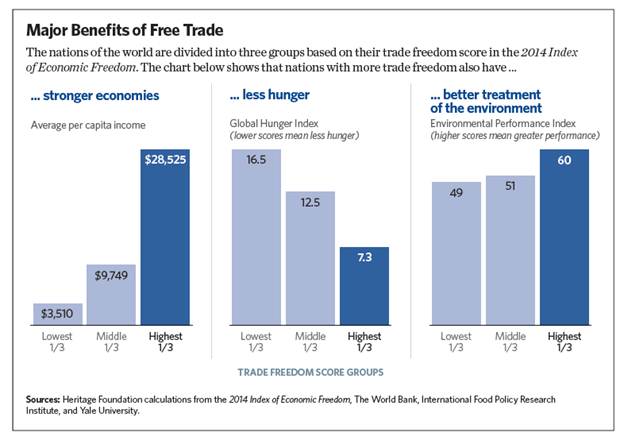
The Truths of Free Trade
- Free trade increases access to higher-quality, lower-priced goods. Cheaper imports, particularly from countries such as China and Mexico, have eased inflationary pressure in the United States. ...
- Free trade means more growth. ...
- Free trade improves efficiency and innovation. ...
- Free trade drives competitiveness. ...
- Free trade promotes fairness. ...
Who benefits from free trade, and how?
Why is trade important?
- Jobs. More than 40 million American jobs depend on trade, and trade is critical to the success of many sectors of the U.S. economy.
- Growth. According to economic data from the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, U.S. ...
- Business. 98% of the roughly 300,000 U.S. companies that export are small and medium-sized businesses, and they account for one-third of U.S. ...
Why America needs to support free trade?
There are at least five important reasons for continuing to support free trade. The most compelling reason to support free trade is that society as a whole benefits from it. Free trade improves people's living standards because it allows them to consume higher quality goods at less expensive prices.
What are the disadvantages of free trade?
Free trade has several advantages, but many businesses and workers do not share the benefits of the policy. Among the disadvantages of free trade is job outsourcing that results in lost jobs, predatory pricing by foreign companies, increased vulnerability for some domestic industries and and more.
What's the problem with "free trade"?
List of the Disadvantages of Free Trade Free trade does not create more jobs. It is a myth to say that free trade encourages employers to send their jobs overseas. ... It encourages more urbanization. When you look at a map of the United States, you will find an interesting trend. ... There are more risks for currency manipulation. ... More items...

How does free trade benefit consumers quizlet?
Lower prices for consumers: When there is free trade, consumers can free to buy goods from the producer who is willing to sell at the lowest prices. Hence consumers gain from lower prices.
How do free trade agreements affect consumers?
According to economic theory, FTAs lower trade barriers on imported goods, leading to consumer welfare gains from increase in product variety, better quality products and lower prices for existing products.
Who benefits and who suffers from free trade?
Consumers benefit from lower prices. Free trade reduces the price of imported goods. This enables consumers to enjoy increased living standards. After the purchase of imports, they have more left over income to spend on other goods. Free trade can also lead to increased competition.
What are three advantages of free trade?
A free trade area offers several advantages, including:Increased efficiency. The good thing about a free trade area is that it encourages competition, which consequently increases a country's efficiency, in order to be on par with its competitors. ... Specialization of countries. ... No monopoly. ... Lowered prices. ... Increased variety.
What are the benefits of foreign trade on consumers and producers?
The benefits of foreign trade to producers and consumers are: It created an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets i.e. markets of their own countries. It gave consumers a wider choice of good quality goods. It helps every country to make optimum utilisation of its natural resources.
How do consumers all benefit from international trade quizlet?
How does International Trade benefit consumers? Consumers benefit from the competition that the foreign companies offer. This competition encourages the production of high-quality goods with lower prices. The variety of goods increases as more producers market their goods in other countries.
How might trade agreements benefit consumers?
Trade agreements between countries lower trade barriers on imported goods and, according to theory, they should provide welfare gains to consumers from increases in variety, access to better quality products and lower prices.
What are the benefits of trade?
Trade is central to ending global poverty. Countries that are open to international trade tend to grow faster, innovate, improve productivity and provide higher income and more opportunities to their people. Open trade also benefits lower-income households by offering consumers more affordable goods and services.
Does everyone benefit from trade?
Trade enables countries to experience economic growth and a rising standard of living by increasing access to physical capital and export markets. However, not everyone is better off as a result of international trade.
What are pros and cons of free trade?
Pros and Cons of Free TradePro: Economic Efficiency. The big argument in favor of free trade is its ability to improve economic efficiency. ... Con: Job Losses. ... Pro: Less Corruption. ... Con: Free Trade Isn't Fair. ... Pro: Reduced Likelihood of War. ... Con: Labor and Environmental Abuses.
Is free trade or fair trade better for consumers?
In general, economists recognize that free trade provides the least amount of overhead during the production of goods and services, so a free trade economist will emphasize the lower end-price for consumers that results from trade policies that do not have government-mandated price minimums.
What is free trade advantages and disadvantages?
They can open new markets, increase gross domestic product (GDP), and invite new investments. FTAs can open up a country to degradation of natural resources, loss of traditional livelihoods, and local employment issues. Countries must balance the domestic benefits of free trade agreements with their consequences.
Why is free trade important?
Free trade fosters support for the rule of law. Companies that engage in international trade have reason to abide by the terms of their contracts and international agreed-upon norms and laws. The World Trade Organization, for example, compels its member countries to honor trade agreements and, in any trade dispute, to abide by the decisions of the WTO's mediating body.
How does free trade promote innovation?
