5 kinds of people who benefit from higher interest rates
- Savers seeking safety. The least-risky types of accounts — bank savings, credit union savings, and money market, to name a few — offer better yields when interest rates rise.
- Vacationers abroad. When interest rates increase, the dollar’s value does too. ...
- Retirees. ...
- Loan seekers. ...
- Credit ignorers. ...
Who benefits from high interest rates?
Who Benefits From an Interest Rate Rise?
- Regular Investors — If rates rise at a manageable pace and are a manifestation of economic growth, regular investors can benefit. ...
- Savers — On top of that, savers often benefit from rising rates. ...
- Bond Investors — Likewise, bond investors can see potential benefits as rates rise. ...
What banks have good interest rates?
- Bask Interest Savings Account
- Earn 0.70% annual percentage yield with no min. balance or monthly account fees
- Easily move deposits between high-yield savings and mileage savings product
Which bank pays the highest interest rate?
The First Step to Getting Higher Interest Rates
- Understanding Higher Interest Rates at International Banks. There are international banks around the world that offer attractive one-year interest rates north of 5 percent.
- Jurisdiction Risks. Jurisdiction risks refer to the specific jurisdiction where the bank is based. ...
- Bank Specific Risks. ...
- Special Consideration. ...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of interest?
List of the Disadvantages of Interest Groups
- The loudest voices usually win when interest groups are active. ...
- It is an easy way to stall all legislative processes. ...
- Most interest groups only focus on a single topic. ...
- Some interest groups promote harmful activities. ...
- Interest group leaders do not always act in the best interest of everyone. ...
- Governing systems can change because of interest groups. ...
Do borrowers benefit from increased interest rates?
Higher interest rates may lead to a slowdown in borrowing as consumers take out fewer loans. However, the rise in interest rates can help lenders earn more profits, particularly variable-rate credit products such as credit cards.
Who benefits from falling interest rates?
When consumers pay less in interest, this gives them more money to spend, which can create a ripple effect of increased spending throughout the economy. Businesses and farmers also benefit from lower interest rates, as it encourages them to make large equipment purchases due to the low cost of borrowing.
What happens if interest rates are increased?
Raising interest rates makes borrowing money more expensive, which can hurt individuals and businesses. Generally, raising interest rates slows down the economy by discouraging people from spending money. Homes cost more to buy for individuals and borrowing money to finance business operations becomes more costly.
Who benefits from a low savings rate?
1. Savers. With low-interest rates, people saving money in a bank gain lower interest rate. For example, pensioners who are relying on interest payments for income will see a fall in relative income.
How do higher interest rates affect the economy?
“In the economy, higher interest rates mean higher borrowing costs for firms, businesses and households. Those higher borrowing costs depress consumer spending [and] investment spending by firms and businesses,” Jalil said. “That will push down overall demand for goods and services.”
Is everybody worse off when interest rates rise?
4. No, not everybody is worse off when interest rates rise. People who borrow to purchase a house or a car are worse off because it costs them more to finance their purchase; however, savers benefit because they can earn higher interest rates on their savings.
What are the disadvantages of high interest rates?
When interest rates are increased, it costs more to borrow money. That means that businesses will not borrow as much in times of higher rates. When that happens, businesses spend less and hire less. In turn, this slows down an economy and if the economy is already slow, it can cause a recession.
How do Increasing interest rates affect businesses?
An increase in interest rates can affect a business in two ways: Customers with debts have less income to spend because they are paying more interest to lenders. Sales fall as a result. Firms with overdrafts will have higher costs because they must now pay more interest.
What are the benefits of higher interest rates?
Here are 5 kinds of people who benefit from higher interest rates: 1. Savers seeking safety. The least-risky types of accounts — bank savings, credit union savings, and money market, to name a few — offer better yields when interest rates rise. 2.
What does higher interest rates mean?
Higher interest rates mean lenders may find more reason to lend. So it could be a little easier than before for borrowers-to-be to become borrowers. But be careful — interest rates on those loans may rise too. 5.
1. Higher returns for savers
If you’re a saver, low interest rates have brought about the financial equivalent of a long drought. Any improvement, even modest, is welcome and overdue.
2. Tamed inflation
Most broad-based measures of prices indicate inflation has continued to remain under control in the U.S. in recent years. The central bank’s target for inflation is 2 percent, but inflation has yet to hit the bull’s-eye on a sustained basis, as measured by personal consumption expenditures, or PCE.
3. More lending
A credit bubble rightfully received some of the blame for the financial crisis in 2007. In the aftermath, lending came to a complete stop.
4. More interest income for retirees
As a rate boost brings better returns to savings vehicles, senior citizens should enjoy better paydays by putting their money in CDs and savings accounts.
