Advantages of Transgenic Plant:
- Improvement in Yield
- Improvement in Insect and Disease Resistance
- Improvement in Quality
- Herbicide Resistance
- Resistance to Abiotic Stresses
- Industrial Products
- Rapid and Accurate Technique
- No Barrier for Gene Transfer
What are the potential risks of transgenic crops?
- United States of America- 70.1 million hectares area under GMCs
- Brazil- 40.3
- Argentina- 24.4
- India- 11.0
- Canada- 10.8
What are the benefits and disadvantages of transgenic plants?
What would be the main advantages and disadvantages of using genetically modified crops in India?
- It improves production and raise farmer’s income. …
- It reduces the use of pesticide and insecticide during farming that might be great moves for the betterment of the food supply.
- It can feed a rapidly increasing population because it shows dramatically increased yields.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of genetically modified crops?
Advantages + disadvantages of GMO's: - GMO's create plants better resistant to weeds, pest and other diseases. - Bigger yields to create more efficient use of land, less uses of herbicides and other pesticides. - Foods with better texture, flavour and nutritional value. - Foods with a longer shelf life for easier shipping.
Are transgenic crops safe to grow and eat?
This makes the plants safer for the consumer and allows the farmer to save money on chemicals. In conclusion, transgenic crops are an economically safer method of producing crop products, which makes them appealing and potentially profitable.

What is a benefit of transgenic plants?
The main advantages of transgenic plants include larger yield, resistance to diseases and pests and capable of growing under stressful conditions, while their main disadvantages include allergic reactions, emergence of super-pests and loss of biodiversity.
What are the benefits of transgenic crops quizlet?
Terms in this set (81)improve growth characteristics & yield of agriculturally valuable crops.increase nutritional value of crops.provide crops with resistance.
What do you mean by transgenic crops?
Definition. Transgenic plants are plants into which one or more genes from another species have been introduced into the genome, using genetic engineering processes.
What is the benefit of a genetically modified organism GMO )? Quizlet?
tremendous potential value. Reducing the harmful effects of modern farming by introducing nitrogen-fixing genes into crops i.e. rice and what, reducing the use of artifial fertilizers.
Points in favor of GM foods
Among the possible disadvantages that transgenics can have, we have the other side of the coin of its advantages, which are summarized in the following list:
Improvements in seeds and GM foods
Home garden. Currently, GM crops have benefits especially for producing huge farms, because the pesticides used for their cultivation are very toxic and eliminate all possible pests, increasing the economic profitability of the crop (but these pesticides also damage the ecosystem and beneficial animals)
Benefits of GMOs for the environment (?)
The second great advantage is that transgenic technology allows plants to be more resistant to certain insects and pests, with the consequent saving of chemicals to eradicate them. The classic example is Bt corn, one of the first transgenic that was produced.
Benefits for the GM farmer
Thanks to the use of specific products for each crop. They can use a very aggressive product, with which many plants die, except GMOs, which are resistant and thus see the profitability of the field increased, with a lower risk of economic losses due to pests (despite the negative impact on the ecosystem).
Will GMOs end hunger in the world?
The problem of hunger in the world is not because of food shortages, but because there are people too poor to buy food. It is a socioeconomic problem.
Nutritious and seemingly safe foods for health (?)
GMOs have proven to be nutritious, as thousands of animals and people are fed daily with food produced from transgenic seeds. However, the long-term health effects are unknown. If any, in the absence of scientific studies and research free of conflicts of interest.
What is the purpose of transgenic plants?
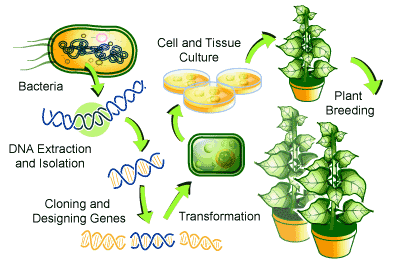
The aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. A transgenic plant contains a gene or genes that have been artificially inserted. The inserted gene sequence is known as the transgene, it may come from an unrelated plant or from a completely different species. The purpose of inserting a combination of genes in a plant, is to make it as useful and productive as possible. This process provides advantages like improving shelf life, higher yield, improved quality, pest resistance, tolerant to heat, cold and drought resistance, against a variety of biotic and abiotic stresses. Transgenic plants can also be produced in such a way that they express foreign proteins with industrial and pharmaceutical value. Plants made up of vaccines or antibodies (Plantibodies) are especially stricing as plants are free of human diseases, thus reducing screening costs for viruses and bacterial toxins.1
Why is it important to use transgenics?
