
- Add together the cost of an employee's fringe benefits for the year
- Divide it by the employee's annual salary
- Multiply the total by 100 to determine the percentage of fringe benefit rate
- Add together the cost of an employee's fringe benefits for the year.
- Divide it by the employee's annual salary.
- Multiply the total by 100 to determine the percentage of fringe benefit rate.
What is the average fringe benefit percentage?
per hour worked or 69.0 percent of total compensation, while benefit costs were $12.06 or 31.0 percent of total compensation. The average cost for health insurance benefits was $3.09 per hour worked or 8.0 percent of total compensation. (See charts 1 and 2, and table 1.) State and local government
What is the percentage of fringe benefits?
Typically, this percentage of annual wage or salary earnings is in the 20-30 percent range, but employer contributions to fringe benefits vary widely. They tend to be lower in smaller companies and in the service sector of the economy. They tend to be higher in larger companies, unionized companies, and in the manufacturing sector of the economy.
What is a prevailing wage fringe?
- Construction companies lose the opportunity to offer the most competitive bid
- Sub-standard employee benefit programs associated with competitive trade unions
- Non-compliance issues that can lead to major financial penalties, loss of the contract, and elimination from future project revenue.
Is paid holiday a fringe benefit?
In general, taxable fringe benefits are subject to withholding when they are made available. The employer may elect to treat taxable noncash fringe benefits as paid in a pay period, or on a quarterly, semiannual or annual basis, but no less frequently than annually. Ann. 85-113 . Alternative Rule for Income Tax Withholding
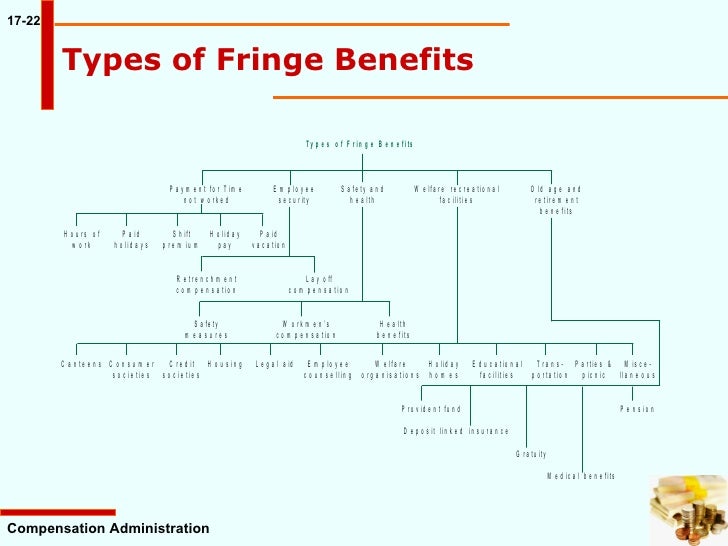
What is the current fringe benefit rate?
Current Fringe RatesDescriptionCoversFY 2024 & BEYONDFull FederalBenefits-eligible employees paid from Federal funds (direct federal and federal flow-through funds*.)26.9%Full Non-Federal^Benefits-eligible paid from non-Federal funds28.8%StatutoryTemporary employees, supplemental pay to regular employees6.5%3 more rows
How are fringe benefits granted calculated?
To determine the grossed-up value/tax base of the fringe benefit, the actual monetary value or the actual amount of benefit furnished, granted or paid shall be divided by sixty-five percent (65%) subject to 35% Fringe Benefit Tax (FBT) or the divisor shall be seventy-five percent (75%) subject to 25% FBT.
What is a typical fringe benefit?
Some of the most common examples of fringe benefits are health insurance, workers' compensation, retirement plans, and family and medical leave. Less common fringe benefits might include paid vacation, meal subsidization, commuter benefits, and more.
How do you calculate fringe benefits subject to FBT?
To calculate an employee's fringe benefit rate, add up the cost of an employee's fringe benefits for the year (including payroll taxes paid) and divide it by the employee's annual wages or salary. Then, multiply the total by 100 to get the fringe benefit rate percentage.
How do you calculate benefits for employees?
Calculating the benefit load — the ratio of perks to salary received by an employee — helps a business effectively plan. Find the benefit load by adding the total annual costs of all employees' perks and divide it by all employees' annual salaries to determine a ratio — that ratio is your company's benefits load.
Are fringe benefits taken out of salary?
Generally, fringe benefits are taxable to the employee, must be included as supplemental income on the employee's W-2, and are subject to withholding and employment taxes. The IRS provides guidance on fringe benefits in a publication titled Employer's Tax Guide to Fringe Benefits For Use in 2021.
What are the 7 fringe benefits?
These include health insurance, life insurance, tuition assistance, childcare reimbursement, cafeteria subsidies, below-market loans, employee discounts, employee stock options, and personal use of a company-owned vehicle.
What is fringe rate?
The fringe rate shows you how much an employee actually costs your business beyond their base wages. Fringe benefit rates vary from business to business. The rate depends on how much you pay employees and how much an employee receives in benefits. Although rates vary, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, ...
What are fringe benefits?
Fringe benefits are benefits employees receive in addition to their wages. Independent contractors and business partners can also receive fringe benefits (not taxed). Examples of fringe benefits include: Company car. Health insurance. Life insurance coverage.
Is fringe benefit taxable?
