
- Other post-retirement benefits include benefits that employees are paid when they retire that are not pension distributions.
- Employees often share the cost of these benefits through co-payments.
- Other post-retirement benefits might include dental, legal services, and tuition credit.
Do postal workers get a pension and Social Security?
Under CSRS, postal employees share in the cost of their retirement plans, thus contributing around 7-8% of their monthly paycheck towards their future. However, they do not pay any social security retirements as under the CSRS; they do not qualify for social security benefits.
What is the retirement age for US Postal Workers?
The standard age for retirement at the USPS is 65, and there are retirement plans placed under both Federal Employment Retirement System (FERS) and Civil Service Retirement System (CSRS) depending on whether service life began before or after 1984. Let’s take a look at both these systems to give you a clearer picture.
What happens to health benefits after retirement?
Qualified payments for which tax-free HSA withdrawals can be made include: 17
- Office-visit copayments
- Health insurance deductibles
- Dental expenses
- Vision care (eye exams and eyeglasses)
- Prescription drugs and insulin
- Medicare premiums
- A portion of the premiums for a tax-qualified long-term care insurance policy
- Hearing aids
- Hospital and physical therapy bills
- Wheelchairs and walkers
What is the average pension of a postal worker?
What is the average pension for a postal worker? As an example of USPS retirement in CSRS, postal workers with an average of 3 around $ 60,000 and 20 years of service earn $ 1,824 a month without deductions. That’s the same as $ 22,000 each year. Workers with the same salary and 40 years of service earn $ 3,837 monthly, or about $ 46,000 annually.

What is monthly post retirement benefit?
The amount of Post Retirement Benefit that you will receive depends on your earnings and your age. If you are 65, the maximum monthly CPP pension that you can receive in 2020 is $1,175.83, and the maximum monthly PRB is about 1/40th of that, or $29.40. The maximum annual PRB is $352.75.
What is post benefit?
Pensions and OPEBs (other post-employment benefits) are arrangements between employers and employees which aim to provide benefits to retired employees as a reward for their service during their working career. Post-employment benefits are also known as post-retirement benefits.
What provides post retirement benefits to employees?
Other post-retirement benefits are benefits, other than pension distributions, paid to employees during their retirement years. Post-retirement benefits may include life insurance and medical plans, or premiums for such benefits, as well as deferred-compensation arrangements.
What do you receive after retirement?
On average, retirement beneficiaries receive a portion of their pre-retirement income from Social Security. As you make your retirement plan, knowing the approximate amount you will receive in Social Security benefits can help you determine how much other retirement income you'll need to reach your goals.
What is post retirement benefit on t4a?
Post-Retirement Benefit - Information for employers The Post-Retirement Benefit (PRB) is a lifetime monthly benefit for employees who work in Canada outside Quebec while receiving a Canada Pension Plan (CPP) or Quebec Pension Plan (QPP) retirement pension.
Are post retirement health benefits taxable?
➢ Tax Reporting While the value of health care coverage provided to both active employees and retirees generally is not income taxable, employers, insurers and health plan sponsors must provide coverage information to employees and retirees and to the IRS.
What is post employment benefit obligation?
Other post-employment benefits (OPEB) are the benefits, other than pension distributions, that employees may begin to receive from their employer once they retire. Other post-employment benefits can include life insurance, health insurance, and deferred compensation.
What does post employment mean?
Post employment is a term used by the Government Accounting Standards Board in the reporting of benefits after a state, federal or local official leaves their position.
What are examples of retirement benefits?
The 5 Most Common Retirement BenefitsProfit-sharing plans. ... Pension plan. ... Fixed company contributions. ... Employee stock ownership plan. ... Stock bonus plans.
