
- A cost-benefit analysis simplifies the complex decisions in a project.
- The analysis gives clarity to unpredictable situations. ...
- It helps to figure out whether the benefits outweigh the cost and is it financially strong and stable to pursue it
- It is easy to compare projects of every type in spite of being dissimilar
How do you calculate cost benefit analysis?
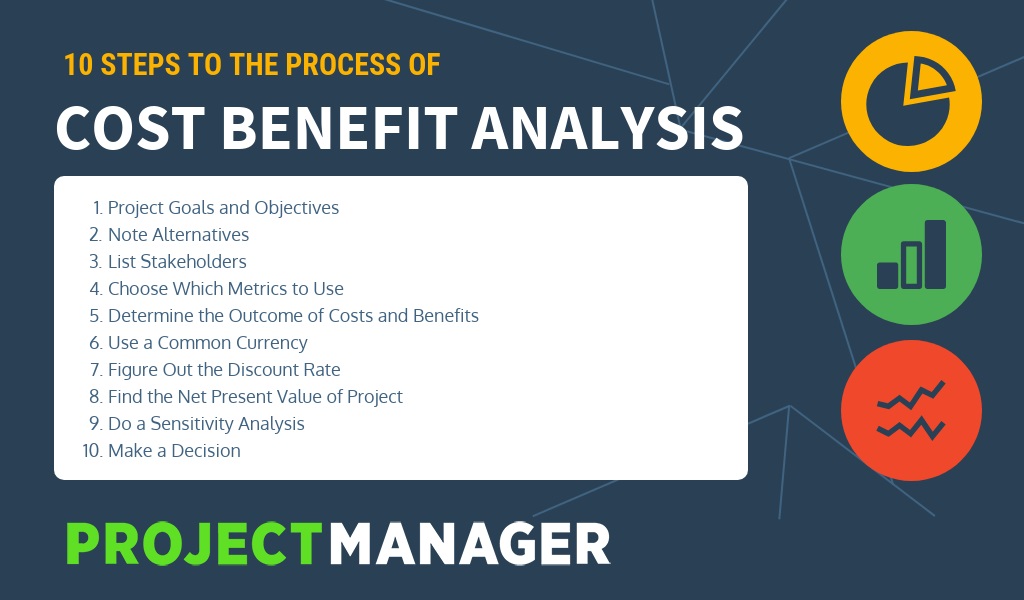
- Establish a framework to outline the parameters of the analysis
- Identify costs and benefits so they can be categorized by type, and intent
- Calculate costs and benefits across the assumed life of a project or initiative
- Compare cost and benefits using aggregate information
- Analyze results and make an informed, final recommendation
How do you calculate cost benefit?
Benefit-Cost Ratio = ∑PV of all the Expected Benefits / ∑PV of all the Associated Costs Step 6: Now, the formula for net present value can be derived by deducting the sum of the present value of all the associated costs (step 4) from the sum of the present value of all the expected benefits (step 4) as shown below.
What are the types of cost analysis?
- Absolute cost quantifies an asset's loss in value.
- Relative cost compares the selected action or decision, and the alternative action or decision that was not selected.
- Opportunity cost is the cost or sacrifice (loss) incurred as a result of selecting one activity or action over another.
How to do a cost analysis?
How high do petrol prices need to go to make electric cars more affordable?
- Supply a bigger speed hump. Consultancy Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) said even if rising petrol prices drove people towards electric cars, they might not be able to get one ...
- Governments drive change. ...
- No incentives for automakers. ...
- Up-front costs more important. ...
- EV rush later this decade. ...
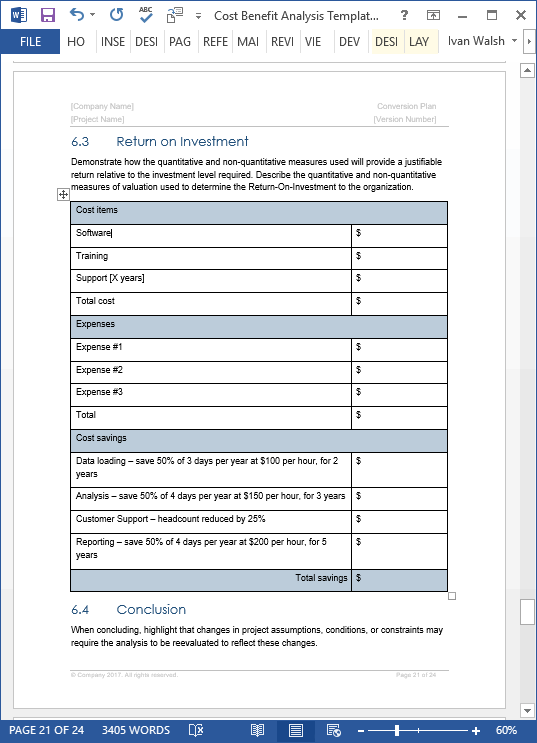
What is the purpose of a cost analysis?
