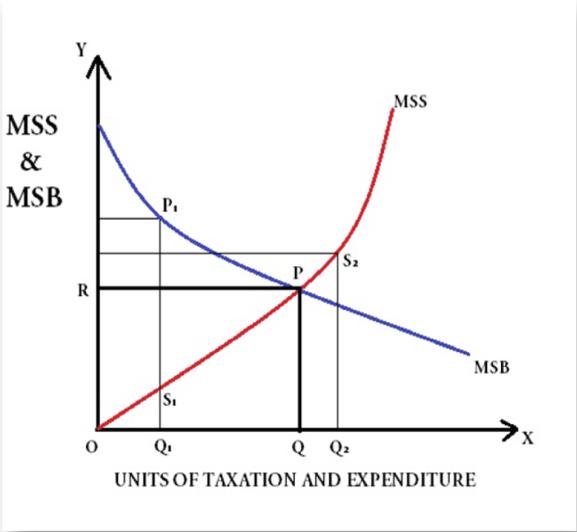
What is the benefits received principle of taxation quizlet?
What is the Benefits-Received Principle? The benefits-received principle of taxation holds that people who benefit directly from public goods should pay for them in proportion to the amount of benefits received.
What is an example of benefit principle?
It follows the same principle as the market - the individuals who receive the benefit of a good or service should pay the tax necessary to supply that good or service. For example, gasoline taxes are typically earmarked for the financing of highway construction and repairs.
What is the benefits principle used to justify?
The benefit principle is the idea that government spending should be met by the people who receive them. In other words, everyone who receives government spending, should contribute towards it. This benefit principle was the justification for Margaret Thatcher's Poll Tax.
Which of the following is an example of the benefits received tax principle?
The benefits received principle of taxation is the theory that citizens who have received advantages from the government (in the form of public goods and services) should pay for them. For example, those who use a certain road system should pay for maintaining those roads.
What are two drawbacks of the benefit principle of taxation?
Two factors: 1) cannot always measure benefits derived from government spending. 2) assumes people with higher income suffer less discomfort when paying taxes.
What are the benefits of taxes for societies and individuals?
Federal taxes are spent on programs such as social security, Medicaid and Medicare, and other safety net programs such as food assistance for low–income Americans. They also fund military, education, infrastructure, food and environmental protections, police, healthcare, science, research, and much more.
What is the benefit principle?
Under the benefit principle, taxes are seen as serving a function similar to that of prices in private transactions; that is, they help determine what activities the government will undertake and who will pay for them. If this principle could be implemented, the allocation of resources through the public sector would respond ...
Why is it so difficult to implement the benefit principle?
In fact, it is difficult to implement the benefit principle for most public services because citizens generally have no inclination to pay for a publicly provided service— such as a police department—unless they can be excluded from the benefits of the service.
What happens when tax laws change?
Frequent changes to tax laws can result in reduced compliance or in behaviour that attempts to compensate for probable future changes in the tax code —such as stockpiling liquor in advance of an increased tariff on alcoholic beverages.
What are the four requirements for the efficient administration of tax laws?
There are four general requirements for the efficient administration of tax laws: clarity, stability (or continuity), cost-effectiveness, and convenience.
Should tax policies be interfering with the market?
Thus, they feel that tax policy should generally refrain from interfering with the market’s allocation of economic resources. That is, taxation should entail a minimum of interference with individual decisions. It should not discriminate in favour of, or against, particular consumption expenditures, particular means of production, ...
Should equity and economic rationality be sacrificed for the sake of cost considerations?
Clearly, equity and economic rationality should not be sacrificed for the sake of cost considerations. The costs to be minimized include not only government expenses but also those of the taxpayer and of private fiscal agents such as employers who collect taxes for the government through the withholding procedure.
Should tax laws be changed?
Tax laws should be changed seldom, and, when changes are made, they should be carried out in the context of a general and systematic tax reform, with adequate provisions for fair and orderly transition. Frequent changes to tax laws can result in reduced compliance or in behaviour that attempts to compensate for probable future changes in the tax code—such as stockpiling liquor in advance of an increased tariff on alcoholic beverages.
What is the benefit principle?
In taxation, the benefit principle is a principle based on the notion that those who benefit more from government expenditure or spending should pay more taxes that those that do not. This principle is one that outlines what government expenditure should be tailored at and those that should pay for them.
Why is the benefit principle sometimes compared to prices paid in private transactions?
The benefit principle is sometimes compared to prices paid in private transactions because they serve similar purposes. Implementation of this principle would mean that resources allocated for public projects will be based on the response of consumers in terms of payment of taxes.
What is the importance of clarity in tax administration?
