How to tell if you are eligible for unemployment benefits?
You must be:
- Physically able to work.
- Available for work.
- Ready and willing to accept work immediately.
What state has the best unemployment benefits?
"There are many reasons for the worker shortage, but we need to recognize that, in some cases, it's because the government has ... the state, whose sole job is to help Iowans get back to work. Konfrst said it takes more than cutting unemployment benefits ...
What are the reasons for not receiving unemployment?
- They are ill with COVID-19.
- They might have been exposed to coronavirus.
- They were ordered to stay home by a doctor to prevent the risk of getting exposed to, or spreading, coronavirus.
- Their employer shut down or cut back their business due to coronavirus.
- They were advised not to work by public health officials.
Are employers responsible for paying unemployment taxes?
responsible for paying state unemployment taxes to the Unemploy-ment Insurance Agency (UIA). Most employers are contributing employers and the taxes they pay the UIA are called contributions. A contributing employer files a tax report with the UIA at the end of each calendar quarter, and pays a state unemployment tax on

What are the negatives of unemployment?
Common disadvantages of unemployment for individuals include:Reduced income. ... Health problems. ... Negative familial effects. ... Mental health challenges. ... Don't deny your feelings. ... Think of unemployment as a temporary setback. ... Reach out to friends and family. ... Start networking.More items...•
How does unemployment benefit the economy?
Unemployment benefit programs play an essential role in the economy by protecting workers' incomes after layoffs, improving their long-run labor market productivity, and stimulating the economy during recessions. Governments need to guard against benefits that are too generous, which can discourage job searching.
Do employees pay into unemployment in California?
The UI program is financed by employers who pay unemployment taxes on up to $7,000 in wages paid to each worker. The actual tax rate varies for each employer, depending in part on the amount of UI benefits paid to former employees. Thus, the UI tax works much like any other insurance premium.
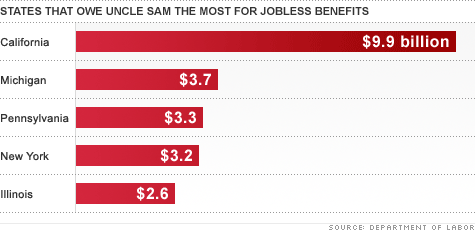
Which state pays the most in unemployment benefits?
MassachusettsThe majority of U.S. states offer unemployment benefits for up to 26 weeks. Benefits range from $235 a week to $823. Policies and benefits vary by state. Mississippi has the lowest maximum unemployment benefits in the U.S. of $235 per week, while Massachusetts has the highest at $823.
What are the pros and cons of unemployment benefits?
The Pros & Cons of Filing for UnemploymentPro: Wage Supplement. Those who qualify for unemployment benefits receive monthly payments to live on while searching for a new job. ... Pro: More Free Time. ... Pro: Improving Credentials. ... Cons: Less Pay. ... Con: Loss of Benefits. ... Con: Resume Gap.
What are the three consequences of unemployment?
Syllabus: Consequences of unemploymenta loss of GDP,loss of tax revenue,increased cost of unemployment benefits,loss of income for individuals, and.greater disparities in the distribution of income.
How much does an employer pay for unemployment insurance in California?
3.4 percentAn employer may earn a lower tax contribution rate when fewer claims are made on the employer's account by former employees. The UI contribution rate for new employers is 3.4 percent for up to three years.
What does EDD send to employers?
Notice of Unemployment Insurance Claim Filed (DE 1101CZ) This notice is mailed to the very last employer when a claim for UI benefits is filed. It provides general information about the claim including the reason the claimant states he/she is no longer working.
How much is EDD paying now 2021?
$167 plus $600 per week for each week you are unemployed due to COVID-19.
What is the most you can get from unemployment?
In most cases, the maximum is around $500 or $600 per week, according to Vroman. But in some states, like Massachusetts, it can be as high as $1,000. Unemployment benefits usually last up to 26 weeks, although in some states it's less.
What US state has the lowest unemployment rate?
Nebraska and Utah had the lowest rates, at 1.9% each. The map below shows the most recent unemployment rate for every state, according to BLS data.
Why are unemployment benefits so low in California?
California's UI Benefits Structure Fails Unemployed Workers As a result, when wages and the overall cost of living rise, benefits fail to keep pace. California already ranks 43rd in the nation for the percentage of the state's average weekly wage that is replaced by its UI benefits – just 29%.
How does unemployment affect the overall growth of an economy?
Unemployment affects the overall growth of an economy as (i) it is a wastage of manpower resource. (ii) it increases the economic overload. (iii) it tends to increase the number of dependent population. (iv) increase in unemployment is an indicator of a depressed economy.
How does unemployment hurt an economy?
