
Full Answer
What is the good side affects about FGM?
The practice has no health benefits for girls and women. FGM can cause severe bleeding and problems urinating, and later cysts, infections, as well as complications in childbirth and increased risk of newborn deaths.
Why FGM is good?
Female genital mutilation
- Types of FGM. Female genital mutilation is classified into 4 major types. ...
- No health benefits, only harm. FGM has no health benefits, and it harms girls and women in many ways. ...
- Cultural and social factors for performing FGM. ...
- A financial burden for countries. ...
- International response. ...
Why FGM should be abolished?
Why FGM should be abolished. FGM is gender-based violence. FGM steals girls' futures. FGM extends poverty. FGM can force girls out of school. FGM leads to child marriage and teen pregnancy. FGM can be traumatising. Young people know about their rights and bodies and want the tradition to end. FGM is a violation of girls' and women's rights.
What is FGM, where does it happen and why?
In many of the countries where FGM is performed, it is a deeply entrenched social norm rooted in gender inequality where violence against girls and women is socially acceptable. The reasons behind the practice vary. In some cases, it is seen as a rite of passage into womanhood, while others see it as a way to suppress a woman’s sexuality.

Is it good to have FGM?
No health benefits, only harm FGM has no health benefits, and it harms girls and women in many ways. It involves removing and damaging healthy and normal female genital tissue, and interferes with the natural functions of girls' and women's bodies.
What is the value of FGM?
For the first time, the current study measured the utility value of FGM/C for different socio-demographic groups. The results indicated that women/girls living with FGM/C had an average health utility of 0.971 (SE: 0.003) with a median of 0.968 (IQR: 1–0.95).
What is FGM and why is it important?
Female genital mutilation (FGM) is a procedure performed on a woman or girl to alter or injure her genitalia for non-medical reasons. It most often involves the partial or total removal of her external genitalia. FGM is a violation of girls' and women's fundamental human rights.
What is the social impact of FGM?
As girls grow up and marry, the sexual dysfunction caused by FGM may put stress on their marriages. And over the long term, FGM can leave serious psychological scars. Girls and women who experienced it may suffer anxiety, depression, memory loss, sleep disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Why do you iron breasts?
IMPORTANT FACTORS BEHIND BREAST IRONING Specifically, it is performed as a way to help disguise the onset of puberty in girls, which it is believed will help to deter male attention and protect them from sexual harassment, assault, exploitation, and rape or sexually transmitted diseases.
Which country has the highest rate of FGM?
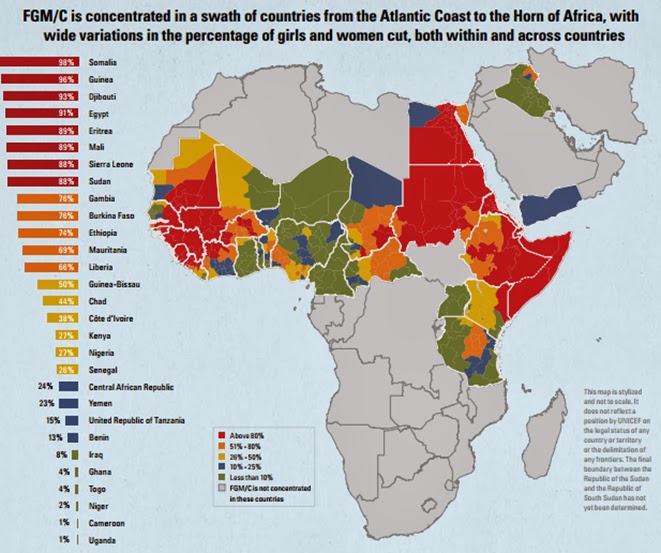
Somalia"Somalia, for example, has the highest rate of FGM in the world, with around 98 per cent of women having undergone the procedure," explains Martine Pochon, regional protection adviser for the Greater Horn of Africa.
How painful is FGM?
Almost all women who have undergone FGM experience pain and bleeding as a consequence of the procedure. The event itself is traumatic as girls are held down during the procedure. Risk and complications increase with the type of FGM and are more severe and prevalent with infibulations.
How does FGM affect childbirth?
What are the consequences for childbirth? A recent study found that, compared with women who had not been subjected to FGM, those who had undergone FGM faced a significantly greater risk of requiring a Caesarean section, an episiotomy and an extended hospital stay, and also of suffering post-partum haemorrhage.
What are the three types of FGM?
