
The formula for cost-benefit analysis can be calculated by using the following steps:
- Firstly, Calculate all the cash inflow from the subject project, which is either revenue generation or savings due to operational efficiency.
- Next, Calculate all the cash outflow into the project, which are the costs incurred in order to maintain and keep the project up and running.
- Next, Calculate the discounting factor based on the current pricing of assets with a similar risk profile.
- Next, based on the discounting factor, calculate the present value of all the cash inflow and outflow. ...
- Now, the formula for a benefit-cost ratio can be derived by dividing aggregate of the present value of all the expected benefits (step 4) by aggregate of the ...
- Now, the formula for net present value can be derived by deducting the sum of the present value of all the associated costs (step 4) from the sum ...
How do you calculate cost benefit?
Benefit-Cost Ratio = ∑PV of all the Expected Benefits / ∑PV of all the Associated Costs Step 6: Now, the formula for net present value can be derived by deducting the sum of the present value of all the associated costs (step 4) from the sum of the present value of all the expected benefits (step 4) as shown below.
What are some examples of cost benefit analysis?
Examples of Cost-Benefit Analysis. An example of Cost-Benefit Analysis includes Cost-Benefit Ratio where suppose there are two projects where project one is incurring a total cost of $8,000 and earning total benefits of $ 12,000 whereas on the other hand project two is incurring costs of Rs. $11,000 and earning benefits of $ 20,000, therefore, by applying cost-benefit analysis the Cost-Benefit ...
How to calculate benefit cost?
- Up to 85% of your Social Security may be taxable.
- If your provisional income is above $25,000 as a single filer or $32,000 as a joint filer, you may owe federal income taxes.
- You can pay estimated taxes quarterly, through benefit withholdings, or in full with your federal tax return.
How to do a cost analysis?
How high do petrol prices need to go to make electric cars more affordable?
- Supply a bigger speed hump. Consultancy Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) said even if rising petrol prices drove people towards electric cars, they might not be able to get one ...
- Governments drive change. ...
- No incentives for automakers. ...
- Up-front costs more important. ...
- EV rush later this decade. ...
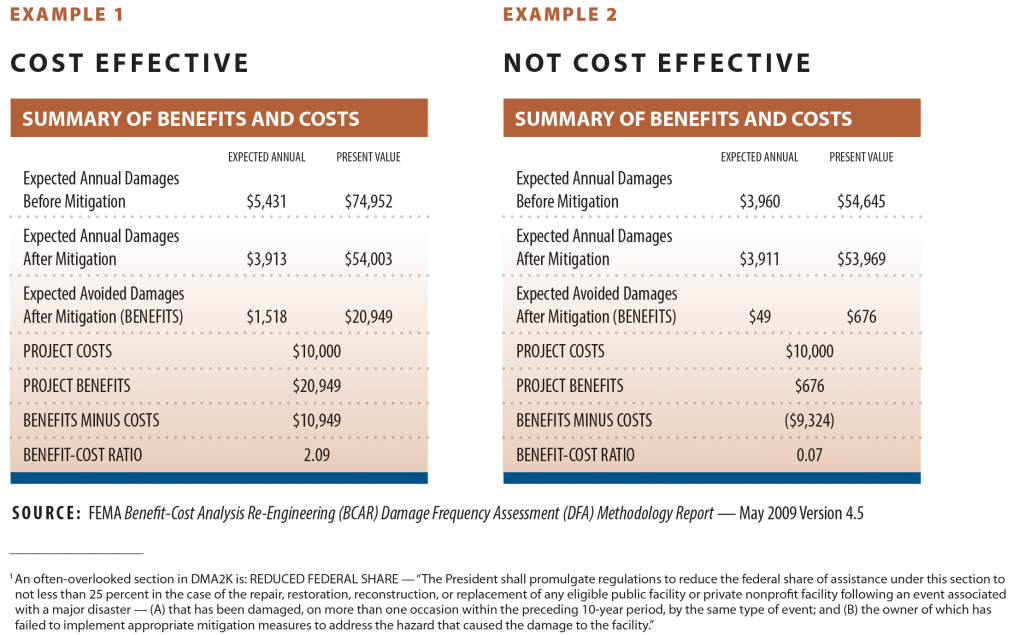
What is a cost-benefit analysis example?
