
How does sleep affect your brain?
Sleep is important to a number of brain functions, including how nerve cells (neurons) communicate with each other. In fact, your brain and body stay remarkably active while you sleep. Recent findings suggest that sleep plays a housekeeping role that removes toxins in your brain that build up while you are awake.
Why does the brain need sleep?
Without sleep you can’t form or maintain the pathways in your brain that let you learn and create new memories, and it’s harder to concentrate and respond quickly. Sleep is important to a number of brain functions, including how nerve cells (neurons) communicate with each other. In fact, your brain and body stay remarkably active while you sleep.
How is sleep clears the brain?
- Skin
- Liver
- Lungs
- Kidneys
- Spleen
- Gall Bladder
- Lymphatic System
What happens to your brain when you sleep?
Scientific studies have shown that prolonged anxiety is correlated with cognitive decline and dementia later in life. On the food front, Dr. Díaz-Santos recommends prioritizing veggies, fruit, protein, fiber, and healthy fats—all of which are linked to supporting brain health both in the short- and long-term.
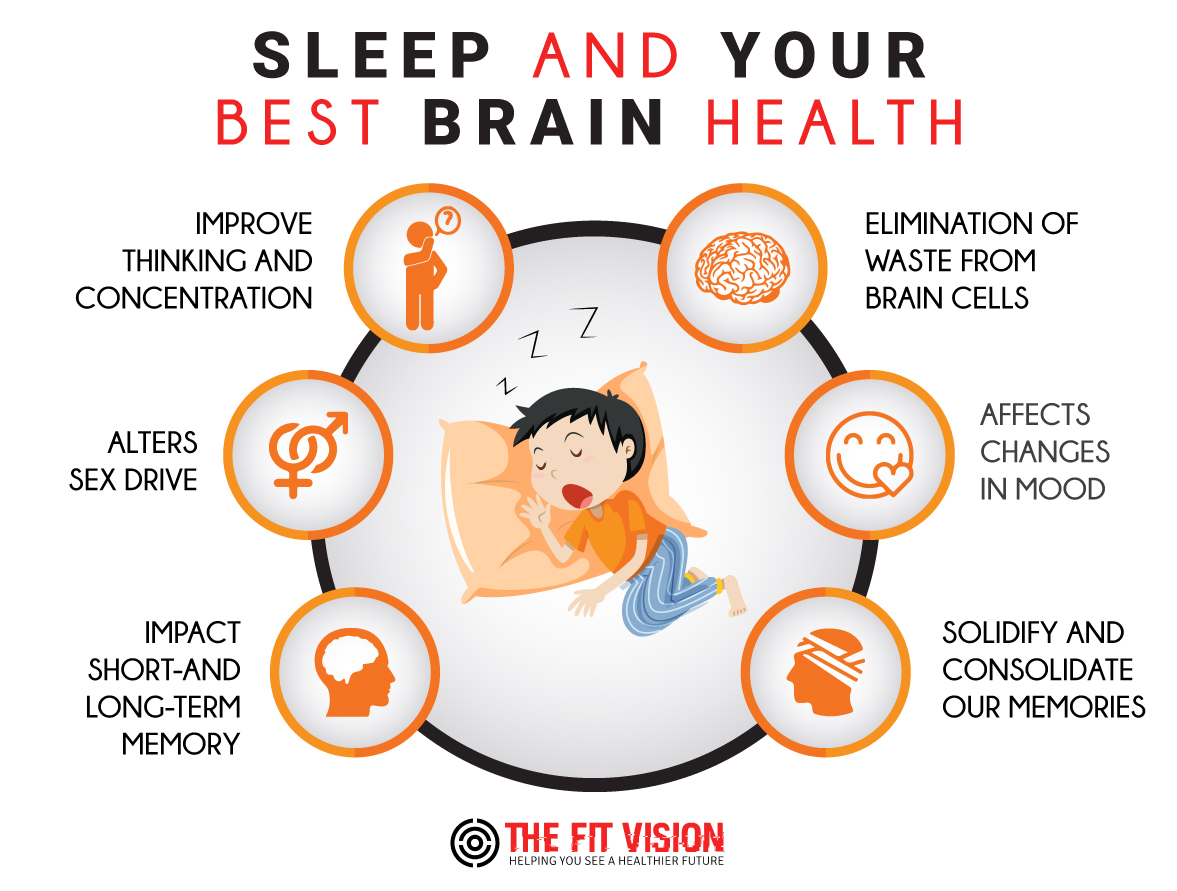
Why is sleep important?
Scientists and philosophers have long wondered why people sleep and how it affects the brain. Sleep is important for storing memories. It also has a restorative function. Lack of sleep impairs reasoning, problem-solving, and attention to detail, among other effects.
What is the system that drains waste products from the brain?
Dr. Maiken Nedergaard and her colleagues at the University of Rochester Medical Center recently discovered a system that drains waste products from the brain. Cerebrospinal fluid, a clear liquid surrounding the brain and spinal cord, moves through the brain along a series of channels that surround blood vessels.
Does the glymphatic system help with Alzheimer's?
The scientists also reported that the glymphatic system can help remove a toxic protein called beta-amyloid from brain tissue . Beta-amyloid is renowned for accumulating in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Other research has shown that brain levels of beta-amyloid decrease during sleep. In their new study, the team tested the idea ...
What happens to brain cells during sleep?
Brain cells operate similarly. When they're busy working and supporting normal function, they are not clearing material. During the sleep phase, they switch roles and get rid of waste products. Previous research seems to support these findings.