Convenience and. Clarity. Clarity in the administration of tax laws means that all tax rules and regulations must not be vague, ambiguous or obscure to taxpayers. Rather, these rules and regulations must be easily understood or comprehensible for taxpayers.
Why is tax system important?
Tax systems must ensure that taxation is cost effective. Cost effectiveness is a system of taxation is crucial to both developing and developed countries. The costs attributed to the control, collection and assessment of taxes must be effective and must also align to the goal of taxation.
Why is clarity important in tax?
Clarity will reduce the amount of errors or oppression from tax administrators who are not even clear about the rules of the tax system. However, countries have tax laws that are not understood by the public. This leads to disregard for the law and discrimination against weak, poor and uneducated citizens.
What is stability in tax laws?
Stability in tax laws means that the laws must not be changed frequently. Rather, they can be adjusted at rare occasions and in ways that will not distort or upturn the tax system. If at all changes need to be made to tax laws and regulations, they must be done within the context of systematic tax reform.
Do citizens need to pay for public services?
In a typical country arrangement, citizens do not see the need to pay for public services or projects funded by the government. Aside from the fact that the provision of social amenities is what citizens should enjoy, citizens lack the urge or natural tendencies to pay for these services.
What is the benefit principle?
The benefit principle takes a market-oriented approach to taxation. The objective is to accurately determine the optimal amount of revenue that should be spent on public goods. More equitable/fair because taxpayers, like consumers, would "pay for what they get".
Who developed the benefit approach?
In its use for assessing the efficiency of taxes and appraising fiscal policy, the benefit approach was initially developed by Knut Wicksell (1896) and Erik Lindahl (1919) , two economists of the Stockholm School. Wicksell's near-unanimity formulation of the principle was premised on a just income distribution.
What is the benefit principle?
Benefit principle. The benefit principle is the idea that government spending should be met by the people who receive them. In other words, everyone who receives government spending, should contribute towards it. This benefit principle was the justification for Margaret Thatcher’s Poll Tax.
Why is poll tax so hard to apply?
In practice the benefit principle is hard to apply because many of those in need of government benefits – the old, sick and unemployed are the least likely to be able to pay.
What are the advantages of a benefits-received system of taxation?
Advantages. By far the clearest advantage of a benefits-received system of taxation is that the choice to pay the tax and receive the service is ultimately in the consumer's hands. That means that the government has to be sure to provide a worthwhile service or it will simply go unused. The tax benefits that come with being married are ...
What are some examples of benefits received tax?
One of the best examples of a benefits-received tax is education . Kindergarten through high school is free at public schools, but what about college? Every state has public universities and colleges, yet these still require tuition payments. The institutions are officially parts of the state, after all. In fact, you can think of your tuition to a particular institution as a tax that you pay for the benefit of receiving an education.
What are the disadvantages of taxpayer support?
That idea of taxpayer support points to one of the big disadvantages of benefits-received tax systems - at some point, someone who doesn't necessarily get anything out of the benefit will often have to pay taxes for it. While it is often a miniscule amount, and often as a part of other larger duties, this still erks some people.
Is tuition a tax?
In fact, you can think of your tuition to a particular institution as a tax that you pay for the benefit of receiving an education. Here's another example. Let's say that you were going to get married. Most jurisdictions require you to pay a license fee to be married in the eyes of the law.
Is benefits received taxation in effect?
In many ways, benefits-received taxation is already in effect. However, it remains controversial in many circles today.
What is the benefit principle of taxation?
The benefit principle holds that people should be taxed in proportion to the benefits they receive from goods and services provided by the government.
What is the main objective of taxation?
The major objective of taxation is to raise revenues. But other objectives are also important in the design of a tax system. The principle of taxation can be chosen only in terms of the goals which are accepted as the appropriate objectives of the economic system.
What is the second concept of fair taxation?
If equals are to be treated equally, it logically follows that un-equals should be treated unequally. This precept is known as vertical equity. This concept has been translated into the ability to pay principle, according to which those most able to pay should pay the maximum amount of taxes. Broadly, the principle suggests that the fairest tax is one based on one’s financial ability to support governmental activities through tax payments.
What is the most important source of government revenue?
The most important source of government revenue is tax . A tax is a compulsory payment made by individuals and companies to the government on the basis of certain well-established rules or criteria such as income earned, property owned, capital gains made or expenditure incurred (money spent) on domestic and imported articles.
What are the three major principles or desirable characteristics of the tax system?
In terms of these goals, three major principles or desirable characteristics of the tax system have come to be generally accepted: 1. Economic effects: The tax structure must be established in such a way as to avoid interference with the attainment of the optimum. 2.