Types of FGMType I – Clitoridectomy. Partial or total removal of the clitoris (a small, sensitive and erectile part of the female genitals) and/or the prepuce (the clitoral hood or fold of skin surrounding the clitoris).Type II – Excision. ... Type III – Infibulation. ... Type IV – Other.
Where is FGM still legal?
Laws by countryCountryCriminalisedSinceUgandaSpecific anti-FGM law : 22United Arab EmiratesNoUnited KingdomSpecific anti-FGM law : 261985United StatesFederal anti-FGM law Specific bans in 40 states96–18, 202191 more rows
Is circumcision considered a social advantage?
Maybe we think male circumcision is acceptable because it has medical advantages, whereas female circumcision only has “social” advantages (eligibility for marriage, greater acceptance by the community, seen as more aesthetic, and so on). I don’t think that’s the solution, either.
Is circumcision good for women?
In countries where female circumcision is relatively common, this is exactly what is claimed for the procedure. Cited health benefits include “a lower risk of vaginal cancer … fewer infections from microbes gathering under the hood of the clitoris, and protection against herpes and genital ulcers.”.
What is a female genital mutilation?
Female genital mutilation (FGM) is a procedure performed on a woman or girl to alter or injure her genitalia for non-medical reasons. It most often involves the partial or total removal of her external genitalia. FGM is a violation of girls’ and women’s fundamental human rights.
How many women in Guinea have genital mutilation?
Over 90 per cent of women and girls in Guinea and Somalia undergo some form of genital mutilation or cutting. Progress to end FGM needs to be at least 10 times faster if the practice is to be eliminated by 2030.
How many women have undergone FGM?
While the exact number of girls and women worldwide who have undergone FGM remains unknown, at least 200 million girls and women aged 15–49 from 31 countries have been subjected to the practice. There has been significant progress made in eliminating the practice in the past 30 years.
How many girls are at risk of FGM?
04 March 2019. Each year, around 4 million girls worldwide are at risk of undergoing female genital mutilation (FGM), with most girls cut before the age of 15.
Why is FGM considered a medical practice?
The “medicalization” of FGM serves to legitimize a violation of human rights and medical ethics, which is why the United Nations, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics, and numerous national medical associations have entirely rejected the practice.
How many women are affected by FGM?
At least 200 million women and girls in 31 countries around the world are living with the results of the dangerous practice of female genital mutilation (FGM), according to a report by UNFPA, the United Nations Population Fund. The practice is recognized internationally as a violation of the human rights of girls and women.
What is female genital mutilation?
Female genital mutilation is defined as the removal of part or all of the female genitalia for nonmedical reasons. It is also called female circumcision and cutting. The procedure is most often done to girls between birth and age 15.
How many FGM cases will there be in 2030?
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic causing disruptions in prevention programs, U.N. health officials fear an additional 2 million cases of FGM will surface by 2030 — cases that would have otherwise been averted.
When is the International Day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation?
To stop the harmful practice, the United Nations created the International Day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation, observed every year on February 6. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals also call to end the practice by 2030.
Is FGM ending in one generation?
World Vision and other organizations are educating and empowering girls and their communities to end FGM. There’s strong evidence that it can be eliminated in one generation.
What is the Tokomeza Ukeketaji project?
Following the launch of the joint FGM elimination project, “Tokomeza Ukeketaji”, by UN Women and the African Medical Research Foundation in 2016, he took up the fight to save girls from FGM and ensure they stay in school.
How many women will be mutilated in 2021?
In 2021, 4.16 million girls and women around the world are at risk of genital mutilation.
What is Gambia Committee on Traditional Practices Affecting the Health of Women and Children?
The Gambia Committee on Traditional Practices Affecting the Health of Women and Children (GAMCOTRAP), an advocacy group supported by the UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women, holds an Anti-FGM workshop aimed at empowering women to claim their rights and those of their daughters in February 2016.
Why are women in Mara poor?
Many women in Mara are poor because they were deprived of the opportunity to go to school. [FGM] is pushing back development in our community and Tanzania as a whole.”. “I am working with other men to advocate for alternative rites of passage initiation that is freeing girls from genital mutilation.
Where is Yatta Fahnbulleh?
Until last year, Yatta Fahnbulleh, 65, owned one of the largest ‘bush schools’ (where girls underwent a series of rituals, including FGM, to initiate them into adulthood) in Tienni, a community in Grand Cape Mount County in northwestern Liberia. She is one of 300 former FGM practitioners in Liberia that participated in the Alternative Economic Livelihood programme launched by UN Women in collaboration with Plan International under the EU-UN Spotlight Initiative in December 2019.
