Statement on Benefits and Risks of Genetically Modified Foods for Human Health and Nutrition
- Food quality and human nutrition. Most consumers in rich countries have access to a relatively inexpensive supply of safe and healthy food.
- Agricultural practice. ...
- Industrial products and processes. ...
- Microorganisms. ...
- Regulation and risk assessment. ...
What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
These include:
- corn starch in soups and sauces
- corn syrup used as a sweetener
- corn, canola, and soybean oils in mayonnaise, dressings, and breads
- sugar derived from sugar beets
What are the dangers of genetically modified food?
For example:
- a GMO canola oil with more lauric acid than traditional canola oil will be labeled “laurate canola oil”
- a GMO soybean oil with more oleic acid than non-GMO soybean oil must be labeled “high-oleic soybean oil”
- a GMO soybean oil with a high level of stearidonic acid, which does not naturally occur in the oil, must be labeled “stearidonate soybean oil”
Are genetically modified foods good or bad?
Genetically modified (GM) crops have been proven safe through testing and use, and can even increase the safety of common foods. As astrophysicist Neil deGrasse Tyson explained, “Practically every food you buy in a store for consumption by humans is genetically modified food. There are no wild, seedless watermelons.
What are the health benefits of GMO foods?
- iron-biofortification of rice, beans, sweet potato, cassava and legumes;
- zinc-biofortification of wheat, rice, beans, sweet potato and maize;
- provitamin A carotenoid-biofortification of bananas, sweet potato, maize and cassava; and
- amino acid and protein -biofortification of sorghum and cassava.

What are the risks of genetically modified foods?
It is known that the main concerns about adverse effects of GM foods on health are the transfer of antibiotic resistance, toxicity and allergenicity. There are two issues from an allergic standpoint.
What are benefits of genetically modified food?
Some benefits of genetic engineering in agriculture are increased crop yields, reduced costs for food or drug production, reduced need for pesticides, enhanced nutrient composition and food quality, resistance to pests and disease, greater food security, and medical benefits to the world's growing population.
What are 5 Advantages and disadvantages of GMOs?
10 Advantages and Disadvantages of GMOsThey offer more useful knowledge for genetics. ... They allow for more profit. ... They add more value to crops. ... They are known to decrease the prices of food. ... They yield products that are found to be safe.
What are the 5 disadvantages of GMOs?
What Are the Disadvantages of GMOs?It can be dangerous to other insects that are important to our ecosystem. ... It sparks concerns on changing the field of agriculture. ... It can damage the environment. ... It causes unwanted residual effects. ... It can create more weeds. ... It threatens crop diversity. ... It has trade issues.
What are 5 environmental disadvantages of genetically modified foods?
Perceived disadvantages of genetically modified crops may be grouped into five categories: 1) potential impact on non-target species; 2) potential for increased weediness; 3) increase in toxin levels in the soil; 4) exchange of genetic material between the transgenic crop and related plant species; and 5) selection for ...
Pros of Genetically Modified Foods
Here are the primary benefits of GMO foods:1. Better overall quality and taste.Through the modification of foods, the flavors can be enhanced. Pepp...
Cons of Genetically Modified Foods
Here are the primary problems with GMO foods:1. Environmental damage.By growing plants or raising livestock in environmental conditions that normal...
Do The Benefits Outweigh The Risks?
Why evaluate the pros and cons of genetically modified foods? The answer to this is, the benefits need to outweigh the risks when it comes to their...
Why do manufacturers use genetic modification?
Manufacturers use genetic modification to give foods desirable traits. For example, they have designed two new varieties of apple that turn less brown when cut or bruised. The reasoning usually involves making crops more resistant to diseases as they grow.
Why is genetic modification important?
Because genetic modification can make plants resistant to disease and tolerant of herbicides, the process can increase the amount of food that farmers are able to grow. This can reduce prices and contribute to food security.
How are GMOs created?