What is the Protected Brain?
The Protected Brain. This growing body of research not only reaffirms the importance of sleep; it also hints at potential new strategies for slowing the onset and progression of AD and cognitive impairment.
Why is it important to keep your bedroom dark?
Keeping your bedroom as dark as possible at night helps promote the production of melatonin and the onset of sleep (and getting enough sun during the day can help you stay alert and awake).
What does it mean when you snore and you have a daytime sleepiness?
If you have daytime sleepiness and you snore, you may have obstructive sleep apnea, which is very treatable. If your sleep problems persist, keep a sleep diary, noting the type of problems you're experiencing and when they occur. It will serve as a useful tool when you talk to your doctor.
What happens to interstitial space volume when mice are asleep?
The results: interstitial space volume increased by 60 percent when the mice were asleep. In addition, toxic waste products, including beta-amyloid, disappeared at twice the rate in the brains of sleeping mice compared to those who were awake.
How to fall asleep before hitting the sack?
Shut down your computer, cell phone, and yes, even the TV, at least an hour before you hit the sack. Some experts recommend hiding your clock, too. If you take a look at the clock mid-slumber, you transition from sleep to full awakening, and you've made it harder to fall back to sleep. Watch what and when you eat.
What percentage of Americans report not getting enough sleep?
More than 60 percent of Americans report their sleep needs aren't being met during a typical week. Illness, psychological distress, and medication can all interfere with adequate sleep. Add to that the normal physiological changes of the aging brain, and it's no wonder that older adults commonly complain of insomnia.
Why is sleep important?
Sleep Helps Your Brain Keep Your Body Looking Good. Seriously, they call it beauty rest for a reason. Sleep is the time that your brain gives the green light for releasing the growth hormone that your body uses to grow new cells and repair damaged tissue.
Why do we sleep?
Sleep Helps You Make Sense Of New Information. Believe it or not, your brain can actually process complex information when you’re sleeping. Experts have long known that your brain maintains some level of awareness even when your brain is fully engaged in the sleep process.
Why does sleep deprivation affect memory?
That’s because sleep deprivation interferes with your hippocampus, the part of your brain that’s responsible for processing memories. When you’re sleeping, your brain decides what stuff from the day is worth keeping—and what’s worth forgetting about so you can free up space for taking in new information tomorrow.
What happens during stage 5 of REM sleep?
During stage 5, you experience rapid eye movement (REM) that gives your brain and body the energy boost you’ll use to get through the day tomorrow. Since your brain is at its most active during REM sleep, this is also when you’ll have dreams (or nightmares, yikes!).
What is the time when your brain is prepping for the next day?
Sleep is really the time when your brain is prepping so you can be on your game for the next day —thinking fast without making mistakes, making smart choices, coming up with genius ideas, and more. Without adequate rest, your brain ends up on the fast track to going haywire.
Why do we need to snooze?
That’s because snooze time is prime time for your brain to get busy processing memories. As you sleep, your brain works to solidify memories that you formed throughout the day. It also links these new memories to older ones, helping you make connections between different pieces of information to come up with new ideas.
What are the stages of NREM sleep?
Your brain waves start to slow down. Stages 3 and 4. These are the last stages of NREM sleep. By now, you’re fully engrossed in the show and are getting your deepest, most restorative sleep. In this stage, your brain signals your body to let your blood pressure drop, slow down your breathing, and relax your muscles.
How sleep affects the brain
Sleep is governed by a small, almond-sized part of the brain called the hypothalamus. As well as regulating your body temperature, managing emotional responses and controlling appetite, it’s also responsible for releasing hormones and setting your internal body clock.
How to have healthier sleep habits
The key to a good night of sleep is mastering what’s called your ‘sleep hygiene’. Put simply, that’s all the things you need to put in place before bed in order to maximize your chances of sleeping soundly, ranging from putting your phone down well before bed to learning which is the best sleeping position.
How Much Sleep Do I Need?
You might be thinking that you’re sleeping an adequate amount each night. The truth is, you could be severely under-sleeping according to the current recommended sleep duration (2) for your age group.
Helps Improve your Health
Losing sleep can mean that your body is less prepared to fight off viruses, infections and can make you more susceptible to conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure (3). When you are tired your body produces more cortisol, a hormone that impacts stress. This hormone is also closely linked to heart attacks and heart disease.
Helps With Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer (6), among many other health concerns. Researchers have found that sleep deprivation can seriously impact your body’s inflammation levels, enough that people who sleep poorly are more likely to develop chronic inflammation.
Reduces Impact of Depression
Getting a good night’s sleep helps everyone feel refreshed and ready for the day ahead, but people who suffer from depression may experience an even greater benefit.
Reduces Impact of Anxiety
Anxiety disorders, which affect 20% of Americans (13), can substantially impact both health and well-being. As with many mental health conditions, anxiety disorders can also make it harder to sleep. Symptoms of anxiety (14), both physical and mental, can prevent people from getting the rest they need.
Helps With Weight
Exhausted adults who sleep less than their peers are more likely to be overweight or obese (18). A 2019 study found that making up for sleep debt by sleeping in during the weekend had no counter effects on weight gain (19), meaning that people who want to maintain a lower weight may want to consider making sleep a nightly priority.
Helps Improve Memory and Learning
If you want to do well on an upcoming test, you better make sure you’re getting enough sleep! Research shows that sleep directly impacts our ability to retain and learn new information (22). It also improves our mood, problem-solving ability, and overall memory.