The primary reason for conducting cost analysis is generally to determine the true (full) costs of each of the programs under analysis (services and/or products). You can then utilize this knowledge to: Identify and prioritize cost-saving opportunities.
What is one purpose for doing a cost-benefit analysis?
CBA has two main applications: To determine if an investment (or decision) is sound, ascertaining if – and by how much – its benefits outweigh its costs. To provide a basis for comparing investments (or decisions), comparing the total expected cost of each option with its total expected benefits.
What is cost-benefit analysis and why is it important?
A cost-benefit analysis is the simplest way of comparing your options to determine whether to go ahead with a project. The idea is to weigh up project costs against benefits, and identify the action that will give you the most bang for your buck.
What is the purpose of cost-benefit analysis quizlet?
Cost benefit analysis allows evaluators to compare the economic efficiency of program alternatives, even when the interventions are not aimed at common goals.
What is the importance of cost-benefit analysis for a business firm?
It helps them understand whether the revenue generated is sufficient to cover costs or should they explore another project. Cost benefit analysis helps companies to estimate the likely costs and benefits of potential projects. This offers companies the opportunity to identify and evaluate each upcoming expenditure.
What is cost-benefit analysis explain with an example?
What are cost benefit analysis examples? The output of cost benefit analysis will show the net benefit (benefits minus cost) of a project decision. For example: Build a new product will cost 100,000 with expected sales of 100,000 per unit (unit price = 2). The sales of benefits therefore are 200,000.
Why is it important to do a cost-benefit analysis in HRM activities?
A cost-benefit analysis provides both a framework and system for achieving these critical goals. Not only does a cost-benefit analysis allow HR to determine the potential returns of human capital investments but also provides a way to compare alternatives.
How do you present a cost benefit analysis?
How to do a cost-benefit analysisStep 1: Understand the cost of maintaining the status quo. ... Step 2: Identify costs. ... Step 3: Identify benefits. ... Step 4: Assign a monetary value to the costs and benefits. ... Step 5: Create a timeline for expected costs and revenue. ... Step 6: Compare costs and benefits.
What is cost benefit analysis in EIA?
Cost benefit Analysis (CBA) is a tool used either to rank projects or to choose the most appropriate option. The ranking or decision is based on expected economic costs and benefits. The rule is that a project should be undertaken if lifetime expected benefits exceeds all expected costs.
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a process or tool to support decision making in projects.CBA evaluates the cost versus the benefit of a project to d...
What are cost benefit analysis examples?
The output of cost benefit analysis will show the net benefit (benefits minus cost) of a project decision. For example:Build a new product will cos...
What is the process for cost benefit analysis?
Here are some suggested steps to follow to ensure you can get the most out of CBA in your project decision making:1. Define the project2. Quantify...
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost-benefit analysis is a form of data-driven decision-making most often utilized in business, both at established companies and startups. The basic principles and framework can be applied to virtually any decision-making process, whether business-related or otherwise.
What are the limitations of cost-benefit analysis?
Limitations of Cost-Benefit Analysis 1 It’s difficult to predict all variables: While cost-benefit analysis can help you outline the projected costs and benefits associated with a business decision, it’s challenging to predict all the factors that may impact the outcome. Changes in market demand, materials costs, and global business environment can occasionally be fickle and unpredictable, especially in the long term. 2 It’s only as good as the data used to complete it: If you’re relying on incomplete or inaccurate data to finish your cost-benefit analysis, the results of the analysis will be similarly inaccurate or incomplete. 3 It’s better suited to short- and mid-length projects: For projects or business decisions that involve longer timeframes, cost-benefit analysis has greater potential of missing the mark, for several reasons. It typically becomes more difficult to make accurate predictions the further out you go. It’s also possible that long-term forecasts will not accurately account for variables such as inflation, which could impact the overall accuracy of the analysis. 4 It removes the human element: While a desire to make a profit drives most companies, there are other, non-monetary reasons an organization might decide to pursue a project or decision. In these cases, it can be difficult to reconcile moral or “human” perspectives with the business case.