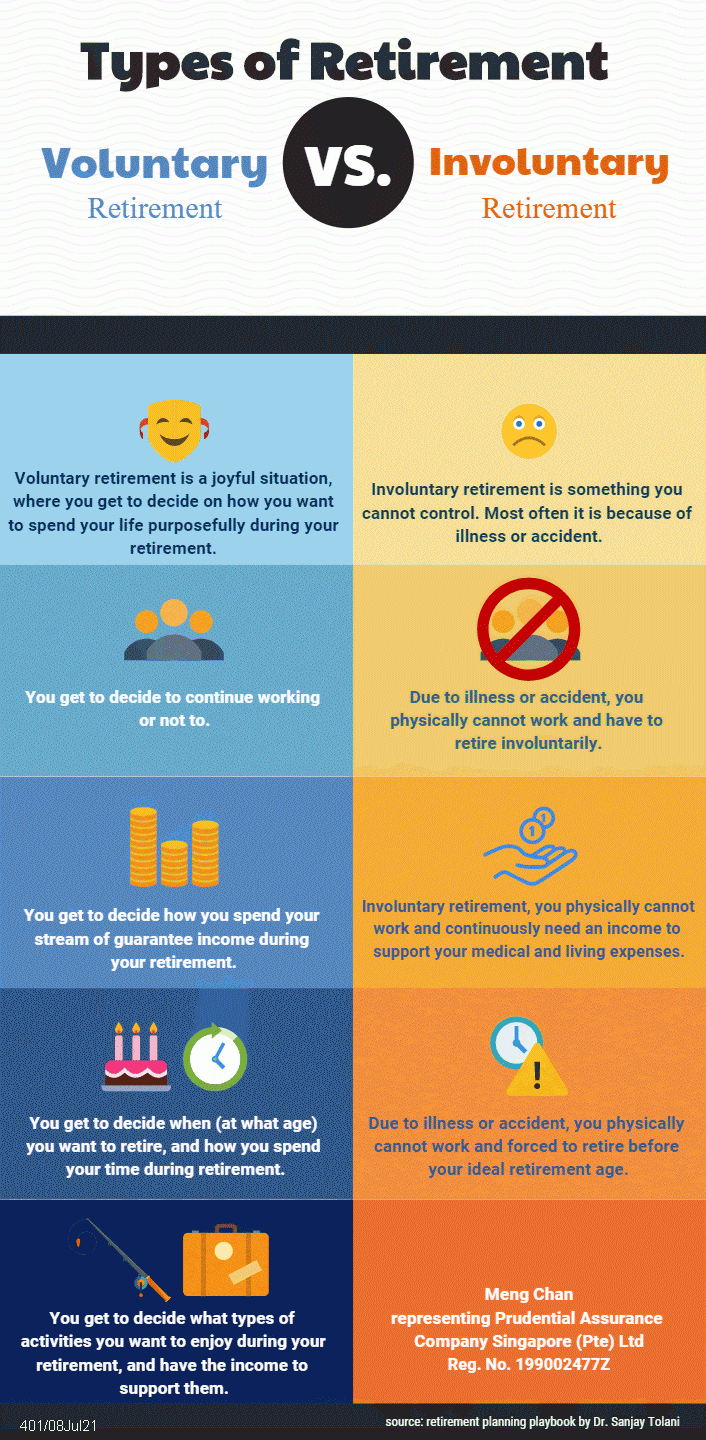
What are the 3 types of retirement?
Three types of retirement and how to plan for eachTraditional Retirement. Traditional retirement is just that. ... Semi-Retirement. ... Temporary Retirement. ... Other Considerations.
What's the difference between a pension and a retirement?
A pension is more controlled and constructed according to salary and service. The time in the company is represented by the company's contribution to the pension. Retirement comes at an age when the employee decides to withdraw from the workplace and continue as a consultant or find other part-time work.
What is the best age to retire?
When asked when they plan to retire, most people say between 65 and 67. But according to a Gallup survey the average age that people actually retire is 61.
What is ASC 715?
The rules governing how companies report pension costs and obligations, as well as the disclosure of pension assets and obligations, are covered under Accounting Standards Codification Section 715 ( ASC 715 ), formerly called the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards Nos. 87/88/158. The American Society of Pension Professionals & Actuaries (ASPPA) provides a guide on how to manage the ASC 715 process, which describes the disclosure information for a client’s financial reports, as well as lists the methodology used to complete the required actuarial calculations.