Where is Natalie from FGM?
Our lives are basically taken away from us.”. Natalie was born in the Kuria community, southwest Kenya. Growing up, she faced the same challenges as other girls in her community. “FGM is a social norm in Kuria, similar to having to knock when you go to someone’s home.
Where does Amal Ahmed live?
Amal Ahmed* – a wife and mother of an 11-year-old girl and three boys aged 15, 18 and 19 – lives in Cairo Governorate, Egypt. When Amal was 10 years old, she and her sister were tricked by their family into undergoing FGM. Since that experience, their lives have never been the same.
What is circumcision in the Bible?
Circumcision is one of the Sunnahs of the fitrah, as is indicated by the words of the Prophet (peace and blessings of Allaah be upon him): "The fitrah is five things – or five things are part of the fitrah – circumcision, shaving the pubes, plucking the armpit hairs, cutting the nails, and trimming the moustache.".
What does the Prophet of Mercy say about circumcision?
This does in fact lead to frigidity but it is contrary to the kind of circumcision enjoined by the Prophet of mercy (peace and blessings of Allaah be upon him) when he said: “Do not destroy” i.e., do not uproot or excise.
Is circumcision obligatory for women?
Circumcision is prescribed for both males and females. The correct view is that circumcision is obligatory for males and that it is one of the symbols of Islam, and that circumcision of women is mustahabb but not obligatory.
Is circumcision harmful to women?
In the book on Traditions that affect the health of women and children, which was published by the World Health Organization in 1979 it says: With regard to the type of female circumcision which involves removal of the prepuce of the clitoris, which is similar to male circumcision, no harmful health effects have been noted.
Will circumcision become known in the future?
If the benefits are not apparent now, they will become known in the future, as has happened with regard to male circumcision – the world now knows its benefits and it has become widespread among all nations despite the opposition of some groups.
Who narrates the Fitrah?
narrated by al-Bukhaari (5889) and Muslim (257). Undoubtedly with regard to the Sunnahs of the fitrah, some of the wisdom behind them is obvious, and that includes circumcision. There are clear benefits to it which we should pay attention to and understand the wisdom behind it.
The 3 Cons of Female Circumcision
The following is the list of reasons that make the practice a disadvantage and harmful to women.
What Makes of Female Circumcision Now
Thinking of what a woman has to endure through the female circumcision procedure already makes it hard to think. It may be practiced for a good reason, but it does not leave the possibility of the risks they might face.
What Is Female Genital Mutilation?
Why Is It practiced?
- In many of the countries where FGM is performed, it is a deeply entrenched social norm rooted in gender inequality where violence against girls and women is socially acceptable. The reasons behind the practice vary. In some cases, it is seen as a rite of passage into womanhood, while others see it as a way to suppress a woman’s sexuality. Many communities practice genital muti…
Why Is Female Genital Mutilation A Risk For Girls and Women?
- FGM has no health benefits and often leads to long-term physical and psychological consequences. Medical complications can include severe pain, prolonged bleeding, infection, infertility and even death. It can also lead to increased risk of HIV transmission. Women who have undergone genital mutilation can experience complications during childbirth,...
How Prevalent Is Female Genital Mutilation?
- While the exact number of girls and women worldwide who have undergone FGM remains unknown, at least 200 million girls and women aged 15–49 from 31 countries have been subjected to the practice. There has been significant progress made in eliminating the practice in the past 30 years. Young girls in many countries today are at much lower risk of being subjecte…
How Is The Practice Evolving?
- In many countries, FGM is increasingly carried out by trained health care professionals – in violation of the Hippocratic Oath to “do no harm”. Around 1 in 3 adolescent girls (15-19 years) who have undergone FGM were cut by health personnel. Medicalizing the practice does not make it safer, as it still removes and damages healthy and normal tissue and interferes with the natural f…
What Is UNICEF Doing to Stop Female Genital Mutilation?
- Ending FGM requires action at many levels, including by families and communities, protection and care services for girls and women, laws, and political commitment at the local, regional, national and international levels. UNICEF and the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) jointly lead the largest global programmeto end FGM. The programme supports zero tolerance laws and policie…
What Has Been UNICEF's Impact?
- Since the UNICEF/UNFPA programme was established in 2008, 13 countries have passed national legislation banning FGM. The programme has also provided access to prevention, protection and treatment services. In 2018 alone, nearly 7 million people across 19 countries participated in education, discussions and social mobilization promoting the elimination of FGM.