For example: Build a new product will cost 100,000 with expected sales of 100,000 per unit (unit price = 2). The sales of benefits therefore are 200,000. The simple calculation for CBA for this project is 200,000 monetary benefit minus 100,000 cost equals a net benefit of 100,000.
How do you calculate NPV in cost-benefit analysis?
NPV is calculated by subtracting the discounted costs from the discounted benefits. All projects with a positive NPV provide a net economic benefit. NPV should be used when comparing mutually exclusive project options.
How do I calculate BCR in Excel?
ExamplesThe formula for Calculating BCR = PV of Benefit expected from the Project / PV of the cost of the Project.Project B.Step 2: Insert the relevant formula in cells C10 and C11.Step 3: Insert formula =B9*C9 in cell D9.Step 4: Drag the formula from cell D9 up to D11.More items...
How do you calculate PVR in Excel?
The PVR can be calculated by dividing the NPV of a project by the net present value of the capital expenditure outflows, discounted at the same rate as used for the NPV valuation.
What is cost benefit ratio formula?
The benefit-cost ratio formula is the discounted value of the project's benefits divided by the discounted value of the project's costs: BCR = Discounted value of benefits/ discounted value of costs.
How do you calculate NPV and BCR?
There are two main criteria used for evaluating projects in Benefit: Cost Analysis (BCA): the Net Present Value (NPV = benefits minus costs) and the Benefit: Cost Ratio (BCR = benefits divided by costs).
What is a cost-benefit analysis PDF?
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) measures a project's societal value by quantifying the project's societal effects and making costs and benefits comparable in monetary terms. CBA is the most widely applied tool for the appraisal of transport projects.
What is cost benefit analysis?
The term “cost-benefit analysis” refers to the analytical technique that compares the benefits of a project with its associated costs. In other words, all the expected benefits out a project are placed on one side of the balance and the costs that have to be incurred are placed on the other side. The cost-benefit analysis can be executed ...
How to calculate cash inflow from a project?
Step 1: Firstly, Calculate all the cash inflow from the subject project, which is either revenue generation or savings due to operational efficiency. Step 2: Next, Calculate all the cash outflow into the project, which are the costs incurred in order to maintain and keep the project up and running.
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost-benefit analysis is a form of data-driven decision-making most often utilized in business, both at established companies and startups. The basic principles and framework can be applied to virtually any decision-making process, whether business-related or otherwise.
What are the limitations of cost-benefit analysis?
Limitations of Cost-Benefit Analysis 1 It’s difficult to predict all variables: While cost-benefit analysis can help you outline the projected costs and benefits associated with a business decision, it’s challenging to predict all the factors that may impact the outcome. Changes in market demand, materials costs, and global business environment can occasionally be fickle and unpredictable, especially in the long term. 2 It’s only as good as the data used to complete it: If you’re relying on incomplete or inaccurate data to finish your cost-benefit analysis, the results of the analysis will be similarly inaccurate or incomplete. 3 It’s better suited to short- and mid-length projects: For projects or business decisions that involve longer timeframes, cost-benefit analysis has greater potential of missing the mark, for several reasons. It typically becomes more difficult to make accurate predictions the further out you go. It’s also possible that long-term forecasts will not accurately account for variables such as inflation, which could impact the overall accuracy of the analysis. 4 It removes the human element: While a desire to make a profit drives most companies, there are other, non-monetary reasons an organization might decide to pursue a project or decision. In these cases, it can be difficult to reconcile moral or “human” perspectives with the business case.
What happens if you don't give all the costs and benefits a value?