A manufacturer creates GMOs by introducing genetic material, or DNA, from a different organism through a process called genetic engineering. Most currently available GMO foods are plants, such as fruit and vegetables. All foods from genetically engineered plants on sale in the United States are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
What are the most common GMO crops?
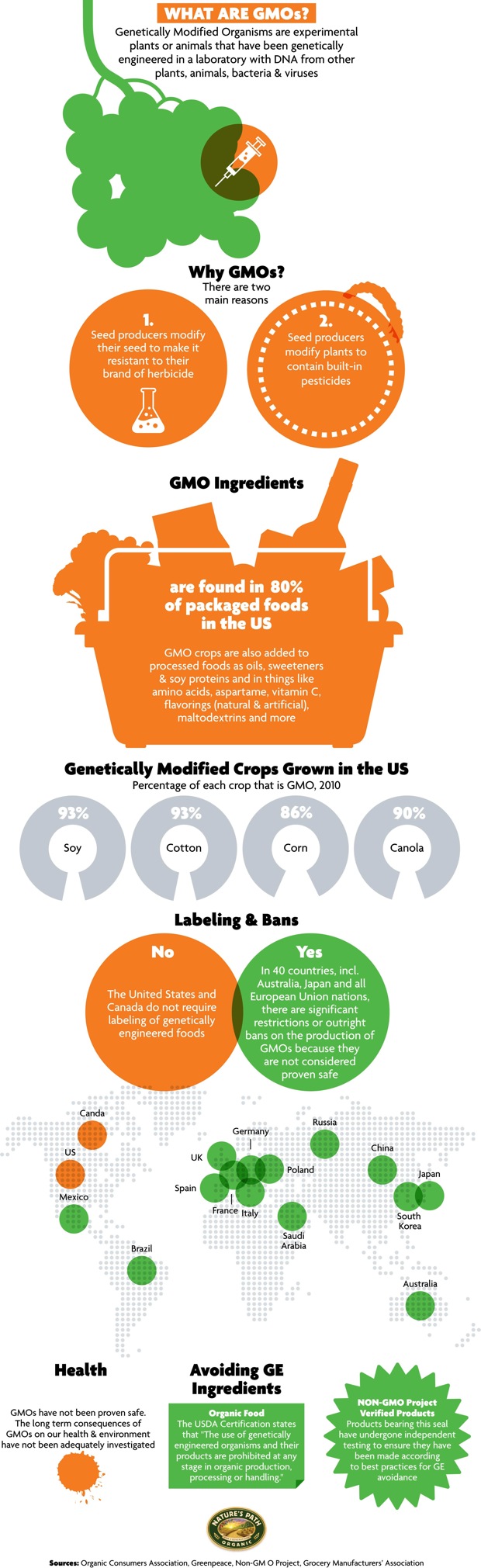
The most common GMO crops grown in the country are cotton, corn, and soybeans. Herbicide-tolerant crops allow for a more effective use of pesticides. The U.S. Department of Agriculture have reported that 94 percent of soybean and 91 percent of cotton crops were genetically modified by 2014.
What are the pros and cons of GMOs?
What are the pros and cons of GMO foods? Engineers design plants using genetically modified organisms, or GMOs, to be tougher, more nutritious, or taste better. However, people have concerns over their safety, and there is much debate about the pros and cons of using GMOs. A manufacturer creates GMOs by introducing genetic material, or DNA, ...
Why are plants more resistant to diseases?
Plants that are more resistant to diseases spread by insects or viruses result in higher yields for farmers and a more attractive product. Genetically modification can also increase nutritional value or enhance flavor. All of these factors contribute to lower costs for the consumer.
Why do engineers use GMOs?
Engineers design plants using genetically modified organisms, or GMOs, to be tougher, more nutritious, or taste better. However, people have concerns over their safety, and there is much debate about the pros and cons of using GMOs. A manufacturer creates GMOs by introducing genetic material, or DNA, from a different organism through ...