Unemployed people usually buy fewer things. Unemployed people may not be able to repay their loans. Unemployed people may have to change their financial goals. everyone benefits if the economy is strong.
How is unemployment an economic as well as a social problem?
Unemployment is an economic and social problem. Unemployment is an economic problem in the sense that unemployed persons will be consumers only without being a producer. Non utilisation of human resources due to unemployment involves double cost of maintenance and loss of output.
What are the 5 effects of unemployment?
The personal and social costs of unemployment include severe financial hardship and poverty, debt, homelessness and housing stress, family tensions and breakdown, boredom, alienation, shame and stigma, increased social isolation, crime, erosion of confidence and self-esteem, the atrophying of work skills and ill-health ...
COVID-19 Unemployment Benefits
COVID-19 extended unemployment benefits from the federal government have ended. But you may still qualify for unemployment benefits from your state...
How to Apply for Unemployment Benefits
There are a variety of benefit and aid programs to help you if you lose your job. CareerOneStop.org is a good place to start. It can help with unem...
Continuation of Health Coverage: COBRA
Learn how you can continue your health care coverage through COBRA.What is COBRA?COBRA is the Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act. COBRA...
Short-Term and Long-Term Disability Insurance
If you can't work because you are sick or injured, disability insurance will pay part of your income. You may be able to get insurance through your...
Workers' Compensation for Illness or Injury on the Job
Workers' compensation laws protect employees who get hurt on the job or sick from it. The laws establish workers’ comp, a form of insurance that em...
Wrongful Discharge/Termination of Employment
If you feel that you have been wrongfully fired from a job or let go from an employment situation, you may wish to learn more about your state's wr...
Welfare or Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF)
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) is a federally funded, state-run benefits program. Also known as welfare, TANF helps families achiev...
How to calculate unemployment tax?
However, each state confine the tax you have to pay with respect to any one employee by detailing a maximum wage amount to which the tax applies. Once an employee’s wages for the calendar year surpass that maximum amount, your state tax liability with respect to that employee ends.
What is the liability of an employer for unemployment?
In order to fund unemployment compensation benefit programs, employers are subject to federal and state unemployment taxes depending on several factors. These factors include the sums employers pay their employees, the unemployment claims filed against the business, and the type & age of the business.
How much is a FUTA tax?
The FUTA tax is imposed at a single flat rate on the first $7,000 of wages that you give each employee. Once an employee’s wages for the calendar year go beyond $7000, you have no additional FUTA liability for that employee for the year.
How much do you pay in a quarter for a FUTA?
You pay wages totaling at least $1,500 to your employees in any calendar quarter; or. You have at least one employee on any given day in each of 20 different calendar weeks. Once you fulfill either of the tests, you become liable for the FUTA tax for the whole calendar year and for the next calendar year as well.
Why is unemployment tax so high?
When you first open your UI account, your tax rate will be fairly high because you have no track record. If you work for several years without laying off an employee, your tax rate will go down. If you continually lay off employees, your tax rate will increase.
What is the premium rate for new non-governmental employers?
All other new employers are allotted a 2.7% new employer premium rate. In the past, mining and construction are the only industries with new employer rates higher than 2.7%.
Which states have unemployment taxes?
If you have employees in New Jersey, Alaska, or Pennsylvania you will also be withholding unemployment taxes from your employees’ wages since these states assess unemployment taxes on employees.
What is unemployment?
Unemployment insurance, also known as unemployment, is a social support precaution designed to help people who lose their jobs due to external circumstances. Unemployment allows eligible applicants to receive a portion of their former wages for a set period of time or until they secure employment again.
How does unemployment work?
Unemployment insurance works by collecting tax from employers each year and redistributing those funds to people who apply for unemployment benefits after losing their job. Individuals fill out forms at their state’s unemployment office and, pending approval, receive 13 to 26 weeks of supplemental pay.
Who pays for unemployment benefits?
Unemployment insurance is funded through a company’s payroll taxes. Each individual state has its own unemployment office that manages applications and payments, with the requirements to qualify for benefits varying from state to state.
What responsibilities do employers have when managing unemployment?
Your company has a few key responsibilities when it comes to setting up employment benefits:
What happens after an employee files an unemployment claim?
As an employer, you may eventually have to deal with unemployment claims from former employees. If one of your former employees files for unemployment, you will receive a notice explaining their claim and giving you a deadline to contest it.
Frequently asked questions about unemployment
Employers can disagree with an unemployment claim and submit evidence that it is not a valid claim, but they themselves do not have the authority to deny an unemployment claim. They have to fill out the proper paperwork and let the unemployment office choose to deny or approve the claim.
How is unemployment insurance funded?
Department of Labor’s Unemployment Insurance program is funded through unemployment insurance taxes paid by employers and collected by the state and federal government. The taxes are part of the often-discussed payroll taxes all employers pay.
