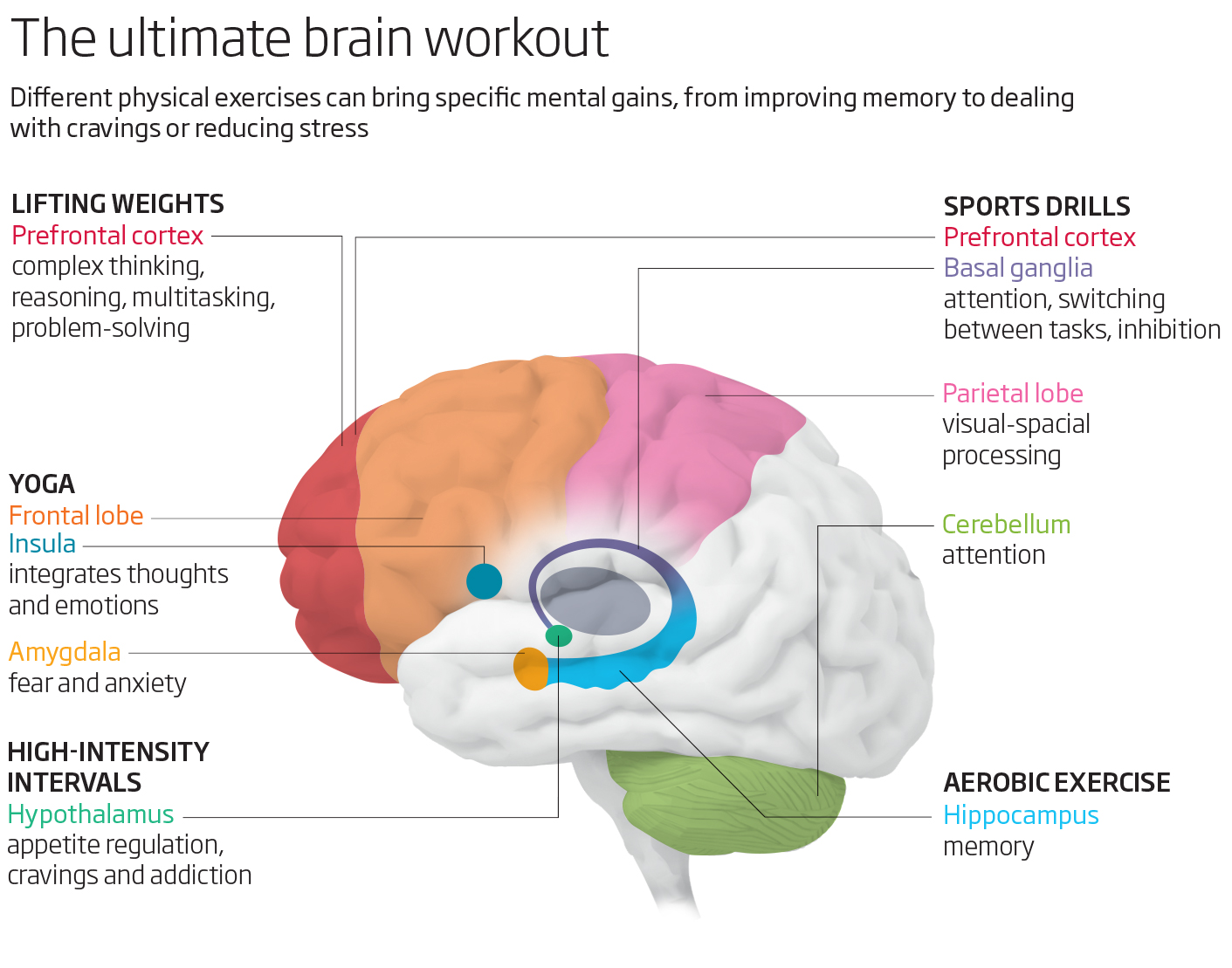
What kind of exercise is best for the brain?
The Benefits of Neurobic Brain Exercises
- Switch Hands. If you are right-handed, try using your left hand to do things like brushing your teeth, eating, and using your computer mouse.