5. Stronger dollar to boost purchasing power
As the Fed continues to boost rates (and with the outlook for more rate hikes to come), the U.S. dollar gets more support. Ultimately, that means more purchasing power with the greenback compared with other currencies.
6. Stocks will trade on fundamentals
As the Federal Reserve embarks on what officials have called “normalization” (that is, a backing away from record-low rates), stock prices may start to make more sense and not reflect the central bank’s easy monetary policy quite so much.
7. Would-be homebuyers may get off the fence
As the Fed continues to raise rates, higher mortgage rates likely will follow. If the prospect of higher mortgage rates compels you to a home sooner than later, you won’t be alone.
Why are there concerns about rising interest rates?
The list of worries about rising rates is long and varied: Lower valuations in stocks because of competition from bond yields. Higher interest payments for corporations, governments and individuals in debt. Any of these risks could certainly cause investors or the economy problems.
What are the risks of interest rates?
It’s human nature to be risk-averse, so when interest rates rise the first thing investors do is worry about the risks involved. The list of worries about rising rates is long and varied: 1 Principal losses in bonds 2 Lower valuations in stocks because of competition from bond yields 3 Higher inflation 4 The end of the economic expansion 5 Higher interest payments for corporations, governments and individuals in debt
What is the cure for low returns in bonds?
Unfortunately, the only cure for low returns in bonds is higher interest rates. Savers. Anyone looking for income from certificates of deposit, money market funds or savings accounts over the past few years has been disappointed in their minuscule yields.
Do fixed income bonds have to be short term?
So fixed-income investors have to experience short-term pain in the form of lower bond prices to eventually see higher expected returns over the long term. As bonds mature or come to market, investors can expect to see their yields rise, and thus, their expected returns.
Does the Federal Reserve raise interest rates?
The Federal Reserve has raised short-term interest rates and the markets have followed suit, which have helped this situation. For example, Marcus, the online bank run by Goldman Sachs, currently offers a five-year CD for 2.60 percent.
Is rising interest rates bad for the economy?
Any of these risks could certainly cause investors or the economy problems. But rising rates are not all bad. There are groups and strategies that would benefit from higher interest rates: Hedge fund managers and commodity trading advisers.
What are the advantages of high interest rates?
Higher interest rates raise the cost of borrowing money, but they also mean higher income for people who depend on bond portfolios or retirement funds for their income. While corporations growl that they must pay more to fund inventories or build factories, insurance companies occasionally reduce their policy ...
When an economy is overheating due to strong business growth, will the Federal Reserve tighten monetary policy?
When an economy is overheating due to strong business growth, the Federal Reserve will tighten monetary policy and raise interest rates to discourage speculative trading funded by low interest rates and easy lending of money by banks funding excessive business and consumer spending.
What happens when a lot of money is chasing few goods?
When a lot of money is chasing few goods, prices will rise and low interest rates will supply inexpensive money to the system. Higher rates will remove money from the system, business will slow and prices of goods, particularly food and fuel, will decline. Advertisement.
When a government must issue bonds to pay for economic stimulus, as the U.S. did in 2009, what
When a government must issue bonds to pay for economic stimulus, as the U.S. did in 2009, higher interest rates in later years allow that country's Treasury to purchase back bonds at much lower prices. For example, a 2 point increase in interest rates will reduce the bid on 30-year Treasury bonds from $1,000 to $750 per bond.
Can banks lock in high interest rates?
During low interest rate periods, fund s and banks are tempted to invest in low-quality credits to meet their income needs, but during high interest rate periods they can lock in high investment and loan income by extending their maturities as far as possible. Advertisement.
Do insurance companies reduce premiums?
While corporations growl that they must pay more to fund inventories or build factories, insurance companies occasionally reduce their policy premiums. It seems logical that low interest rates would be better than high interest rates, but that is not necessarily true. Advertisement.
What happens to interest rates as interest rates rise?
As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases for purchases like a car, a home, and college tuition. In addition, existing debt that is tied to a floating-rate index, such as some home equity loans will also rise in cost.
Why do companies pay more for their debt?
Companies will also pay more for their debt. When interest rates were low, companies loaded up on cheap debt.
What was the Fed's response to the 2008 economic crisis?
In response to the 2008 market and economic collapse, The Federal Reserve Bank (the Fed) began a multi-year policy of accommodative monetary policy, which kept both consumer and corporate interest rates low. At the same time, overseas financial institutions, like The Bank of Japan and The European Central Bank, ...
Why does the dollar rise against foreign currencies?
The dollar could rise against foreign currencies . Higher interest rates could attract overseas capital, thereby causing the value of our currency to rise on a relative basis against other countries. Of course, many factors impact currency exchange rates, but higher relative interest rates are a key factor.
Is the Fed raising interest rates?