If you don’t give all the costs and benefits a value, then it will be difficult to compare them accurately. Direct costs and benefits will be the easiest to assign a dollar amount to. Indirect and intangible costs and benefits, on the other hand, can be challenging to quantify.
What are intangible costs?
Intangible Costs: These are any costs that are difficult to measure and quantify. Examples may include decreases in productivity levels while a new business process is rolled out, or reduced customer satisfaction after a change in customer service processes that leads to fewer repeat buys.
What are indirect costs?
Other cost categories you must account for include: Indirect Costs: These are typically fixed expenses, such as utilities and rent, that contribute to the overhead of conducting business. Intangible Costs: These are any costs that are difficult to measure and quantify.
How to make an analysis more accurate?
1. Establish a Framework for Your Analysis. For your analysis to be as accurate as possible, you must first establish the framework within which you’re conducting it. What, exactly, this framework looks like will depend on the specifics of your organization.
Is cost benefit analysis difficult?
It’s difficult to predict all variables: While cost-benefit analysis can help you outline the projected costs and benefits associated with a business decision, it’s challenging to predict all the factors that may impact the outcome. Changes in market demand, materials costs, and global business environment can occasionally be fickle and unpredictable, especially in the long term.
Why is cost benefit analysis useful?
This makes it useful for higher-ups who want to evaluate their employees’ decision-making skills, or for organizations who seek to learn from their past decisions — right or wrong .
What is cost benefit ratio?
Cost benefit ratio is the ratio of the costs associated with a certain decision to the benefits associated with a certain decision. It’s more commonly known as benefit cost ratio, in which case the ratio is reversed (benefits to costs, instead of costs to benefits). Since both costs and benefits can be expressed in monetary terms, ...
How is the cost and benefit tool used?
It’s made possible by placing a monetary value on both the costs and benefits of a decision. Some costs and benefits are easy to measure since they directly affect the business in a monetary way.
Is cost benefit analysis a guiding tool?
In these cases, consider cost benefit analysis as a guiding tool, but look to other business analysis techniques to support your conclusion.
Can cost benefit ratios be numerically expressed?
Since both costs and benefits can be expressed in monetary terms, these ratios can also be expressed numerically. As a result, cost benefit or benefit cost ratios lend themselves well to comparison, which is why cost benefit analysis can be used to compare two or more definitions. The process is simple. For each decision or path in question, ...
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost benefit analysis is a powerful but simple tool that allows a business to determine whether or not to make a change. It takes into account both the assumed risks and costs associated with a project, as well as the immediate and future benefits. The changes the analysis deals with are often projects, such as constructing a new office, ...
Why assign dollar amounts to intangibles?
It is not easy to assign a monetary benefit to saving a piece of the environment, but it is possible. Employee benefits will make employees happier , which will make them more loyal and productive , and also increase the retention rate, meaning your business will be more consistently productive.
Is cost benefit analysis necessary?
In a simple cost benefit analysis, it is not necessary to do this, but it makes the process more accurate. Intangibles may be things such as the amount of land saved from pollution, improved quality of life in the workplace or an increase in employee benefits. Assign dollar amounts to the intangibles. It is not easy to assign a monetary benefit ...
What is cost benefit analysis?
A cost benefit analysis (also known as a benefit cost analysis) is a process by which organizations can analyze decisions, systems or projects, or determine a value for intangibles. The model is built by identifying the benefits of an action as well as the associated costs, and subtracting the costs from benefits.
Why do organizations use cost benefit analysis?
Organizations rely on cost benefit analysis to support decision making because it provides an agnostic, evidence-based view of the issue being evaluated—without the influences of opinion, politics, or bias. By providing an unclouded view of the consequences of a decision, cost benefit analysis is an invaluable tool in developing business strategy, ...
What are the risks and uncertainties of cost benefit analysis?
These risks and uncertainties can result from human agendas, inaccuracies around data utilized, and the use of heuristics to reach conclusions.
