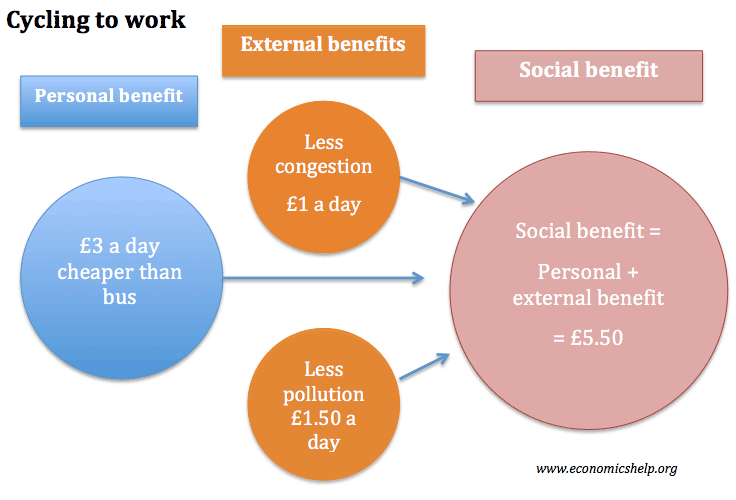
Key Takeaways
- Marginal benefit is the maximum amount a consumer will pay for one additional good or service.
- Marginal benefit generally decreases as consumption increases.
- Marginal cost of production is the change in cost for making one additional good or incremental unit of service.
What is the formula for calculating marginal cost?
where:
- MC – marginal cost;
- ΔTC – change in the total cost;
- ΔQ – change in the quantity
How to calculate marginal benefits?
- Where MB is the marginal benefit
- B1 and B0 are the final and initial benefits respectively
- Q1 and Q2 are the final and initial quantities respectively
How is marginal cost calculated?
What is Marginal Cost and How is it Calculated?
- Change in Costs. The production cost of any product or service is directly connected to what is required to produce a single item.
- Change in Number of Additional Units Produced. ...
- Variable Costs. ...
- Marginal Cost Formula Example. ...
- Practical Application of Marginal Cost. ...
- The Economy of Scale Factor. ...
What is marginal cost benefit analysis?
What is marginal cost benefit analysis? Marginal analysis is an examination of the additional benefits of an activity compared to the additional costs incurred by that same activity. Companies use marginal analysis as a decision-making tool to help them maximize their potential profits.
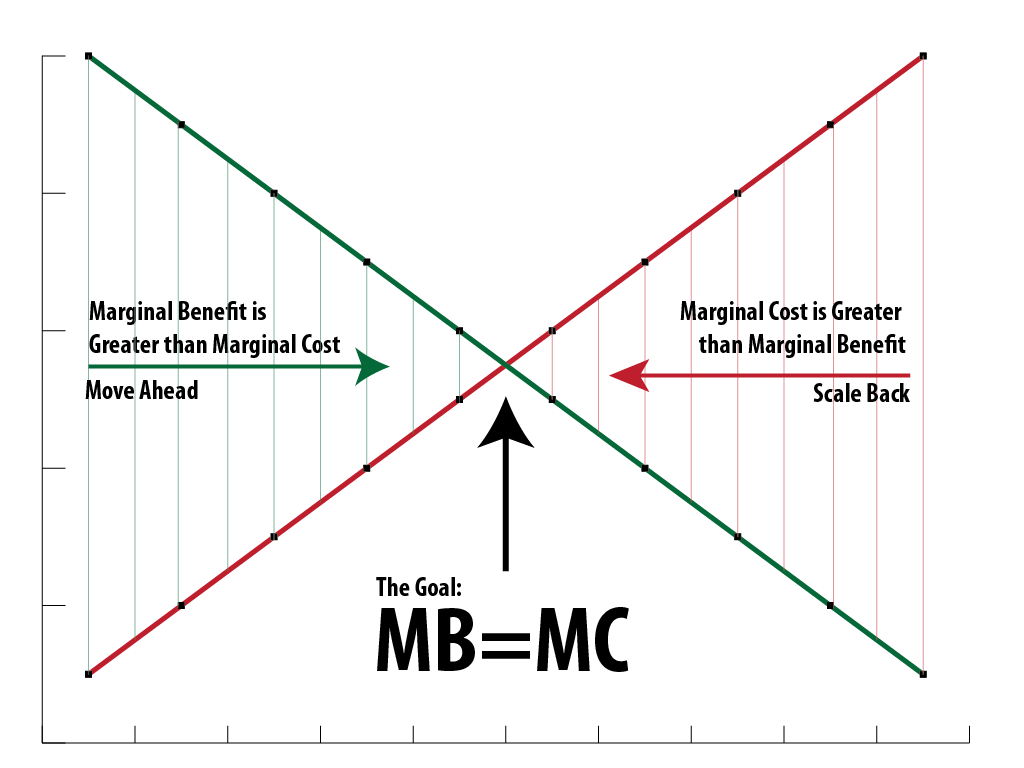
What is the difference between marginal cost and marginal benefit quizlet?
Marginal benefit is: the increase in total benefits as a result of a change in output of a good by one unit. Marginal Cost is: the increase in total cost as a result of a change in output of a good by one unit.
What is marginal cost and marginal benefit examples?
For example, a marginal cost would be how much it would cost a company to produce 1 more of a good. Their marginal benefit would be the extra revenue they get from producing that one extra good.
What is the best definition of marginal benefits?
Marginal benefits are the maximum amount a consumer will pay for an additional good or service. A marginal benefit is also the additional satisfaction that a consumer receives when the additional good or service is purchased.
What is the difference between marginal cost and marginal opportunity cost?
Marginal cost is the cost incurred during the production of a unit or item while opportunity cost is the cost incurred during the consumer's choice of which product to buy or use.