Although fringe benefits are typically taxable, some are nontaxable. Taxable fringe benefits can include personal use of a company car, bonus pay, and paid time off. Some nontaxable fringe benefits include group-term life insurance up to $50,000 and employee discounts.
How much is fringe benefits for employee one?
The value of their fringe benefits package is $3,200.
What is fringe benefit?
Fringe benefits are the variety of benefits some employers give to employees in addition to their hourly wage or salary. They can be offered to all employees or as a benefit to those in certain positions or with certain accomplishments. After you identify the fringe benefits you as an employer are offering, or the benefits you as an employee are ...
What are the disadvantages of fringe benefits?
2. Think about the disadvantages of offering fringe benefits. Especially if you are a small employer, fringe benefits may be prohibitively expensive to provide. For example, paying an employee's healthcare (or multiple employees) can become very expensive.
Why do employees prefer fringe benefits?
In addition, employees might prefer fringe benefits for the reduced tax liability when fringe benefits aren't taxed (while your sala ry will be ). For example, companies that provide health insurance can ensure their workforce stays healthy so they can come to work and be productive.
How to determine if a wage is fringe?
1. Determine what types of wages are required by law . If a wage is required by law, it will not be considered a fringe benefit. One easy way to identify fringe benefits is to eliminate the benefits you know are not fringe. Examples of non-fringe benefits include: Base wages and salaries; Payments to fund social security;
What are non-fringe benefits? What are some examples?
Examples of non-fringe benefits include: Base wages and salaries; Payments to fund social security; Unemployment compensation; and. Workers' compensation. [1] X Trustworthy Source US Department of Labor Federal department responsible for promoting the wellbeing of workers Go to source.
Is a company car a fringe benefit?
If your employer states you will have access to a company car, this would be a fringe benefit as well. In another example, your employment contract may state your employer will pay you a salary of $75,000 per year. This type of payment is required by law and will therefore not be considered a fringe benefit.
What is the average fringe benefit rate?
Under the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average fringe benefit rate is 30% .
What do you need to know about fringe benefits?
There are several fringe benefits out there like health insurance, employee stock options, etc. These fringe benefits can affect the fringe benefit rate.
What is the annual fringe benefit for an hourly employee?
The hourly employee has the following annual fringe benefits: $800 for unemployment tax. $2,200 for retirement benefits. $722 for worker's compensation. $754 for employer portion of Medicare tax. $3,224 for employer portion of Social Security tax. $3,740 for employee's life, disability, and health insurances.
What is fringe benefit?
A fringe benefit is a type of salary apart from money given for the performance of services by an employee. If a fringe benefit is given in the form of money like reimbursement or bonus for travel, it'll be subject to income tax. Some examples of fringe benefits are:
Is fringe income taxable?
Fringe benefits given to employees are taxable income for them unless tax law excludes them from taxation. Taxable fringe benefits must be included as income on the employee's W-2. Taxable fringe benefits are also subject to withholding. Fringe benefits are generally taxable, but some are tax-free.
What is the supplemental rate for fringe benefits?
The employer may elect to add taxable fringe benefits to employee regular wages and withhold on the total or may withhold on the benefit at the supplemental wage flat rate of 22% (for tax years beginning after 2017 and before 2026). Treas. Regs. 31.3402(g)-1 and 31.3501(a)-1T
What is fringe benefit?
De minimis fringe benefits include any property or service, provided by an employer for an employee, the value of which is so small in relation to the frequency with which it is provided, that accounting for it is unreasonable or administratively impracticable. The value of the benefit is determined by the frequency it’s provided to each employee, or, if this is not administratively practical, by the frequency provided by the employer to the workforce as a whole. IRC Section 132(e); Treas. Reg. Section 1.132-6(b)
What is wage recharacterization?
Generally, wage recharacterization occurs when the employer structures compensation so that the employee receives the same or a substantially similar amount whether or not the employee has incurred deductible business expenses related to the employer’s business. If an employer reduces wages by a designated amount for expenses, but all employees receive the same amount as reimbursement, regardless of whether expenses are incurred or are expected to be incurred, this is wage recharacterization. If wage recharacterization is present, the accountable plan rules have not been met, even if the actual expenses are later substantiated. In this case, all amounts paid are taxable as wages. For more information, see Revenue Ruling 2012-25.
How long does it take to return an excess?
If this method is used, substantiation and the return of excess must be made within 120 days after the employer provides the employee with a periodic statement (at least quarterly) stating that any excess amounts must be returned. Treas. Reg. Section 1.62-2(g)(2)(ii)
How to prevent financial hardship to employees traveling away from home on business?
To prevent a financial hardship to employees traveling away from home on business, employers often provide advance payments to cover the costs incurred while traveling. Travel advances may be excludable from employee wages if they are paid under an accountable plan. (Allowable travel expenses are discussed in Transportation Expenses) There must be a reasonable timing relationship between when the advance is given to the employee, when the travel occurs and when it is substantiated. The advance must also be reasonably calculated not to exceed the estimated expenses the employee will incur. Treas. Reg. Section 1.62-2(f)(1)
When to use per diem rate?
If the employee is traveling to more than one location in one day, use the per diem rate for the area where the employee stops for rest or sleep. Rev. Proc. 2011-47
Is fringe benefit taxable?
In general, taxable fringe benefits are subject to withholding when they are made available. The employer may elect to treat taxable noncash fringe benefits as paid in a pay period, or on a quarterly, semiannual or annual basis, but no less frequently than annually. Ann. 85-113
