
Feedback inhibition allows the body to avoid many potentially dangerous situations, including:
- Waste. Without feedback inhibition, energy or raw materials that could be used for important cellular functions might be wasted on unnecessary ones.
- Prevents depletion. ...
- Prevents dangerous build-up. ...
- Maintain homeostasis. ...
What are some examples of feedback inhibition?
This one slowing the enzyme and many
- Review of Enzymes. Ever made a cup from clay? ...
- Feedback Inhibition. Enzymes are very important in speeding up product formation. ...
- Examples. There are many steps to change the amino acid threonine into isoleucine, and the first enzyme involved is threonine deaminase.
- Lesson Summary. ...
How does feedback inhibition regulate a biological pathway?
What are the Similarities Between Feedback Inhibition and Feedback Repression?
- Feedback inhibition and feedback repression are two types of enzyme inhibition mechanisms.
- In both methods, the accumulated end products work for the inhibition of the enzyme.
- These methods control the production of end products of the biochemical pathways.
How does feedback inhibition work in the endocrine system?
How does negative and positive feedback work in the endocrine system? Most hormones are controlled by negative feedback, in which the hormone feeds back to decrease its own production. This type of feedback brings things back to normal whenever they start to become too extreme.
What are feedback mechanisms regulate the rate of enzyme activity?
Ø Feedback inhibition is a specific type of allosteric enzymatic activity regulation mechanism in cells Ø Feedback inhibition definition: in some multi-enzyme pathways, the regulatory enzyme is specifically inhibited by the end product of the pathway whenever the concentration of the end product exceeds the cell’s requirements
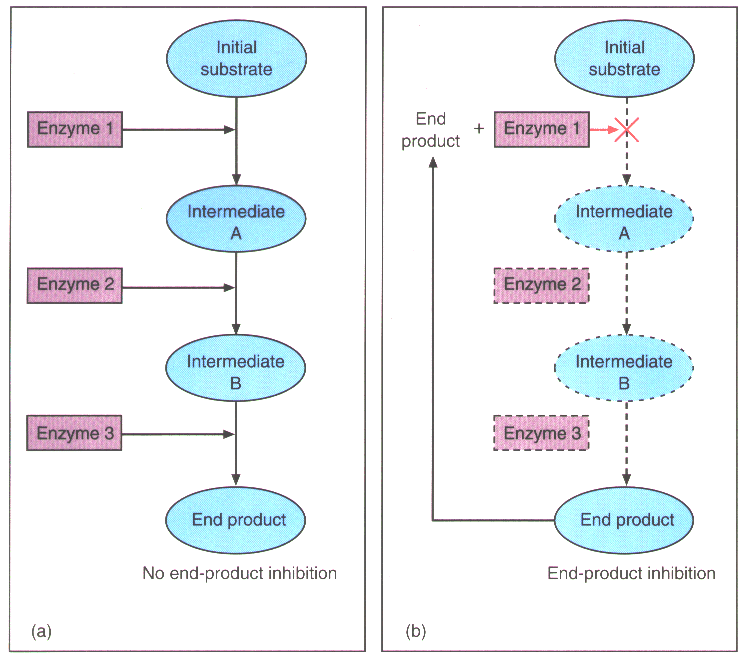
How does enzyme feedback inhibition benefit a cell quizlet?
How does enzyme feedback inhibition benefit a cell? Feedback inhibition benefits the cell by blocking the production of the products by changing the configuration of enzymes. This will prevent the cells from becoming toxic.
What is feedback inhibition and why is it an advantage in cells?
Feedback inhibition benefits the cell by blocking the production of the reactants by changing the configuration of enzymes. This will prevent the cells from becoming toxic.
What is feedback inhibition and what role does it play in metabolism?
Feedback Inhibition in Metabolic Pathways Feedback inhibition is when a reaction product is used to regulate its own further production. Cells have evolved to use feedback inhibition to regulate enzyme activity in metabolism, by using the products of the enzymatic reactions to inhibit further enzyme activity.
How is feedback inhibition important to the body systems?
Feedback inhibition is also necessary to prevent enzymes from breaking down too many molecules that are energy sources for the cell, such as glucose. Inhibition takes place in glycolysis, the process of breaking down the sugar glucose to produce the cell's "energy currency" molecule ATP.
Why is feedback inhibition important to organisms quizlet?
Feedback inhibition allows cells to control the amounts of metabolic products produced. If there is too much of a particular product relative to what the cell's needs, feedback inhibition effectively causes the cell to decrease production of that particular product.
How does feedback inhibition relate to cellular respiration?
ATP, for instance, is a "stop" signal: high levels mean that the cell has enough ATP and does not need to make more through cellular respiration. This is a case of feedback inhibition, in which a product "feeds back" to shut down its pathway.
What is enzyme feedback inhibition?
Definition of feedback inhibition : inhibition of an enzyme controlling an early stage of a series of biochemical reactions by the end product when it reaches a critical concentration.