Free trade promotes innovation because, along with goods and services, the flow of trade circulates new ideas. Since companies must compete with their overseas counterparts, American firms can take note of all the successes as well as the failures that take place in the global marketplace.
How does free trade reduce corruption?
[21] Free trade, reinforced by the rule of law, removes such incentives for corruption by spurring economic growth, increasing the number of better-paying jobs, and ultimately increasing the level of prosperity . But free trade transmits more than just physical goods or services to people.
What is international trade?
International trade is the framework upon which American prosperity rests. Free trade policies have created a level of competition in today's open market that engenders continual innovation and leads to better products, better-paying jobs, new markets, and increased savings and investment.
Which countries have economic freedom?
Nonetheless, a basic structure upon which to build economic freedom can be found in countries as different as Bahrain (an Arab monarchy), Singapore (an authoritarian city-state), the United States (a constitutional democracy), and Switzerland (a federal system of cantons encompassing at least four different cultures).
Who said that traders in the marketplace are like voters in a democracy?
Indian economist Barun Mitra explains it succinctly: "Traders in the marketplace are like voters in a democracy. If [the] free flow of ideas is essential to sustain political freedom and a democratic polity, then free trade is critical to sustain economic freedom and an efficient marketplace.
Who said that free trade creates economic dynamism?
Societies that enact free trade policies create their own economic dynamism--fostering a wellspring of freedom, opportunity, and prosperity that benefits every citizen. In recent years, the United States has demonstrated the power of this principle.
Who were the first economists to argue for free trade?
... First classic economistsDavid Hume, Adam Smith, David Ricardo-recognized the importance of free markets and free trade that stimulates the efficient use of economy`s resources and brings economic prosperity. These assumptions and insights argue that gains from free trade come due to country`s specialization to particular products and comparative advantage [2]. Today in existence of numerous countries and products, Smith, Ricardian and Heckscher-Ohlin models are strong simplifying assumptions, as they didn`t take into account that difference among countries affects productivity and technologies [3], even though gains-from-trade and comparative advantage theories are general and gives robust results. ...
Why is expatriation important?
As companies are becoming more international in their operations global assignments are becoming increasingly popular. Transferring knowledge and developing international management are becoming necessary. Expatriation in turn constitutes necessary part of global management and success of business in worldwide market. For international firms staff with global management skills is becoming significant competitive resource. Living and working in a different country and culture are major change for most people. HR has huge responsibility to make it easier and minimize the risk of adjustment difficulties of the expatriates. It is also largely their responsibility guarantee a smooth re-adjustment at difficult moment of the expats international assignment. Purpose of this paper is to find reasons that contribute to ineffective repatriation of expatriates and how companies can organize an affective repatriation process.
Why do economists favor free trade?
Most economists favor free trade because (at least under classical assumptions) when the government imposes a tariff, the monetary gains to the winners are outweighed by the monetary losses to the losers.
What is the case for free trade?
In this article, Roberts reiterated his position that "the case for free trade" rests on the assumption that factors of production cannot move between countries (or at least, cannot move as easily as final products can). According to Schumer and Roberts, in the modern world of multinational corporations, reduced shipping costs, ...
Why is the average real income in a small country reduced?
But it is theoretically possible that the average real income in a small country might be reduced because of a technological innovation. For example, suppose that there is a small island nation in the Pacific composed of 10,000 people.
Can tariffs make people poorer?
Trade policy in this case can alter things (so that the new innovation is not exploited), but in that case people on net are poorer because of the tariff. In conclusion, no matter what the scenario, enacting tariffs can only make people poorer on average.
Is free trade the best policy?
Free trade is still the best policy. Imposing a tariff will still make the people in the "losing" country poorer on average, relative to how poor they would be with the change in factor mobility and free trade.
Is Paul Craig Roberts arguing for tariffs?
At this point, Paul Craig Roberts would go through the roof. As he has repeatedly emphasized, he is not arguing in favor of tariffs. All he is doing is pointing out that the case for free trade does not hold up when factors are mobile.
Can office workers stop buying copiers?
Office workers who formerly imported paper copiers from our hypothetical island—in order to make copies of important documents and send them to their associates in other countries, say—now can stop buying so many copiers. They just fax or email the relevant documents to their associates in other countries.
How much of the value of a trade agreement must be produced locally?
Most trade agreements require that 55% of the value be produced locally. For products with complex supply chain such as cars the UK would find it difficult to prove that they were made in Britain, therefore, they would and could not be covered by the new trade agreements signed independently by the UK.
What is the central tenet of trade theory?
A central tenet of trade theory is that lowering trade barriers increases welfare. Trade agreements between countries lower trade barriers on imported goods and according to theory, they should provide welfare gains to consumers from increases in variety, access to better quality products and lower prices. Although a large literature estimates the ...
Why did the UK blame the EU for Brexit?
Part of the Brexit camp blamed the EU for impeding the signature of new trade agreements. According to them, the UK should be free to negotiate and set the course of its trade policy. Therefore, when Economics Professor Giuseppe Berlingieri decides to look closely at the impact of trade agreements - implemented by the EU between 1993 ...
Why did the UK leave the EU?
The United Kingdom voted to leave the European Union after a historic referendum in which the people rejected the advice of the main Westminster party leaders and instead took a plunge into the political unknown . Even though the “leave” campaign focused on “emotional arguments” about immigration, there were many ...
Is the EU a trade negotiator?
It may be true that negotiations and trade agreements handled by the EU are complex. This being said, it is also true that the EU has been a prolific negotiator over the past few decades. And it turns out that the UK has benefited the most out of this trade policy.