- Eat With Chopsticks. This will force you to eat mindfully which is good for your brain, digestion, and calorie consumption.
- Do Chores With Your Eyes Closed. ...
- Do Things Upside Down or Backwards. ...
- Read Books Aloud. ...
How does exercising your body give your brain a workout?
Part 1 of 5: Enhancing Your Thinking and Word Skills
- Read as much as you can. Reading is great brain exercise. ...
- Increase your vocabulary. You can also learn new words from a word-a-day calendar or dictionary. ...
- Write something. Writing requires loads of thinking! ...
- Learn a new language. ...
- Post-problem solve. ...
- Turn off the television. ...
- Use your non-dominant hand. ...
- Learn to play a musical instrument. ...
What are the best exercises for the brain?
To test this theory, try this cognitive-boosting activity:
- Keep a notebook with you when you read.
- Write down one unfamiliar word, then look up the definition.
- Try to use that word five times the next day.
What kind of exercise benefits your brain most?
Science of Exercise and the Brain
- Exercise Increases the Size of the Hippocampus. The area of your brain responsible for learning and verbal memory is called the hippocampus. ...
- Working Out Reduces Stress Hormones that Inhibit Brain Activity. Many people seek solace from stress in a walk or jog. ...
- Sleep Improves With Exercise. ...
- Aerobic Exercise Triggers the Release of Growth Factors. ...

Why is exercise important for the brain?
Exercise also induces the release of beneficial proteins in the brain. These nourishing proteins keep brain cells (also known as neurons) healthy, and promote the growth of new neurons. Neurons are the working building blocks of the brain. As a result, individual neuron health is important to overall brain health.
How can physical activity improve memory?
There are a number of mental abilities that are improved with regular exercise: Physical activity can improve your long-term and short-term memory. Children and young adults who were asked to exercise just a few times a week showed big improvements in their ability to remember what they read.
Why is neuron health important?
As a result, individual neuron health is important to overall brain health . Exercise boosts your mood and reduces stress . When you exercise, your body releases chemicals such as dopamine (pronounced doh-pa-meen) and endorphins (en-door-fins) in your brain that make you feel happy. Not only is your brain dumping out feel-good chemicals, ...
Why is being active important?
Being active gives you more energy during the day and helps you sleep better at night. In turn , better sleep improves creativity and brain function. Being active gives you more energy during the day and helps you sleep better at night. In turn , better sleep improves creativity and brain function.
How to keep your mind sharp?
According to experts, the recommended amount of exercise to keep your mind sharp is about an hour a day. One of the best ways to get exercise is to play sports. Being on a team can build self-confidence, and regular practice schedules are good for your health.
What are some examples of exercise?
A few other examples of exercise are: dancing, walking, biking, swimming, or throwing a Frisbee.
Does exercise help with anger?
People who exercise tend to be happier and less stressed than those who don’t exercise. Regular exercise can also help you control your emotions when you do feel angry or upset. Exercise may improve your grades. That’s right! Exercise has been shown to improve mental abilities.
Effects of Exercise on Your Brain
To begin explaining the positive effects of exercise on your brain, a simple understanding of something called brain-derived neurotrophic factor, or BDNF, is helpful.
Best Exercise for Your Brain
From a clinical research perspective, some preliminary comparisons between moderate-intensity continuous training, or MICT, and high-intensity interval training, or HIIT, suggest increased BDNF in circulation after HIIT compared to MICT.
Long-Term Effects of Exercise on Your Mental Health
The long-term effects of exercise on the brain and mental health are also incredible. In general terms, exercise increases concentrations of dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, all of which contribute to an individual’s sense of well-being, memory enhancement and reward sensations.
Cognitive Benefits of Exercise on the brain
Executive functions include inhibition, planning, shifting, etc. Regarding benefits of exercise on the brain, researchers have found that healthy people who engage in exercise optimize their higher order brain functions.
Psychological Benefits of Exercise on the brain
Ever heard of the “runner’s high”? Well, it’s a real thing! Endorphins are the body’s own pain killers, causing you to feel happy after intense exercise. The body also releases a chemical called endocannabinoid, which causes feelings of calmness after challenging exercise.