Now, with the U.S. economy roaring ahead, the Fed is raising U.S. interest rates.
Is rising interest rate bad for the economy?
And when interest-rate increases occur rapidly, the damage could be exacerbated. Consumers, corporations, investors, and just about anyone involved in the economic activity of our country may be impacted.
Is forecasting interest rates a science?
Therefore, it makes prudent sense to look at your current investments and overall situation and position yourself accordingly. Forecasting interest rates is a very inexact science, but if the U.S. economy continues its very strong trajectory, the likelihood that our interest rates decline also declines.
How does higher interest rate affect economic growth?
Higher interest rates tend to moderate economic growth. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, reduce disposable income and therefore limit the growth in consumer spending. Higher interest rates tend to reduce inflationary pressures and cause an appreciation in the exchange rate. Higher interest rates have various economic effects:
What happens when interest rates rise?
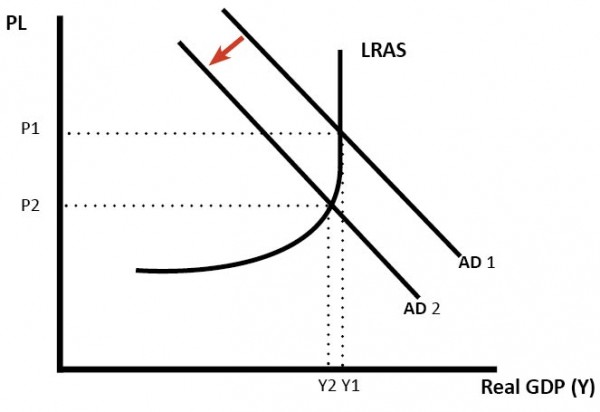
A rise in interest rates discourages investment; it makes firms and consumers less willing to take out risky investments and purchases. Therefore, higher interest rates will tend to reduce consumer spending and investment. This will lead to a fall in Aggregate Demand (AD).
How does raising interest rates affect inflation?
Effect of raising interest rates. The Central Bank usually increase interest rates when inflation is predicted to rise above their inflation target. Higher interest rates tend to moderate economic growth. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, reduce disposable income and therefore limit the growth in consumer spending.
Why are credit cards so expensive?
Increases the cost of borrowing. With higher interest rates, interest payments on credit cards and loans are more expensive. Therefore this discourages people from borrowing and spending. People who already have loans will have less disposable income because they spend more on interest payments.
What will happen to mortgage rates in the 20s?
Those consumers with large mortgages (often first time buyers in the 20s and 30s) will be disproportionately affected by rising interest rates. For example, reducing inflation may require interest rates to rise to a level that causes real hardship to those with large mortgages.
How did the increase in interest rates in 2004-06 affect the housing market?
Increased interest rates 2004-06 had a significant impact on US housing market. Higher mortgage costs led to a rise in mortgage defaults – exacerbated by a high number of sub-prime mortgages in the housing bubble.
Why did the UK go into recession in 1980?
In 1980 and 81, the UK went into recession, due to the high-interest rates and appreciation in Sterling. (see Recession 1981) Interest rates also rose to 15% to tackle high inflation of the late 1980s (and also protect value of Pound in ERM.
Why are interest rates rising?
Rising interest rates are often connected to economic growth. When the economy is improving and people are able to spend more money, inflation can be a driver of higher interest rates.
Why does the Federal Reserve raise interest rates?
The Federal Reserve often drives rates, as they can raise or lower rates to stimulate economic growth. While rising interest rates can often mean an increase in things like mortgage rates, there can be opportunities for investors looking to expand their equities.
Why is it harder to pay off debt?
Borrowers — Borrowers are also at risk from rising interest rates. If you have high-interest variable debt, like credit cards, rising rates can cause financial issues. It’s harder to pay off debt when more of your monthly payment goes toward interest charges.
What sectors do well when interest rates rise?
There are some sectors that do well when interest rates rise including: Healthcare: People need healthcare no matter what’s going on. That makes healthcare a sector worth considering, especially during a period of rising interest rates.
What are the factors that affect the risk of investing?
In general, there are four main factors that impact the risk in your portfolio: Market risk: The risk presented by the stock market in general. Interest rate risk: How rising or falling interest rates impact stock performance.
Why are consumer goods stocks stable?
That’s why consumer goods stocks are often stable, as people will still need to buy groceries during a recession. Financials: As we mentioned earlier, financial stocks often benefit the most from rising interest rates because of their connection to products like mortgages and loans.
Do insurance companies invest in bonds?
Insurers can also do reasonably well as rates rise. Many insurance companies rely on bond investments — particularly long-term Treasuries — as base investments. When interest rates rise, so, too, do bond yields. This provides higher returns for these investments.