
The Benefits of Rotating Crops
- Reduce the risk of disease – If there is a specific disease (bacteria) present in the soil, it can feast on the same crop over and over again. ...
- Prevent soil erosion – Planting the same crops repeatedly, leaves certain areas of the soil at risk for erosion. ...
- Increase water conservation – Health soil is better able to absorb water. ...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of crop rotation?
- According to Agriculturists and Agronomists, there are many benefits of crop rotation. ...
- There is some scientific evidence that proves a 10 to 25% increase in yield of the crop in crop rotation rather than going for monoculture.
- The cost of production of the following crop decreases to an extent which mostly depends on the crop we select.
Why should you rotate crops?
Rotating in a small space
- Raised beds. By making raised beds, you create a physical barrier between your different garden areas. ...
- Use pots for disease-prone plants. If you have a variety you love to grow (such as heirloom tomatoes), but you're concerned about significant diseases, consider planting them in a separate ...
- Coordinating with neighbors and friends. ...
How does crop rotation help soil conservation?
Tech Notes
- Crops must be suited to your soils.
- Design crop rotations to meet the residue needs of your crop residue management plan. ...
- Small grains and corn (grain) can be used to replace any low residue crop to gain better erosion control.
Why do farmers rotate crops?
General Principles:
- Follow a legume crop . ...
- Grow less nitrogen demanding crops . ...
- Grow the same annual crop for only one year . ...
- Don’t follow one crop with another closely related species. ...
- Use crop sequences that promote healthier crops.
- Use crop sequences that aid in controlling weeds.
- Use longer periods of perennial crops on sloping land.
- Try to grow a deep-rooted crop . ...
What is crop rotation what are its advantages Short answer?
Crop rotation is the practice of planting different crops sequentially on the same plot of land to improve soil health, optimize nutrients in the soil, and combat pest and weed pressure.
How is crop rotation beneficial for agriculture?
Good soil structure starts at the roots. Farmers that rotate between corn and soybeans to increase soil fertility can also add a cover crop to provide diverse root systems that benefit the soil.
What are benefits of crops?
Cover crops improve soil by: Speeding infiltration of excess surface water. Relieving compaction and improving structure of overtilled soil. Adding organic matter that encourages beneficial soil microbial life.
What are the five advantages of crop rotation?
Advantages of Crop RotationIncreases Soil Fertility. ... Increases Crop Yield. ... Increases Soil Nutrients. ... Reduces Soil Erosion. ... Limits the Concentration of Pests and Diseases. ... Reduces the Stress of Weeds. ... Improves the Soil Structure. ... Reduces Pollution.More items...
Answer
Reduction in populations of insect pests is a benefit of crop rotation.
New questions in Biology
Mitosis is just one small part of the cell cycle! Describe what would occur if cells were in mitosis more than they were in interphase.
What are the benefits of crop rotation?
Improving the soil organic matter and nutrient pools is also a benefit of crop rotation that results in increasing water-holding capacity of the soil. The Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education Program (SARE) investigated about this better soil caused by crop rotation.
Why is crop rotation important?
Crop rotation plays a key role in reducing the risk of nitrate, leaching into surface and groundwater. The system improves the availability ...
How does crop rotation affect nitrogen?
Along with the other benefits of crop rotation, it may impact the rate of nitrogen mineralization .#N#Even on the conversion of organic nitrogen to mineral nitrogen by change of soil temperature, moisture, plant residue, pH and tillage practices. A common use of nitrogen it is been showing up over the past 50 years.#N#The use of this in large amounts, especially to maximize farming production, increases the nitrogen within the soil profile of certain farms.#N#Rotations that include nitrogen by producing legumes such as peas, beans, and alfalfa give to next crops with large amounts of this critical nutrient.#N#A research shows that nitrogen from legumes remains in the soil longer than the nitrogen in synthetic fertilizers, leaving less to leach into groundwater or runoff fields and pollute streams.#N#Crop rotation plays a key role in reducing the risk of nitrate, leaching into surface and groundwater. The system improves the availability of soil nitrogen and reducing the nitrogen fertilizer used.
What is the logic behind crop rotation?
The logic behind crop rotation is when the same crop is grown at the same place for several years the soil is depleted of certain nutrients. Doing rotation, a crop that draws one kind of nutrient from the soil is followed during the consequent season by a crop that returns the nutrient to the soil or draws a distinct ratio of nutrients.
Why is my crop yield decreasing?
This is because if the same type of crop is planted in the same area, the plant will continue to drain same nutrients from the soil. . Second, certain pests can reach levels that are hard to control.
Why is nitrogen used in agriculture?
The use of this in large amounts, especially to maximize farming production, increases the nitrogen within the soil profile of certain farms .
How old is crop rotation?
The crop rotation is a thousand years old technique that has been proven to help the environment, improve the soil and so many other things.
Why is rotation important for crops?
Crop rotation can help reduce the risk of adverse environmental stress, such as drought, early frost, and wet springs that result in a delayed planting window. It can help reduce the risk of an economic insect infestation from insects that are specific to a crop for a part of their life cycle, such as the corn rootworm complex and soybean aphid. Most foliar plant diseases are specific to a certain crop species therefore, rotation can help reduce the risk of economic loss as the result of plant diseases, such as Northern corn leaf blight, brown stem rot of soybean, and tar spot in corn.
What is crop rotation?