Neurobiological Benefits of Exercise on the brain
Your brain is the most important organ in your body as we explained previously. Exercise enhances the connections in your brain and helps neuroplasticity develop and maintain itself.
Benefits of Exercise on the brain- Choosing the right workout
Choosing the right type of exercise can pose a difficult task. Here are a few questions to help you get on track to achieve all the benefits of exercise on the brain.
Why is physical activity important?
Regular physical activity is an important part of a healthy lifestyle. Not only is it good for your muscles and bones, it can keep your brain healthy, too. Physical activity can improve your cognitive health— helping you think, learn, problem-solve, and enjoy an emotional balance. It can improve memory and reduce anxiety or depression.
What to do when you have cognitive decline?
When adults with cognitive decline are not able to meet the physical activity guidelines, encourage them to do whatever regular physical activity they can and avoid inactivity. For example, patients with cognitive decline and their caregivers may take “buddy” walks in a park, their neighborhood, or a shopping mall.
How to reduce sedentary time?
For example, keep a list of quick activities, like squats or marching in place, near the remote so that you can be active during commercial breaks. Add physical activity into your daily routine. Walking is a good way to start being active.
Can older adults have cognitive decline?
Healthy older adults can have cognitive decline. Learn about the important health benefits of physical activity for healthy aging. Being active is easier than you may think. It doesn’t have to happen in one stretch. You can break up your activity across the week, and some activity is better than none.
Why is exercise important?
The beauty of exercise is that it provides us a powerful, socially acceptable way to demolish stress while pushing our bodies and minds to the limit. Some people hit the punching bag, others pound the pavement on long trail runs.
Is stress good for you?
Anxiety and depression aside, stress can be an entirely different animal. A little bit of stress is actually good for us, since it motivates us to succeed and stay focused. However, things can get a bit out of hand and stress can mount up over time into a genuine burden.
What actually happens to your brain when you work out?
Exercise can provide a way to maintain brain function, according to a study in the Trends in Neuroscience journal. The research shows that your session on the track or the treadmill increases the molecules in your brain that aid learning and protect against cognitive decline. Psychologist and mental game coach Dr.
Which exercise is best for the brain?
If you want to increase your gray matter, you need to be prepared to break a sweat. Dr Coffey said that exercises most beneficial to the brain are aerobic-style workouts. "Studies show that swimming and running seem to be best for brain health," said Coffey.
Can exercise improve your mood?
Whether you achieve the so called 'runner’s high', or not, exercise has been found to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. A study in the International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology found that the antidepressant effect of running is due to more cell growth in the hippocampus.
Why is exercise important for the brain?
Due to its high metabolic demand, the brain demands good circulation , and exercise aids it. An increase in blood flow is not only extremely beneficial, it is essential. Exercise induces good blood flow to deliver all the nutrients required to carry out the brain’s job, while it also increases production molecules important to brain function, ...
How does exercise improve memory?
Exercise improves memory by increasing molecular targets like the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). This molecular factor increases synaptogenesis, forming new synapses that mediate learning and memory, making it easier to absorb information and form long-term memories.
How does BDNF affect memory?
The more BDNF, the more the memory improves in function and capacity. If you aren’t motivated to work out, consider how priceless your memories are and start moving to preserve them. Exercise lowers stress impact. Exercise is not a direct solution to stress, but it does pacify the experience.
Does exercise decrease stress hormones?
It is important to note that exercise does not decrease stress hormones, but it does decrease the number of stress receptors in the hippocampus. Reducing stress receptors minimizes the effect of stress hormones on the brain, decreasing the impact of stressful experiences. The phenomenon most commonly known as “runner’s high” is another ...
Is exercise a good way to reduce stress?
Exercise is an indirect but effective treatment for stress. The Lifestyle series provides practical tips to enhance the quality of your every-day life through the outstanding scientific expertise and research of the faculty within the eight departments of the College of Life Sciences.
Does exercise improve cognition?
Exercise boosts physical capabilities and can even change physical appearance, but it also improves the condition of the brain and cognition. BYU cell biology and physiology professor Jeff Edwards’ research findings validate those new year’s resolutions to get the heart pumping and exercise more. He provides information on three ways ...