What happens if you don't give all the costs and benefits a value?
If you don’t give all the costs and benefits a value, then it will be difficult to compare them accurately. Direct costs and benefits will be the easiest to assign a dollar amount to. Indirect and intangible costs and benefits, on the other hand, can be challenging to quantify.
What are intangible costs?
Intangible Costs: These are any costs that are difficult to measure and quantify. Examples may include decreases in productivity levels while a new business process is rolled out, or reduced customer satisfaction after a change in customer service processes that leads to fewer repeat buys.
What are indirect costs?
Other cost categories you must account for include: Indirect Costs: These are typically fixed expenses, such as utilities and rent, that contribute to the overhead of conducting business. Intangible Costs: These are any costs that are difficult to measure and quantify.
How to make an analysis more accurate?
1. Establish a Framework for Your Analysis. For your analysis to be as accurate as possible, you must first establish the framework within which you’re conducting it. What, exactly, this framework looks like will depend on the specifics of your organization.
Is cost benefit analysis difficult?
It’s difficult to predict all variables: While cost-benefit analysis can help you outline the projected costs and benefits associated with a business decision, it’s challenging to predict all the factors that may impact the outcome. Changes in market demand, materials costs, and global business environment can occasionally be fickle and unpredictable, especially in the long term.
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost-Benefit Analysis can make sources of bias explicit and open up the possibility for change, though admittedly it can sometimes bind readers and analysts to their fixed ideas. Cost-Benefit Analysis portrays assumptions, calculations and conclusions, and renders these subject to criticism, revision and improvement.
Why is cost benefit analysis important?
Formal Cost Benefit Analysis is needed because the world is complex and constantly changing. Policies, projects and decisions can have numerous consequences, benefits and costs at different points in time. The consequences are difficult to determine, subject to change and often interdependent.
What is a CBA in accounting?
In some cases, it is necessary to analyze alternatives as well. Usually, a CBA measures literal cost in terms of money, but, in cases where money is not an issue, CBAs can measure cost in terms of time, energy usage, and more. The next section is a detailed listing of costs.
When was the CBA first used?
The application of CBA to transport investments started in the UK with the M1 motorway project, which opened in 1959 but was conceived in 1923, and was later applied on many projects including London Underground's Victoria line.
What is the guiding principle of evaluating benefits?
The guiding principle of evaluating benefits is to list all (categories of) parties affected by an intervention and add the (positive or negative) value, usually monetary, that they ascribe to its effect on their welfare. Risk associated with project outcomes is usually handled using probability theory.
How are benefits and costs expressed in CBA?
In CBA, benefits and costs are expressed in monetary terms, and are adjusted for the time value of money, so that all flows of benefits and flows of project costs over time (which tend to occur at different points in time) are expressed on a common basis in terms of their net present value.
Who created the CBA?
Otto Eckstein, laid out a welfare economics foundation for CBA and its application for water resource development and wider application for public policy in 1958. In the early 1960s, CBA was applied in the US for water quality, recreation travel, and land conservation.
Why is cost benefit analysis useful?
This makes it useful for higher-ups who want to evaluate their employees’ decision-making skills, or for organizations who seek to learn from their past decisions — right or wrong .
How is the cost and benefit tool used?
It’s made possible by placing a monetary value on both the costs and benefits of a decision. Some costs and benefits are easy to measure since they directly affect the business in a monetary way.
What is cost benefit ratio?
Cost benefit ratio is the ratio of the costs associated with a certain decision to the benefits associated with a certain decision. It’s more commonly known as benefit cost ratio, in which case the ratio is reversed (benefits to costs, instead of costs to benefits). Since both costs and benefits can be expressed in monetary terms, ...
Is cost benefit analysis a guiding tool?
In these cases, consider cost benefit analysis as a guiding tool, but look to other business analysis techniques to support your conclusion.
Can cost benefit ratios be numerically expressed?