What are the advantages of genetically modified foods?
The primary advantage of genetically modified foods is that crop yields become more consistent and productive, allowing more people to be fed.
Why are genetically modified foods good for you?
Instead of relying on preservatives to maintain food freshness while it sits on a shelf, genetically modified foods make it possible to extend food life by enhancing the natural qualities of the food itself. According to Environmental Nutrition, certain preservatives are associated with a higher carcinogen, heart disease, and allergy risk.
Why are genetically modified foods easier to transport?
Genetically modified foods are easier to transport. Because GMO crops have a prolonged shelf life, it is easier to transport them greater distances. This improvement makes it possible to take excess food products from one community and deliver it to another that may be experiencing a food shortage.
How can genetic modification improve GMO crops?
2. Nutritional content can be improved. Genetic modifications do more than add pest resistance or weather resistance to GMO crops. The nutritional content of the crops can be altered as well, providing a denser nutritional profile than what previous generations were able to enjoy.
How many companies control the GMO market?
6 companies control most of the genetically modified foods market at the core level. Because most GMO foods are made from corn, wheat, or soybeans, even food manufacturers that use these crops are at the mercy of the manufacturer’s preferences.
How have genetically modified foods changed the way people view their food?
Although genetic modifications have occurred throughout history with selective breeding and growing methods, scientific advances have allowed this practice to advance to the genetic level. In the modern GMO, plants can be resistant to specific pesticides and herbicides while becoming adaptive to changing environmental conditions.
Why are herbicides bad for crops?
Herbicides and pesticides create certain hazards on croplands that can eventually make the soil unusable. Farmers growing genetically modified foods do not need to use these products as often as farmers using traditional growing methods, allowing the soil to recover its nutrient base over time.
What are the benefits of genetically modified foods?
Pros of Genetically Modified Foods. Here are the primary benefits of GMO foods: 1. Better overall quality and taste. Through the modification of foods, the flavors can be enhanced. Peppers can become spicier or sweeter. Corn can become sweeter.
Why are GMOs good?
For some, the idea of GMO food is a good one because the modifications allow crops to become resistant to drought and infestations, letting more people have more regular meals. Some research even shows that the world produces 17% more food ...
How much more food does the world produce than it needs to produce?
Some research even shows that the world produces 17% more food than it needs to produce to provide each current human with three squares per day! Others look at genetically modified foods as a dangerous proposition. From allergic reactions to potential intestinal damage, many people wish to avoid GMO foods because of animal studies ...
Why are genetic modifications justified?
Genetic modifications of plants and animals are justified by the potential for improvement of the food situation worldwide, an increase in yield crops, an increase in the nutritional value of food, and the development of pharmaceutical preparations of proven clinical significance.
What is modified organism?
Scientists employing methods of genetic engineering have developed a new group of living organisms, termed 'modified organisms', which found application in, among others, medicine, the pharmaceutical industry and food distribution. The introduction of transgenic products to the food market resulted in them becoming a controversial topic, ...
How does genetic modification affect plants?
Genetic modification significantly accelerates this process by using scientific techniques that give the plant the specific desired trait. For example, one of the most common GMO crops is Bt corn, which is genetically modified to produce the insecticide Bt toxin.
What is GMO in agriculture?
Definition. Pros. Cons. Identification. Bottom line. GMOs, short for genetically modified organisms, are subject to a lot of controversy. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), GMO seeds are used to plant over 90% of all maize (corn), cotton, and soy grown in the United States, which means that many of the foods you eat likely ...
What are GMO crops?
GMO crops grown and sold in the United States include corn, soybean, canola, sugar beet, alfalfa, cotton, potatoes, papaya, summer squash, and a few apple varieties ( 29. Trusted Source. ). In the United States, no regulations currently mandate the labeling of GMO foods.
Why do people fear eating foods with added genes?