Why is feedback inhibition important?
The result of feedback inhibition is This allows them to adjust their rate of reaction depending on how much of their end product is needed, and prevent their end product from building up to dangerous levels.
What is feedback inhibition?
Feedback inhibition is a cellular control mechanism in which an enzyme’s activity is inhibited by the enzyme’s end product. This mechanism allows cells to regulate how much of an enzyme’s end product is produced.
What happens when you break down too much ATP?
Producing too much ATP results in energy loss, and glucose depletion could mean big trouble in circumstances where food is scarce. To control the amount of glucose that is broken down to produce ATP, the first enzyme in this breakdown chain is allosterically regulated by ATP.
Why is it important to reduce cholesterol?
In the case of cholesterol, allosteric regulation is of a transcription factor that leads to more cholesterol-producing enzyme being made.
What happens when the end product drops?
When levels of the end product drop, the enzyme will encounter fewer particles of the end product and its activity will increase again. Feedback inhibition prevents waste that occurs when more of a product is made than the cell needs.
What is the site of an enzyme that catalyzes the transformation of one or more substrates into an end
Active Site – The site of an enzyme where it catalyzes the transformation of one or more substrates into an end product. Allosteric Site – A site on an enzyme that changes the enzyme’s shape and activity when a molecule, such as a feedback inhibitor, binds to it.
What happens to energy without feedback inhibition?
Without feedback inhibition, energy or raw materials that could be used for important cellular functions might be wasted on unnecessary ones. Prevents depletion. Without feedback inhibition, raw materials and energy might be depleted by biochemical processes that don’t stop, even when their end product is not needed.
Why is feedback inhibition important?
Feedback inhibition is also necessary to prevent enzymes from breaking down too many molecules that are energy sources for the cell, such as glucose. Inhibition takes place in glycolysis, the process of breaking down the sugar glucose to produce the cell's "energy currency" molecule ATP.
How does feedback inhibition affect the body?
Feedback inhibition can have a major impact if it shuts off, or if the inhibitor product is synthesized despite the inhibition. For example, cholesterol is synthesized in the body and is regulated by silencing the enzyme that uses the sterol compounds to produce cholesterol.
Why do enzymes have a second active site?
These enzymes have a second active site for the reaction product to bind to. This causes the enzyme to spatially re-arrange so it can no longer bind to the initial reagent and the reaction stops. Sometimes, the enzymes -- such as pyruvate kinase, which helps break down glucose -- are also chemically modified to halt the reaction.
What is feedback inhibition?
Feedback inhibition occurs when the end product of a reaction interferes with the enzyme that helped produce it. The inhibitor does this by binding to a second active binding site that's different from the one attached to the initial reactant. The enzyme then changes its shape and can't catalyze the reaction anymore.
How does ATP slow down enzymes?
ATP slows down the enzymes until they're structurally modified and stop catalyzing reactions. The enzymes are inhibited when blood glucose levels are low, so there isn't a total depletion and the cell then has a chance to accumulate more glucose for later use.
What happens when the enzyme threonine deaminase is inhibited?
If the reaction weren't shut off, the enzyme couldn't synthesize other amino acids that the cell needs. However, the reaction restarts when there is not enough isoleucine.

Feedback Inhibition Definition
Examples of Feedback Inhibition
- Production of ATP
ATP is created from glucose via a series of enzymatic reactions in our cells. Glucose is a stable form of energy currency, which can be absorbed from food or transported around the body as needed. ATP, on the other hand, is unstable, and will spontaneously lose its energy if it sits arou… - Production of Amino Acids
The human body uses twenty different amino acids– the “building blocks” of protein. All amino acids share some common features, and some are very similar to each other. This means that different amino acids are made from the same raw materials. However, the cell may need differ…
Related Biology Terms
- Active Site– The site of an enzyme where it catalyzes the transformation of one or more substrates into an end product.
- Allosteric Site – A site on an enzyme that changes the enzyme’s shape and activity when a molecule, such as a feedback inhibitor, binds to it.
- Enzyme– A protein that catalyzes the chemical change of one or more substrates into one o…
- Active Site– The site of an enzyme where it catalyzes the transformation of one or more substrates into an end product.
- Allosteric Site – A site on an enzyme that changes the enzyme’s shape and activity when a molecule, such as a feedback inhibitor, binds to it.
- Enzyme– A protein that catalyzes the chemical change of one or more substrates into one or more products. Enzymes drastically increase the speed of chemical reactions, making life as we know it pos...
Quiz
- 1. Which of the following would NOT qualify as feedback inhibition? A. An enzyme is inhibited by its own end product. B. The first enzyme in a biochemical pathway is inhibited by the end product of the last enzyme in the pathway. C. The cell detects that there is too much of a substance in its cytoplasm, so it makes a chemical messenger to inhibit the enzyme that’s making it. D.None of t…