Since both costs and benefits can be expressed in monetary terms, these ratios can also be expressed numerically. As a result, cost benefit or benefit cost ratios lend themselves well to comparison, which is why cost benefit analysis can be used to compare two or more definitions. The process is simple. For each decision or path in question, ...
What is a cost benefit analysis?
Cost benefit analysis, CBA, benefit cost analysis or if one loves hyphens (or incorrect depending on your perspective) cost-benefit analysis / benefit-cost analysis. All effectively mean the same thing - how much the benefits of a project investment outweigh the costs.
What is the formula for CBA?
The output of cost benefit analysis will show the net benefit (benefits minus cost) of a project decision. For example:
What is the process for CBA?
Like any project process, there are multiple versions out there on what the steps are and it is always best to find what works best for you. Here are some suggested steps to follow to ensure you can get the most out of CBA in your project decision making.
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a decision-making process many businesses use to determine the expected pros and cons of particular business decisions.
Why is cost benefit analysis important?
A cost-benefit analysis can be a valuable tool for businesses to use to determine the impact and profitability of specific business decisions. First, this analysis can help firms to analyze the pros and cons of a single business decision.
What are intangible costs?
Your intangible expenses could include the impact on your employees or the effect on your customers and the way they see your company. Intangible costs could also include the social and environmental impact of a particular decision.
How to calculate the benefit to cost ratio?
First, add up the monetary value of each (meaning the sum of all of your costs and the sum of all of your benefits). Then, you’re going to take the total dollar value of your benefits and divide it by the total dollar value of your costs. The resulting number is your benefit-to-cost ratio.
What are indirect costs?
Indirect costs are those the company will incur, but that aren’t directly related to production. These costs would include overhead such as rent, utilities, and management. These are tangible costs, but there isn’t a direct correlation between production and these costs.
Why do companies use cost benefit analysis?
Many companies use cost-benefit analysis to help them make important short-term and long-term business decisions. While the process likely looks a little different for every company, the steps are roughly the same.
What is opportunity cost?
It works the same way with business decisions. With every significant business decision, the opportunity cost is the profit they could have made from a different choice. With a cost-benefit analysis, companies can look at all of those factors at once.
What is cost benefit analysis?
Cost-benefit analysis is a process that project managers and business executives use to determine the expenses and incentives of a major company project. When companies perform a cost-benefit analysis, they calculate the costs and benefits for the project or decision and determine which calculation is larger.
Why is cost benefit analysis important?
Provides a competitive advantage. Cost-benefit analysis can help companies develop an advantage over competing businesses because it can help them quickly create innovative ideas and determine how they can stay relevant in the current market. Continuously generating new ideas and performing a cost-benefit analysis on them can help companies stay ...
What are the costs of a project?
When performing a cost-benefit analysis on your project, it's important to analyze a comprehensive list of expenses and positive outcomes the project will create. Costs or expenses that the project creates can include: 1 Direct costs: Direct costs are purchases that a business makes that directly relate to the creation of its goods and services. These costs can include material purchases, employee salaries and equipment or tool rentals. 2 Indirect costs: Indirect costs are other expenses that help keep the business or company operating, including insurance, facility rentals and utility costs. 3 Intangible costs: Intangible costs are costs that companies can't easily quantify. These costs can include customer satisfaction, employee morale or overall productivity. 4 Potential risks: Potential risks are any challenges or issues that a company might face during a project or after the project's completion. These can include other direct or indirect costs, such as spending more than the company expected, and intangible costs, such as loss of business or profit. 5 Opportunity costs: Opportunity costs are the loss of potential benefits or profit from making one decision over another. For example, if a company decides to sell some property, they might be missing out on potential profit from renting the property on a monthly basis.
What are intangible costs?
Intangible costs: Intangible costs are costs that companies can't easily quantify. These costs can include customer satisfaction, employee morale or overall productivity. Potential risks: Potential risks are any challenges or issues that a company might face during a project or after the project's completion.
Why do companies use cost benefit analysis?
Companies and businesses often use a cost-benefit analysis to determine and evaluate all the expenses and revenues that a project might generate. The analysis helps companies examine the feasibility of the project in terms of finances and other important factors, such as opportunity costs. Opportunity costs consider alternative benefits ...
What are opportunity costs?