Crop rotation is a component of crop production and an implement for farm management as it balances agronomy and economic market realities. From an agronomic perspective, crop rotation can increase nutrient cycling and nutrient use efficiency, decrease plant diseases and insect pests, assist in managing weeds, reduce soil erosion, ...
How does crop rotation help weeds?
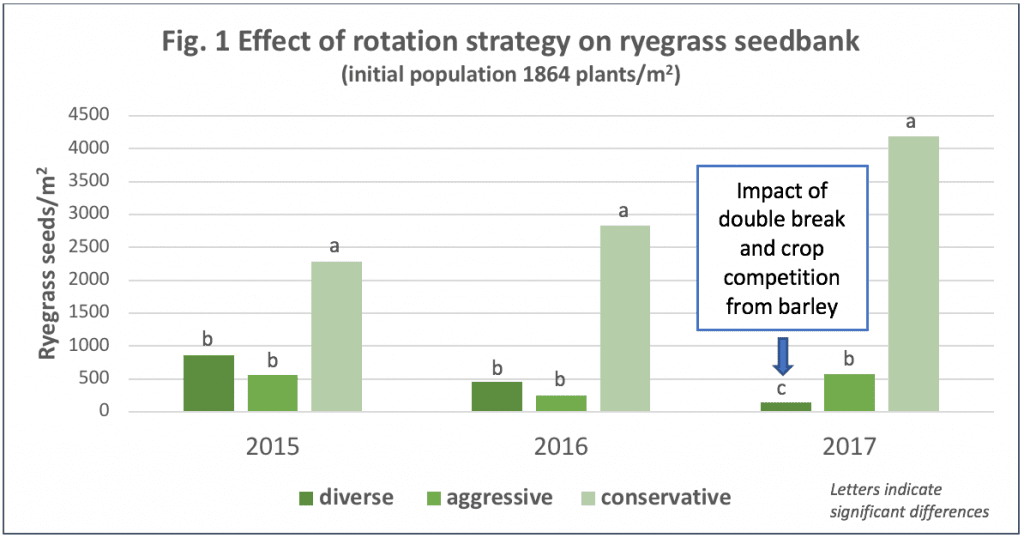
Many weed management plans include crop rotation as a tactic to help manage weeds. Continuous cropping of a single crop can become infested with a weed species that has adapted to the crop and management system being used. Whereas, a crop rotation that is diverse can exert selection pressure on weeds, preventing any one weed species from becoming dominant and help slow the overreliance on a single herbicide that can result in herbicide resistance. A survey of scientific literature indicated that crop rotation resulted in weed densities that were lower in 21 cases, higher in 1 case, and equivalent in 5 cases when compared to continuous cropping of a single crop. Additionally, in 12 studies where weed seed bank density was reported, crop rotation was lower in 9 cases and equivalent in 5 when comparing crop rotation with continuous cropping .3
How much carbon does corn lose in Illinois?
In a long-term study in Illinois, a continuous corn production system lost about 30% of the soil carbon when compared to a corn-oats-clover rotation system. However, recent studies have indicated that the tillage system, specifically no-till systems, in conjunction with crop rotation can play a major role in maintaining or increasing soil carbon content. 4
Is rotational cropping bad for wheat?
The cropping sequence of the rotational system should also be considered as it may be detrimental and increase risk. For example, corn grown before wheat can increase the incidence of fusarium head blight (wheat scab) in wheat. Additionally, there are some root and crown diseases in wheat that can also increase with this rotation system as corn ...
Why is rotation important for crops?
Crop rotation can help reduce the risk of adverse environmental stress, such as drought, early frost, and wet springs that result in a delayed planting window. It can help reduce the risk of an economic insect infestation from insects that are specific to a crop for a part of their life cycle, such as the corn rootworm complex and soybean aphid. Most foliar plant diseases are specific to a certain crop species therefore, rotation can help reduce the risk of economic loss as the result of plant diseases, such as Northern corn leaf blight, brown stem rot of soybean, and tar spot in corn.
How does crop rotation affect agriculture?
From an agronomic perspective, crop rotation can increase nutrient cycling and nutrient use efficiency, decrease plant diseases and insect pests, assist in managing weeds, reduce soil erosion, and increase soil health. A common rotational system in the Corn Belt is corn followed by soybean for a two-year rotational program. Research at Iowa State University on extended multi-year rotations of three to four years found that net economic returns did not differ among the cropping systems, corn and soybean yield potential increased, soil health improved, soil erosion decreased, herbicide and nitrogen (N) fertilizer use decreased, and some plant diseases were reduced. 1
How does crop rotation help weeds?
Many weed management plans include crop rotation as a tactic to help manage weeds. Continuous cropping of a single crop can become infested with a weed species that has adapted to the crop and management system being used. Whereas, a crop rotation that is diverse can exert selection pressure on weeds, preventing any one weed species from becoming dominant and help slow the overreliance on a single herbicide that can result in herbicide resistance. A survey of scientific literature indicated that crop rotation resulted in weed densities that were lower in 21 cases, higher in 1 case, and equivalent in 5 cases when compared to continuous cropping of a single crop. Additionally, in 12 studies where weed seed bank density was reported, crop rotation was lower in 9 cases and equivalent in 5 when comparing crop rotation with continuous cropping .3
How much carbon does corn lose in Illinois?
In a long-term study in Illinois, a continuous corn production system lost about 30% of the soil carbon when compared to a corn-oats-clover rotation system. However, recent studies have indicated that the tillage system, specifically no-till systems, in conjunction with crop rotation can play a major role in maintaining or increasing soil carbon content. 4