Why is it important to maintain non neutrality?
Sometimes it becomes essential to maintain non-neutrality for meeting certain social objectives. These objectives can be secured by providing tax incentives. This means that in some cases, it may be desirable to disturb the private market.
Which principle is similar and equally impracticable?
Similar and equally impracticable is the cost of service principle, according to which a person’s tax liability would be based on the cost of the public services which he enjoys. Economics, Principles of Taxation, Taxation.
What is the main assumption of the Benefit Theory of Taxation?
The more the benefit a citizen derives, the more taxes he should bear, is the main assumption of the theory. The Benefit Theory of Taxation justifies the payment of taxes. It also measures benefits received by the individuals in the case of certain special taxes such as petrol tax, betterment tax etc. Limitations of Benefit Theory of Taxation.
Why do the poor pay higher taxes?
if benefits accrued to an individual is the basis of taxation, the poor must pay higher taxes because in a welfare State the poor get more benefits than the rich from the expenditure of the Government.
Can you divide the benefits of national defence?
For example, it is not possible to divide the benefits of national defence, etc. (5) Fifthly. certain benefits accrue only to definite persons and in definite proportion. If this principle is followed, the whole of the benefit, they should return to the State as taxes.
What are the taxation principles?
Taxation Principles are the set of guidelines that help the lawmakers and governing bodies to formulate strategies and plan their execution to ensure devising a robust tax structure which is aimed at not only increasing revenues but also bring social and economic equality to its citizens.
Why is taxation important?
Importance. Though the taxation system at large is focused on increasing the revenue of the government, it can also be used to revive the economy. Let’s discuss this aspect in detail. Public expenditure tends to increase as the economy grows or more quantifiably as the GDP numbers grow.
How does taxation help the economy?
Public expenditure tends to increase as the economy grows or more quantifiably as the GDP numbers grow. Taxation is the only mechanism that makes sure the revenues of the lawmakers increase proportionately. This growth is indispensable as to maintain the economic growth, the government must spend on infrastructure which acts as a foundation on which economic growth survives.
What is the only mechanism that makes sure the revenues of the lawmakers increase proportionately?
Taxation is the only mechanism that makes sure the revenues of the lawmakers increase proportionately. This growth is indispensable as to maintain the economic growth, the government must spend on infrastructure which acts as a foundation on which economic growth survives.
Should there be discrimination between savings and expenditures?
There should be no discrimination between any two persons regarding their savings, expenditure, and deductions claimed but should be leviable with the same income tax. read more. . This concept is based on the assumption that individuals at similar levels should have the same tax obligation.
Can there be a difference between tax liability and tax payable?
There can be a difference in tax liability and tax payable as common people might not be able to take advantage of various tax-saving opportunities. They might have to reach out to tax experts to seek guidance, which would have an economic cost of its own. These scenarios are very common in developing economies.
Is tax structure fair?
To do so, it is imperative that the tax structure is fair and is not harsh on any particular section of society or individuals. It should be easily understandable and devoid of any ambiguities. To ensure all these conditions are met, there are certain guidelines that are commonly known as taxation principles.

Summary
Overview
- Economists maintain that the efficiency of a tax system depends on the nature of market economy operating at a particular time. Economic decisions relating to production, consumption and allocation of resources is done by the market or by market factors and this should not be interfered with by the tax system. Hence, economists maintain that taxati...
Examples
Passages
The benefit principle is a concept in the theory of taxation from public finance. It bases taxes to pay for public-goods expenditures on a politically-revealed willingness to pay for benefits received. The principle is sometimes likened to the function of prices in allocating private goods. In its use for assessing the efficiency of taxes and appraising fiscal policy, the benefit approach was initially developed by Knut Wicksell (1896) and Erik Lindahl (1919), two economists of the Stockholm School. …
Criticism
Thus, considered in themselves, in their own nature, in their normal state, and apart from all abuses, public services are, like private services, purely and simply acts of exchange. - Frédéric Bastiat
The benefit principle takes a market-oriented approach to taxation. The objective is to accurately determine the optimal amount of revenue that should be spent on public goods.
See also
Here are a few of the public services that are currently funded, in some part, on the basis of the benefit principle...
• Public college tuition (only paid by the people who attend public colleges)
• National park admission fees (only paid by the people who visit public parks)
Further reading
Until people are made to bear the full costs of their decisions, those decisions are unlikely to be socially sound, in this as in other areas of public policy. - Bird, Richard M. (1976). Charging for Public Services: A New Look at an Old Idea
The doctrine of consumer sovereignty is applied to the provision of social goods in so far as the consumer buys national defence, police service, fire protection and electricity or water supply fr…