What are some examples of marginal benefit?
Example of Marginal Benefit For example, a consumer is willing to pay $5 for an ice cream, so the marginal benefit of consuming the ice cream is $5. However, the consumer may be substantially less willing to purchase additional ice cream at that price – only a $2 expenditure will tempt the person to buy another one.
What is marginal cost example?
The marginal cost of production includes all of the costs that vary with that level of production. For example, if a company needs to build an entirely new factory in order to produce more goods, the cost of building the factory is a marginal cost.
What is meant by marginal costs?
Marginal cost refers to the increase or decrease in the cost of producing one more unit or serving one more customer. It is also known as incremental cost.
What is the best definition of the marginal cost?
Marginal cost is the additional cost incurred in the production of one more unit of a good or service.
How do you calculate marginal cost and marginal benefit?
The formula used to determine marginal cost is 'change in total cost/change in quantity. ' while the formula used to determine marginal benefit is 'change in total benefit/change in quantity. '
Is marginal benefit the same as opportunity cost?
For example, Marginal Opportunity Cost (marginal cost) is the cost of foregoing one more unit of the next best alternative. Marginal Benefit is the benefit derived from choosing one more unit of the preferred good.
What is the difference of marginal opportunity cost and opportunity cost are they important why?
Opportunity cost is described as the sacrifice of the highest value of a good that one has to forego to obtain another while marginal cost is the cost incurred on producing an additional unit in a factory. There are some who equate marginal cost with opportunity cost.
What is the difference between money cost and opportunity cost?
Opportunity cost represents the quantum of profit that is let go, when an entity chooses one resource utilization alternative over another. Money costs are the actual cash (or credit) costs that an entity incurs during its business operations.
What is an example of marginal thinking?
If you think at the margin, you are thinking about what the next or additional action means for you. How many additional tomatoes can you get by taking better care of your garden? If an hour extra work weeding means you will get 12 more tomatoes, then one additional hour of work results in 12 additional tomatoes.