Opportunity costs: Opportunity costs are the loss of potential benefits or profit from making one decision over another.
What happens if the benefits exceed the costs?
If the benefits exceed the costs, the project or decision is generally a positive one for the company to make. However, if the costs exceed the benefits, the company often evaluates that project's plan and determines if there's a way to adjust it or save money.
What is the purpose of a cost analysis?
The primary goal of cost analysis is to determine the true (full) costs of each of the programs (services and/or products) under consideration. After that, you can use this information to: Identify and prioritize cost-cutting opportunities.
Why is cost-benefit analysis needed?
Using a cost benefit analysis, businesses can select the best options, rank projects in order of merit, and eliminate biases for the betterment of the organization.
What is a cost-benefit analysis and why is it important?
In a cost-benefit analysis, the anticipated or anticipated costs (or opportunities) associated with a particular project decision are compared with the projected or estimated benefits (or opportunities).
What is the importance of cost benefit ratio?
The benefit-cost ratio is used to determine the viability of cash flows from an asset or project; the higher the ratio, the more appealing the project's risk-return profile; a faulty benefit-cost ratio would result from poor cash flow forecasting or an incorrect discount rate.
What are the key elements of a cost-benefit analysis?
Activities and Resources, Cost Categories, Personnel Costs, Direct and Indirect Costs (Overhead), Depreciation, and Annual Costs are all factors that must be taken into consideration. As a return on investment, benefits are the features, capabilities, and qualities of each alternative system.
What is cost-benefit analysis used for?
A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a method of weighing the advantages of a decision or action against the costs of doing so.
Where can cost-benefit analysis be used?
Cost-Benefit Analysis in Project Management A cost-benefit analysis is used in project management to compare the costs and benefits of your project proposal and business case. As with many other processes, it starts with a list.
Benefits and limitations of cost-benefit analysis
Ofcourse, there are multiple reasons for a business or an organization to choose cost-benefit analysis as a part of their decision-making process. CBA includes several potential benefits and limitations that must be considered before leaning at the cost-benefit analysis. Some are listed below its benefits;
Endnotes
Putting our discussion towards the end, it can be concluded that a cost benefit analysis facilitates businesses to rectify complicated business decisions and to measure the benefits of a decision (benefits of considering an action from the cost associated while looking at that action).
Understanding Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Before building a new plant or taking on a new project, prudent managers conduct a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate all the potential costs and revenues that a company might generate from the project. The outcome of the analysis will determine whether the project is financially feasible or i…
The Cost-Benefit Analysis Process
- A cost-benefit analysis should begin with compiling a comprehensive list of all the costs and benefits associated with the project or decision. The costs involved in a CBA might include the following: 1. Direct costs would be direct labor involved in manufacturing, inventory, raw materials, manufacturing expenses. 2. Indirect costs might include electricity, overhead costs from manag…
Limitations of The Cost-Benefit Analysis
- For projects that involve small- to mid-level capital expenditures and are short to intermediate in terms of time to completion, an in-depth cost-benefit analysis may be sufficient enough to make a well-informed, rational decision. For very large projects with a long-term time horizon, a cost-benefit analysis might fail to account for important financial concerns such as inflation, interest …
What Is A Cost-Benefit Analysis?
- A cost-benefit analysisis the process of comparing the projected or estimated costs and benefits (or opportunities) associated with a project decision to determine whether it makes sense from a business perspective. Generally speaking, cost-benefit analysis involves tallying up all costs of a project or decision and subtracting that amount from the...
How to Conduct A Cost-Benefit Analysis
- 1. Establish a Framework for Your Analysis
For your analysis to be as accurate as possible, you must first establish the framework within which you’re conducting it. What, exactly, this framework looks like will depend on the specifics of your organization. Identify the goals and objectives you’re trying to address with the proposal. W… - 2. Identify Your Costs and Benefits
Your next step is to sit down and compile two separate lists: One of all of the projected costs, and the other of the expected benefits of the proposed project or action. When tallying costs, you’ll likely begin with direct costs, which include expenses directly related to the production or develo…
Pros and Cons of Cost-Benefit Analysis
- There are many positive reasons a business or organization might choose to leverage cost-benefit analysis as a part of their decision-making process. There are also several potential disadvantages and limitations that should be considered before relying entirely on a cost-benefit analysis.