Which states require employees to contribute to unemployment insurance?
There are only three states—Arkansas, New Jersey and Pennsylvania —that ask employees to contribute and only in specific situations. Similar to varying car insurance rates, state unemployment insurance rates vary for employers based on their history.
How much do employers pay in taxes?
Employers pay federal taxes of 6 percent on the first $7,000 in annual income earned by every employee. Employers who pay on time get a tax break at 5.4 percent. The amount collected by each state varies as does the amount of income it is collected on—the first $7,000 to $34,000 an employee earns each year, depending on the state.
How long can you get unemployment benefits?
This usually comes in the form of extending the time individuals can receive benefits over the 26 week maximum offered in most states. The loan fund is reserved for bridging gaps for states that run out of unemployment insurance money during times of heightened unemployment.
What are some online services that can help you find work from home jobs?
Several online services—like FlexJobs, 360training, or MyPerfectResume —can help you find work-from-home jobs, build a better resume, or earn training certifications.
Is unemployment insurance set aside?
As you can see, the Unemployment Insurance program operates similarly to other insurance programs—money is set aside and reserved for times of need. During greater times of the need, the system has adapted to continue fulfilling its mission of bridging the gap in income for out of work individuals.
How long does unemployment last?
Extended unemployment insurance benefits last for 13 weeks. You can apply for extended benefits only once you've run out of regular benefits. Check with your state; not everyone qualifies. You must report unemployment benefits as income on your tax return.
What is the extension for unemployment in 2021?
The American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 temporarily authorized: An extension for people already receiving unemployment benefits. Automatic, additional payments of $300 per week to everyone qualified for unemployment benefits. Extension of the Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) program for self-employed or gig workers.
What to do if you are terminated by an employer?
If you are an employer seeking information about legal termination of employees, you may wish to contact both the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) and your State Labor Office to ensure you do not violate any federal or state labor laws. You may wish to consult with a licensed attorney.
What to do if you get hurt working for a private company?
Private Sector and State or Local Government Employees. If you get hurt working for a private company or state or local government, seek help through your state. Your state workers' compensation program can help you file a claim. If your claim is denied, you can appeal.
What is workers comp?
Workers' compensation laws protect employees who get hurt on the job or sick from it. The laws establish workers’ comp, a form of insurance that employers pay for. These laws vary from state to state and for federal employees.
What to do if you lose your job?
Apply for Unemployment Benefits. There are a variety of benefit and aid programs to help you if you lose your job. CareerOneStop.org is a good place to start. It can help with unemployment insurance benefits, job training, and finding a job. Open All +.
What is unemployment insurance?
Unemployment Benefits Comparison By State. The Unemployment Insurance (UI) benefits are given to those who have lost their jobs through no fault of their own. Though the U.S. Department Of Labor oversees the UI program and ensures compliance within each state, the state governments administer and determine the eligibility criteria, ...
How is unemployment benefit determined in Delaware?
Your Weekly Benefit Amount in Delaware is determined by dividing your average earnings in your two highest latest quarters by 46. If you collect wages while on UI benefits, the state will disregard $10 or 50% of your weekly benefit, whichever is greater.
How is weekly benefit determined in Tennessee?
Your Weekly Benefit Amount in Tennessee is determined by dividing your wages in the highest quarter of your base period by 26. If you collect wages while on UI benefits, the state will disregard $50 or 1/4th of your WBA, whichever is greater.
How to calculate weekly benefits in Louisiana?
Your Weekly Benefit Amount in Louisiana is determined by dividing your average wages over the last four quarters of your base period by 25 and multiplying by 1.2075. If you collect wages while on UI benefits, the state will disregard $50 or an amount equal to 1/2 of your WBA, whichever is less.
How much is your weekly benefit in Illinois?
Your Weekly Benefit Amount in Illinois would be 47% of your average weekly wages in the two highest quarters of your base period. If you collect wages while on UI benefits, the state will disregard an amount equal to 1/2 of your WBA.
How is Hawaii's weekly benefit determined?
Your Weekly Benefit Amount in Hawaii is determined by dividing your earnings in the highest quarter of your base period by 21. If you collect wages while on UI benefits, the state will disregard $150.
How to determine weekly benefits in Georgia?
Your Weekly Benefit Amount in Georgia is determined by dividing your two highest earning quarters by 42, or your earnings in your highest earning quarter by 21. If you collect wages while on UI benefits, the state will disregard $50.
How much does unemployment cost?
The average amount paid out on an unemployment claim is $4200, but can cost up to $12,000 or even more.
How do state governments get money to pay claims?
State governments get the money to pay claims by debiting the employer’s UI account (in states that require an account balance) or by raising the employer’s UI taxes. A deduction in the account balance may also cause a rate increase, as the ratio between taxable payroll and the account balance changes. Each claim assessed to an employer’s account ...