What is OPEB in retirement?
Other post-retirement benefits may also be referred to as " other post-employment benefits (OPEB) .".
What are non cash benefits?
The benefits that fall within this category are all of the non-cash payment benefits available to employees, including dental, vision care, legal services, and tuition credits. These additional benefits, along with traditional pension benefits, can be a large expenditure for companies offering these plans, especially if the plans are fully funded by the company.
Do post retirement benefits have to be reported?
As with other forms of retirement compensation, other post-retirement benefits can come with stringent reporting requirements due to their costs to an organization, as well as for the overall return on investment compared to the value of the work employees have performed before retirement.
Who pays for post retirement benefits?
Post-retirement benefits may be provided by local and federal government agencies, private and public companies, and nonprofit institutions, such as charities, religious groups, colleges, and universities. Such benefits may be paid for (in full or in part) by the employer, the retiree, or a combination of the two.
Who is Julia Kagan?
Julia Kagan has written about personal finance for more than 25 years and for Investopedia since 2014. The former editor of Consumer Reports, she is an expert in credit and debt, retirement planning, home ownership, employment issues, and insurance.
Is a retired employee more likely to incur higher medical expenses?
Typically, a retired worker will be older than the average current employee, and will, therefore, be more likely to incur higher medical expenses.
Who administers retirement benefits?
Whichever plan you are enrolled in, your retirement benefits are administered by the U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM). Regardless of how many more years you may work before retirement, it's a good idea to understand all the benefits you earn and to plan early.
What is the difference between CSRS and FERS?
The Federal Employee Retirement System (FERS), which covers all workers hired after 1984. Though FERS pays a smaller monthly benefit than CSRS , FERS retirees also receive Social Security and Thrift Savings Plan payments.
What is the purpose of the APWU?
The APWU and other federal unions have worked with Congress for many decades to ensure retirement income security for employees who spend their careers in government service.
What is post retirement benefit expense?
Post-retirement benefit expense refers to the cost of pension recognizable for the period. There are several components in computing for post-retirement benefit expense, but they depend on the type of plan established by your company. These plans can either be a defined contribution plan or a defined benefit plan.
What is considered employee benefits?
All forms of consideration given to employees for their services are employee benefits. They include post-employment benefits , short-term and long-term benefits, as well as termination benefits. Post-employment benefits are also known as post-retirement benefits. They refer to the compensation received by your workers at the end ...
What is defined contribution plan?
A defined contribution plan calls for fixed contributions. You and your employees contribute into a separate fund. Your contribution to the retirement fund will be the post-retirement benefit expense. A defined benefit plan aims to provide agreed benefits to your employees.
Is a defined contribution pension an expense?
Under the defined contribution plan, accounting of your expenses is simple. Any amount contributed to the pension fund is recognized as an expense. On the other hand, a defined benefit plan 's recognition of pension expense is more complex since the amount to be contributed is still to be determined.
What is the maximum amount of CPP in 2015?
If you are 65, the maximum monthly CPP pension that you can receive in 2015 is $1,065.00, and the maximum monthly PRB is about 1/40th of that, or $26.63. The maximum annual PRB is $319.56. If you are any age other than 65, both CPP and PRB amounts are adjusted — reduced ...
How much does a low wage earner contribute to the CPP?
No one contributes to the CPP on the first $3,500 of their income (the Year’s Basic Earnings). So in effect, a low wage earner is contributing less than 4.95 per cent of their overall earnings to the CPP (4.95 is the percentage of their earnings that employees currently pay into the CPP).
How to stop CPP contributions?
If you are over 65 and want to stop contributing to the CPP, you must complete the CPT30 form and give a copy to your employer. If you are self-employed, you must complete the appropriate section of the CRA CPP contributions on Self-Employment and Other Earnings and file it with your income tax return.
Do PRB payments continue?
The PRB payments will continue for the rest of your life. They are indexed to the cost of living, the same as the regular CPP retirement pension. Each additional year that you continue working and contributing after you start collecting CPP will earn you a new PRB that will be added to your monthly CPP benefit the following year.