Because cancers are caused by DNA mutations, some people fear that eating foods with added genes may affect your DNA. This worry may stem partly from an early mice study, which linked GMO intake to a higher risk of tumors and early death. However, this study was later retracted because it was poorly designed ( 18.
Is GMO food safe for humans?
Still, a review of multiple studies concluded that the low amounts of glyphosate present on GMO foods are safe for human consumption ( 28. Trusted Source. ). GMO crops also allow for fewer pesticide applications, which is a positive for the environment.
Is it mandatory to label food with GMOs?
In the United States, it’s currently not mandatory to label foods that contain GMOs. However, as of 2022, all foods that contain GMO ingredients must have the term “bioengineered food” somewhere on the packaging or a scannable code to show that it has GMO ingredients. Last medically reviewed on July 2, 2020.
Is corn a GMO?
Trusted Source. ). GMO crops are incredibly common in the United States, with at least 90% of soy, cotton, and corn being grown through genetic techniques ( 4. Trusted Source.
What percentage of soybeans are genetically modified?
McLean is referring to the fact that GMOs have been on the market for almost a decade without U.S. consumers being alerted to their presence. About 50 percent of soybeans grown in the United States last year were genetically modified, and those soybeans became part of countless processed foods from oils to cereals.
What does Calkins think about GMOs?
Calkins thinks that those who want to see further development of GMOs are going to have to establish trust with the other side, but he doesn’t see that happening by simply conducting more laboratory experiments to prove the safety of genetic engineering. With biotech opponents appealing to imagery and folklore, Calkins says, "businesses need to develop counter-images or offsetting cases about their good character."
Who said GMOs take mankind into realms that belong to God and God alone?
England’s Prince of Wales , for example, has argued that GMOs take "mankind into realms that belong to God and God alone.". Even for the non-religious, transgenic crops can violate the maxim so memorably stated in the old margarine commercials: "It’s not nice to fool Mother Nature.".
Can GMOs cause harm?
So far, no medical harm to humans has been traced to ingesting GMOs. Of course, the fact that no harm has been established is not the same as proving that GMOs pose no dangers. One concern is the potential for allergic reactions.
Do GMOs harm the environment?
Aside from the danger of super-weeds, GMOs may pose dangers for other creatures in the ecosystem. "Crops that are engineered to be pesticidal may harm insects other than those they were intended to repel," says Rebecca Goldburg, senior scientist at the Environmental Defense Fund.
Why is GMF important?
The development of crops resistant to biotic and abiotic stresses is critical for sustainable food production in the developing world. The use of GMF crops should go hand-in-hand with other technologies such as plant tissue culture, marker-assisted breeding and conventional plant breeding.
What are the concerns of gene technology?
Public concerns about gene technology lie in four major areas, namely ethical concerns, socio-economic issues, effects on the environment and food safety and human health. Although acknowledging the importance and the interconnectivity of all these areas, the principal focus of this statement is the scientific basis for assessing ...
What is the principle assumption of GM?
A principle assumption is that the resolution of food and nutrition problems and challenges of today and tomorrow have technological dimensions. Transgenic modification (GM), traditional and modern, applied to plant and animal food sources (GMFs) hold potential for improving human nutrition and health provided that the capabilities ...
What are the health risks associated with the approaches that are reviewed?
Health risks associated with the approaches that are reviewed generally also fall into four categories – allergies, toxicities, nutrient imbalances, and decreasing diet diversity. Food quality and human nutrition. Most consumers in rich countries have access to a relatively inexpensive supply of safe and healthy food.
What are the benefits of food security?
Four categories of health benefits are recognized: enhancement of food security; enhancement of nutrient security; more targeted health benefits, such as immunization; and reduction of diet related, adult-onset chronic diseases (through the manipulation of specific food components, e.g. manipulation of fat composition).
How is biotechnology used in agriculture?