The transgenics would allow for more crops that last longer and withstand pests and diseases.
What is the target of transgenic DNA?
The nucleus of the plant-cell is the target for the new transgenic DNA. Most genetically modified plants are generated by the biolistic method (Particle gun method) or by Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation method.
How can GM food be used in the future?
In the future, researchers hope to be able to provide vaccinations and medicines in GM foods , which can provide medications to people in developing countries more easily. Medications incorporated into food are easier to transport and store than conventional medicine. The advancements made with transgenic plants have and will continue to have a great impact on the lives of many. Transgenic plants offer a new approach to producing and administering human antibodies. The use of genetic engineering for the production of biopharmaceuticals like erythropoietin to treat anemia and insulin to treat diabetes are well known. Future generations of GM plants are intended to be suitable for harsh environments and for the Enhancement of Nutrient content, production of pharmaceutical agents and production of Bioenergy and Biofuels.
What is the disadvantage of genetically engineered plants?
The only disadvantage of this process is that serious damage can be happened to the cellular tissue. The next method, used for the development of genetically engineered plants, is the “Agrobacterium” method ( Fig. 1 ). It involves the use of soil-dwelling bacteria, known as Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
How does GM technology help the world?
GM Technology has been used to produce a variety of crop plants to date. As the global population continues to expand, food remains a scare resource. Genetically engineered foods offer significant benefits by improving production yield, lowering transportation costs and enhancing the nutritional content. Developments, resulting in commercially produced varieties in countries such as USA and Canada, have centerd on conferring resistance to insect, pests or viruses and producing tolerance to specific herbicides. While these traits had benefits for the farmers, it has been difficult for the consumers to see any benefit other than these. In limited cases, a decreased price owing to reduced cost and increased ease of production. 9, 10 Several GM crops for malnutrition are expected to be revealed for cultivation in the coming five to ten years. 11
Why do plants need genes?
The purpose of inserting a combination of genes in a plant, is to make it as useful and productive as possible. This process provides advantages like improving shelf life, higher yield, improved quality, pest resistance, tolerant to heat, cold and drought resistance, against a variety of biotic and abiotic stresses.
What are the advantages of transgenic breeding?
Advantages: (1) can transfer useful genes from non-plant species into plant species. (2) In some cases, transgenic breeding is faster than convetionaplant breeding. (3) Transgenesis approach is an useful tool for plant researches. etc...
Why is transgenesis important?
From the practical point of view it enables to create in the shortest time new cultivars resistant to pest, diseases, drought, and salinity. It enables also to produce some rare chemicals (therapy).
What are the disadvantages of transgenes?
Disadvantages: (1) without proper control, transgene can escape into environment, ex. to wild relatives, through 'gene flow', or non-intented targets, ex. non-GMO crops in the fields, (2) Not every plant species has an efficient transformation system or selection agents.
Is plant engineering pest tolerant?
With plant engineering, it's sometimes possible to develop pest-tolerant plants that safely target specific pests and are safe for human consumption while reducing pesticide use. ( eg., Bt corn) [ ENV ] [ FS ] Not enough is known about what other organisms might be harmed by a particular transgene.
Can genetically engineered genes be introduced into wild plants?
There's a risk that genetically engineered genes could be introduced into wild plants, reducing biodiversity and creating super-weeds while reducing pesticide use. [ ENV ] The risk of gene flow into wild plants is the same for transgenic plants as for traditionally-bred plants. [ SC ]
Can transgenic plants be used to reduce pesticide resistance?
While pesticides can lead to the creation of pest-resistant �super-pests,� pest-tolerant transgenic plants have been shown to reduce the incidence of pesticide resistance. [ ENV ] [ ECON ] Not enough is known about whether pesticides built into plants are safe for human consumption. [ FS ] [ SC ]