When do you get your PRB?
You don’t need to apply for a PRB; you will automatically receive it the year following your year of contributions. Your PRB is effective in January but you may not receive the payment until April or May, with a retroactive payment to January.
Who is Doug Runchey?
Doug Runchey worked for the Income Security Programs branch of Human Resources and Skills Development Canada for more than 32 years, and was a specialist in the Canada Pension Plan and Old Age Security legislation, regulations and policy areas. He now runs his own company, DR Pensions Consulting, which provides pension advice, including detailed calculations for CPP retirement planning and “credit splitting” purposes. Doug can be reached by email @ [email protected] or check out his website at http://www.drpensions.ca/.
How long does it take to file a retirement claim?
Retirement Services strives to complete retirement claims within sixty days. If we need additional information from you or your former employing agency, however, your claim could take longer to process. It may take more time than average if, for example, your retirement claim has special circumstances (e.g.
How long do you have to be an annuitant before retiring?
for five years immediately before retiring;or, during all of your federal employment since your first opportunity to enroll;or, continuously for full periods of service beginning with the enrollment that started before January 1, 1965, and ending with the date on which you become an annuitant, whichever is shortest.
How many years of service do you have to be to get 80 percent unemployment?
Generally, you reach the 80 percent limitation when you have 41 years and 11 months of service, not including accumulated sick leave. Fewer years of service may result in a computation that produces the maximum benefit under special computation formulas such as for law enforcement personnel.
When does Option B reduce?
If you elect Full Reduction, effective the first day of the second month after your 65th birthday or your retirement date, whichever is later, your Option B full-reduction multiples will reduce by 2 percent of the face value per month for 50 months, at which time this coverage will end.
What are the other benefits of post-retirement?
Other post-employment benefits can include life insurance, health insurance, and deferred compensation. These benefits are also referred to as "other post-retirement benefits.".
What are the implications of post retirement benefits?
As with many forms of retirement compensation, they also involve stringent reporting requirements.
What type of insurance do retirees get?
Life insurance. Like health insurance, the life insurance that employers may provide to retirees is typically part of a group plan and generally comes in the form of term life insurance .
What are the other benefits of OPEB?
Other post-employment benefits can include life insurance, health insurance, and deferred compensation.
What is a deferred compensation plan?
Deferred-compensation arrangements, which are also considered a post-employment benefit, pay the employee a salary or lump sum at some predetermined time, typically after they retire. These plans come in two distinct types— qualified and non-qualified —but serve the same basic purpose, which is to defer taxes while the employee is still working and provide income in the future, ideally when that person is in a lower marginal tax bracket .
Is retiree health insurance the same as group health insurance?
Retiree health insurance is generally provided as part of a group plan, much as it probably was when the employee was still working. The group plan may be the same one offered to current employees, or it may be a separate plan just for retirees. 1
Can you change your post-employment benefits?
Retirees who receive other post-employment benefits should note that unless there is a clear and specific agreement in writing, their employer can often change or eliminate those benefits at its discretion, according to the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL).
What Are Other Post-Retirement Benefits?
Understanding Other Post-Retirement Benefits
- The benefits that fall within this category are all of the non-cash payment benefits available to employees, including dental, vision care, legal services, and tuition credits. These additional benefits, along with traditional pension benefits, can be a large expenditure for companies offering these plans, especially if the plans are fully fundedby the company. The costs of these p…
Other Post-Retirement Benefits and Cost
- Direct contributions that pay for any post-employment benefits can expose an employer to certain risks and liabilities. For example, take the example of a former worker who is granted health insurance coverage at the cost/premium rates as current employees. Typically, a retired worker will be older than the average current employee, and will, therefore, be more likely to incur highe…
Other Post-Retirement Benefits and Compliance
- The rules governing how companies report pension costs and obligations, as well as the disclosure of pension assets and obligations, are covered under Accounting Standards Codification Section 715 (ASC 715), formerly called the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards Nos. 87/88/158. The American Society of Pension Professionals & Actuaries (ASPPA…