Why do employers have to prevent UI?
However, employers must prevent UI benefit charges in order to keep their unemployment tax rate low. This is done by contesting and winning claims when employees should be judged ineligible for benefits, such as employees who quit (in most cases) or are fired for misconduct. Many employers use an outsourced UI claims management/cost control ...
How long does unemployment affect tax rates?
Each awarded unemployment claim can affect three years of UI tax rates. Employers often don’t realize the real cost of a claim since it’s spread out over a long period. The average claim can increase an employer’s state tax premium $4,000 to $7,000 over the course of three years.
Where does unemployment come from?
Many people mistakenly believe that unemployment insurance (UI) benefits come from a fund paid into by employees—like Social Security or Medicare. However, it’s employers who are financially responsible for unemployment benefits, and the costs are far higher than just the amount of a claim.
Which states have unemployment taxes?
Only three states—Alaska, New Jersey and Pennsylvania —assess unemployment taxes on employees, and it’s a small portion of the overall cost. Unemployment is funded, and taxed, at both the federal and state level: The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) tax is imposed at a flat rate on the first $7,000 paid to each employee.
Does each claim increase tax rate?
Each claim assessed to an employer’s account can result in a tax rate increase in future years. So the real story isn’t the cost of an individual claim (though it can be significant). It’s the higher tax rate that will have a long-term impact. The state formulas generally use a three-year moving period to assign a tax rate.
What is unemployment insurance?
Unemployment benefits are part of an employer-paid program that provides temporary, partial income replacement to qualified individuals who are unemployed through no fault of their own.
Why do we share information with U.S. Bank?
If we pay you benefits by debit card, we share information with U.S Bank because it manages your debit-card account. U.S. Bank and government agencies with access to information must agree to comply with state and federal laws regarding the confidentiality of claim information. Return to Top.
Do you pay unemployment if you are working?
Believing that you paid into an unemployment benefits account while you were working. This is not true. Employer taxes pay for unemployment benefits.
Do you report unemployment as income?
Unemployment benefits must be reported as income to the Internal Revenue Service ( IRS ). For more information, see Income Taxes & Your Unemployment Benefits.
Do you pay unemployment taxes in Texas?
Employers pay unemployment insurance taxes and reimbursements that support unemployment benefit payments. Employees do not pay unemployment taxes and employers cannot deduct unemployment taxes from employees' paychecks. Unemployment benefits are available if you meet eligibility requirements set by the Texas Unemployment Compensation Act ( TUCA ).
How does unemployment affect an employer?
The main determinants of how a UI claim will affect a given employer are: the number of employees the company has.
What is the presumption of employment in Texas?
The legal presumption in Texas is that all services are in "employment" and are subject to wage reporting and taxation or reimbursement liability, and the burden of proof is on the employer to show that a particular worker is not in employment.
How does the length of time an employee works affect UI?
Generally, if an employee works a short period of time, and files a UI claim fairly soon after losing that short-term job, the employer will not fall into the base period of the claim. The longer the employee works for the employer, the greater the chance is that a subsequent UI claim will involve the employer in the base period. In addition, since an employer's chargeback liability is directly proportional to the amount of wages it reported during the claimant's base period, the longer the employee works, the more wages will be reported, and the higher the potential chargeback liability will be. That is why, as a general matter, it is better to separate a clearly unsuitable employee from the company as soon as it becomes clear that, despite your best efforts at counseling and retraining, the employee will not work out in the long term.
Can an independent contractor claim UI?
As noted above, some workers (independent contractors and employees whose services are exempt from the definition of "employment") will not involve their employing units financially in a UI claim. All other types of workers have the potential to involve their employing units financially, depending upon whether a particular employing unit reported wages for the claimant during the base period of the claim. Here is a summary of the potential claim liabilities:
Do employers pay quarterly UI?
Private taxed employers report their employees' wages, pay quarterly UI tax on such wages (up to the first $9,000 of each employee's earnings in a calendar year), and have potential financial involvement (chargeback liability) in any U I claims that might be filed by such workers. Reimbursing employers report their employees' wages, ...
Is a private sector employer exempt from UI?
For example, a private-sector employing unit that pays less than $1500 in wages in a calendar quarter is exempt (for household/domestic employers, the threshold is $1000 in a calendar quarter).
Is a church exempt from UI?
For the non-exempt employees, they are treated like any other liable employer - see below. Some organizations, such as churches, have nothing but exempt employees and are non-liable . For a complete list of UI exemptions, see the Texas Labor Code, Chapter 201, Sections 201.042-201.078, starting at http://www.statutes.legis.state.tx.us/Docs/LA/htm/LA.201.htm#201.042.