Agricultural practice. Developments in agricultural biotechnology are being used to increase the productivity of crops, primarily by reducing the costs of production. These new crop varieties include insect resistance (cotton, maize), herbicide resistance (maize, soybean), delayed fruit ripening (tomato).
Is there a GM fish?
No GM fish is known to be produced commercially for food at present, although some are being considered for the food market, and for some regulatory approval is pending. Livestock and poultry. Food products derived from GM livestock and poultry are far from commercial use.
What is genetic modification?
Abstract. Genetic modification is a special set of gene technology that alters the genetic machinery of such living organisms as animals, plants or microorganisms. Combining genes from different organisms is known as recombinant DNA technology and the resulting organism is said to be ‘Genetically modified (GM)’, ...
What are the products of GM?
GM products which are currently in the pipeline include medicines and vaccines, foods and food ingredients, feeds and fibres.
What organisms are affected by herbicide residues?
Also, from a toxicological standpoint, further investigation is required to determine if residues from herbicide or pest resistant plants could harm key groups of organisms found in surrounding soil, such as bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and other microorganisms (Allison and Palma 1997).
What is maize used for?
A good amount of the total maize harvested go for livestock feed including the distillers grains. The remaining has been used for ethanol and high fructose corn syrup production, export, and also used for other sweeteners, cornstarch, alcohol, human food or drink.
What crops are resistant to a virus?
Other crops grown commercially and/or field-tested are sweet potato resistant to a virus that could destroy most of the African harvest, rice with increased iron and vitamins that may alleviate chronic malnutrition in Asian countries and a variety of plants that are able to survive weather extremes.
Is papaya genetically engineered?
Without it, the state’s papaya industry would have collapsed. Today 80 % of Hawaiian papaya is genetically engineered, and till now no conventional or organic method is available to control ring spot virus.
Is GM salmon a food?
As of now there are no GM animals approved for use as food, but a GM salmon has been proposed for FDA approval. In instances, the product is directly consumed as food, but in most of the cases, crops that have been genetically modified are sold as commodities, which are further processed into food ingredients.
How effective are genetically modified organisms?
Genetically modified organisms, GMOs, seem to offer the most effective way to feed the 795 million people who don't have enough food. The public, however, has shown resistance to products made using these organisms. Some authors claim that genetic engineering offers no threat, yet reports of negative effects of GMOs like environmental concerns ...
What are the benefits of GMOs?
Unfortunately, the many benefits of GMOs come at a great cost. The main cost is long-term environmental damage. A 2018 report in PNAS describes what can happen when humans try to change ecosystems. It can lead to an uncontrollable chain reaction, which only becomes clear over a long period.
How do GMOs affect the environment?
For example, farmers might fail to limit genetically modified crops to a certain area. Bees take pollen from genetically altered corn, and they might transfer it between fields.
What percentage of corn is genetically modified?
In fact, 94 percent of soybeans and 89 percent of corn grown in the U.S. are genetically modified. Glyphosate residue leaches into the genetically modified food grown in treated fields through a process called desiccation__ .__. When you eat these foods, you might allow glyphosate into your gastrointestinal tract.
Why is genetic engineering important?
Genetic engineering offers a way to feed the world despite global warming. Climate change has led to more drought. Scientists can make GMOs which are more tolerant of high temperatures and dry conditions, according a 2015 paper from Harvard University. Advertisement.
What are some examples of ethical issues caused by GMOs?
Genetically altered salmon, for example, experience physiological changes which many animal rights activists consider cruel. A 2018 article in the Transactions of the American Fisheries showed that these salmon show alterations in their organs and bones. These changes have a negative impact on their swimming ability.
How does genetic engineering help the environment?
Genetic engineering offers many benefits. It can, for example, play a role in combating global warming. The current pesticides used by farmers emit many greenhouse gases. Scientists can alter the genetic makeup of crops so that they need fewer of these harmful chemicals and thereby decrease their carbon footprint.