How do you calculate marginal benefit example?
Change in Number of Units Consumed For example, the change in units consumed from the second and first banana is 1 (2 – 1). When both parts are calculated, the marginal benefit is derived by dividing the change in total benefit by the difference in the number of units consumed.
How do you calculate MC and MB?
The formula used to determine marginal cost is 'change in total cost/change in quantity. ' while the formula used to determine marginal benefit is 'change in total benefit/change in quantity. '
How marginal cost and marginal benefit related to each other?
The marginal cost (MC) is the cost of the last unit produced or consumed, and marginal benefit is the utility gained from that last unit. Both marginal benefit and marginal cost are economic principles that businesses and consumers employ when trying to maximize their utility.
Why is it important to understand marginal cost and marginal benefit?
The differences between marginal cost and marginal benefit are important for companies to understand when developing operational plans for products. Regardless of the product type, these variables may influence company profits. Balancing marginal costs and benefits is valuable for maintaining sustainable business operations and often requires consumer research. In this article, we define marginal cost and marginal benefit, explain their relationship in business operations and provide two examples of how companies may use them.
What is marginal cost?
Marginal cost is the measurable expense change businesses have when they produce additional products or services. Some different marginal costs may include:
Why do companies pay less when purchasing additional products?
If consumers choose to pay less when purchasing additional products, it may help brands increase profits if their marginal costs are lower. Lower marginal costs may allow them to produce more products at lower operational costs, which can help balance decreases in marginal benefits. Otherwise, companies might experience decreased profits if their marginal costs are too high compared to marginal benefits.
What is product cost?
Product costs: These typically focus on costs not affected by batch or unit amounts. Instead, they primarily focus on the cost to design a product or the cost to market and promote a product to consumer target audiences.
What is a positive benefit?
Positive benefit: This type might occur if consumers respond positively to gaining additional products. For example, a consumer who enjoys donuts might experience additional happiness with more donuts.
How do cost measurements help companies?
Both cost measurements can show how product values change, depending on different producer or consumer variables. Considering each of these variables may help companies manage manufacturing, production and promotional processes for their products. Specifically, they can influence each other in relation to a company's revenue.
What is customer cost?
Customer costs: These might include customer service or relations costs. For example, companies may consider service representatives as part of their customer costs.
Marginal Benefit vs. Marginal Cost
Marginal benefit and marginal cost are two measures of how the cost or value of a product changes.
Marginal Benefit
A marginal benefit change in a consumer's advantage if they use an additional unit of a good or service.
Marginal Cost
Producers consider marginal cost, which is the small but measurable change in the expense to the business if it produces one additional unit.
Why is the relationship between marginal costs and marginal benefits important?
The relationship between marginal costs and marginal benefits is also extremely important when governments and voters determine how much, and what type, of public services are provided.
What is marginal cost?
For example, a marginal cost would be how much it would cost a company to produce 1 more of a good. Their marginal benefit would be the extra revenue they get from producing that one extra good.
Why is marginal cost greater than marginal revenue?
If the marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue, the company is making a loss at their current level of production (selling goods for less than the additional cost of making it), so they will reduce their production.
Why do businesses get less revenue for each extra unit?
This is because for each extra unit a business sells, the less revenue they get for each because they need to keep lowering their cost to sell everything they produce.
What is it called when the average cost goes down?
This period, where the average cost is decreasing, is known as Economies of Scale .
Does marginal cost go up or down?
Marginal Cost has the same kind of relationship – as you increase your production, your marginal cost will go up (how much it costs to bring one more carrot to market). In fact, the marginal cost actually starts going up before the average cost, and they share an interesting relationship.
Does the marginal cost curve always intersect the average cost curve?
The Marginal Cost curve will always intersect the absolute minimum point of the average cost curve . This relationship is useful – when an economist wants to calculate the minimum average cost, all they need is a formula for the average cost and marginal cost, and find the quantity where they are equal.