What is sensitivity analysis?
Kaplan recommends performing a sensitivity analysis (also known as a “what-if”) to predict outcomes and check accuracy in the face of a collection of variables. “Information on costs, benefits, and risks is rarely known with certainty, especially when one looks to the future,” Dr. Kaplan says. “This makes it essential that sensitivity analysis is carried out, testing the robustness of the CBA result to changes in some of the key numbers.”#N#EXAMPLE of Sensitivity Analysis#N#In trying to understand how customer traffic impacts sales in Bob’s Pie Shop, in which sales are a function of both price and volume of transactions, let’s look at some sales figures:
What is the difference between tangible and intangible costs?
Tangible costs are easy to measure and quantify, and are usually related to an identifiable source or asset, like payroll, rent, and purchasing tools. Intangible cost s are difficult to identify and measure, like shifts in customer satisfaction, and productivity levels.
What is direct cost?
Direct costs are often associated with production of a cost object (product, service, customer, project, or activity) Indirect costs are usually fixed in nature, and may come from overhead of a department or cost center.
Is there a standard format for cost benefit analysis?
While there is no “standard” format for performing a cost benefit analysis, there are certain core elements that will be present across almost all analyses. Use the structure that works best for your situation or industry, or try one of the resources and tools listed at the end of this article.
What is cost benefit analysis?
A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a process that is used to estimate the costs and benefits of decisions in order to find the most cost-effective alternative. A CBA is a versatile method that is often used for the business, project and public policy decisions. An effective CBA evaluates the following costs and benefits:
What to consider when comparing cost-benefit cash flows?
For this reason, you’ll need to consider the time value of money, discount rate, net present value when comparing cost-benefit cash flows.
What is the purpose of CBA?
There are two main purposes in using CBA: To determine if the project business case is sound, justifiable and feasible by figuring out if its benefits outweigh costs. To offer a baseline for comparing projects by determining which project’s benefits are greater than its costs.
What is a CBA project?
Project managers strive to control costs while getting the highest return on investment and other benefits for their business or organization. A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is just what they need to help them do that. In a project, there is always something that needs executing, and every task has a cost and expected benefits.
What is sensitivity analysis?
A sensitivity analysis is a probability method used in management and business to determine how uncertainty affects your decisions, costs and profits.#N#In a project management CBA, sensitivity analysis is used to determine the benefit-cost ratio of probable scenarios. You can use Excel or more specialized software to do sensitivity analyses.
Can you compare current monetary value with future rate?
As mentioned on the last step, you can’t compare the current monetary value of costs and benefits with future rates. That’s why you’ll have to calculate the time value of money, discount rate, and net present value of cash flows.
Can you do cost benefit analysis without outlining expenses?
You can’t do a cost-benefit analysis without outlining all your expenses first. That’s where our free project budget template comes in. It helps you capture all the expenses related to your project from labor costs, consultant fees, the price of raw materials, software licenses and travel.
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost benefit analysis (CBA) is a systematic method for quantifying and then comparing the total costs to total expected rewards of undertaking a project or making an investment. If the benefits greatly outweigh the costs, the decision should go ahead; otherwise it should probably not.
What are direct costs?
Direct costs would be direct labor involved in manufacturing, inventory, raw materials, manufacturing expenses. Indirect costs might include electricity, overhead costs from management, rent, utilities. Intangible costs of a decision, such as the impact on customers, employees, or delivery times.
What are the forecasts used in a CBA?
The forecasts used in any CBA might include future revenue or sales, alternative rates of return, expected costs, and expected future cash flows. If one or two of the forecasts are off, the CBA results would likely be thrown into question, thus highlighting the limitations in performing a cost-benefit analysis.
Why factor opportunity costs?
Factoring in opportunity costs allows project managers to weigh the benefits from alternative courses of action and not merely the current path or choice being considered in the cost-benefit analysis.
What is a CBA?
A CBA involves measurable financial metrics such as revenue earned or costs saved as a result of the decision to pursue a project. A CBA can also include intangible benefits and costs or effects from a decision such as employee morale and customer satisfaction. 1:39.
What is cost analysis?
Cost analysis, also known as cost-benefit analysis, is the process of calculating the potential earnings from a situation or project, then subtracting the total cost associated with completing that situation or project.
Why is cost analysis important?
Here are several reasons why cost analysis is important for businesses:
How to calculate cost analysis
Follow these steps to assist you in calculating a cost analysis ratio:
What is cost analysis?
Cost analysis is one of four types of economic evaluation (the other three being cost-benefit analysis, cost-effectiveness analysis, and cost-utility analysis). Conducting a cost analysis, as the name implies, focuses on the costs of implementing a program without regard to the ultimate outcome. A cost analysis is an important first step ...
How to keep cost analysis continuity?
If your organization has done cost analyses in the past, use the same or similar methods to categorize costs. Maintaining continuity in this way means the reports can be compared, making them more useful over time.
What is indirect cost?
Indirect costs include general administration or management salaries and benefits, facilities, equipment, and anything else shared across multiple programs or services. What you categorize as an indirect cost will depend on how you have separated the programs or services offered by your organization.
What is a narrower cost analysis?
On the other hand, a narrower or more specific purpose, such as determining whether to bill for a particular service (and how much), might require a narrower cost analysis that only addressed the costs of that particular service.
Is depreciation included in total costs?
If your organization's capital assets, including furniture, equipment, or fixtures, must be used to implement the program or provide the service you're evaluating, depreciation of those assets should be included in your total costs for the program or service. Calculating depreciation can be a complicated endeavor.

Examples of Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula
- Let’s see some simple to advanced practical examples of the cost-benefit analysis equation to understand it better.
Relevance and Uses
- Cost-benefit analysis is useful in making decisions on whether to carry out a project or not. Decisions like whether to shift to a new office, which sales strategy to implement are taken by carrying out a cost-benefit analysis. Generally, it is used for carrying out long term decisions that have an impact over several years. This method can be used by organizations, government as w…
Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula in Excel
- The CFO of Housing Star Inc. gives the following information related to a project. Costs of $1,80,000 are to be incurred upfront at the start of 2019, which is the date of evaluation of the project. Use a discounting rate of 4% to determine whether to go ahead with the project based on the Net Present Value (NPV) method. Solution: Step 1: Insert the formula =1/(1+0.04)^A9 in cell …
Recommended Articles
- This article has been a guide to the Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula. Here we provide a calculation of cost-benefit analysis along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can learn more about accounting and budgeting from the following articles – 1. Cost-Benefit Principle Examples 2. Standard Error Formula 3. Formula to Calculate Gain 4. Examples of Cost-…
What Is A Cost-Benefit Analysis?
- A cost-benefit analysisis the process of comparing the projected or estimated costs and benefits (or opportunities) associated with a project decision to determine whether it makes sense from a business perspective. Generally speaking, cost-benefit analysis involves tallying up all costs of a project or decision and subtracting that amount from the total projected benefits of the project o…
How to Conduct A Cost-Benefit Analysis
- 1. Establish a Framework for Your Analysis
For your analysis to be as accurate as possible, you must first establish the framework within which you’re conducting it. What, exactly, this framework looks like will depend on the specifics of your organization. Identify the goals and objectives you’re trying to address with the proposal. W… - 2. Identify Your Costs and Benefits
Your next step is to sit down and compile two separate lists: One of all of the projected costs, and the other of the expected benefits of the proposed project or action. When tallying costs, you’ll likely begin with direct costs, which include expenses directly related to the production or develo…
Pros and Cons of Cost-Benefit Analysis
- There are many positive reasons a business or organization might choose to leverage cost-benefit analysis as a part of their decision-making process. There are also several potential disadvantages and limitations that should be considered before relying entirely on a cost-benefit analysis.