
How do creditors benefit from inflation?
Debtors gain from inflation because they repay creditors with dollars that are worth less in terms of purchasing power. 3. Anticipated inflation, inflation that is expected, results in a much smaller redistribution of income and wealth.
Is inflation good or bad for a debtor?
As a debtor, I benefitted by the inflation, PROVIDED INFLATION AND CONSEQUENTIAL PRICE INCREASES ARE HIGHER THAN RATE OF INTEREST. Inflation is higher in developing countries, and I am from India.
Who is the debtor and creditor in case of inflation?
The benificiary will be the Debtor in case of inflation and Creditor in case of deflation. Before understanding why, first let me tell you some basics.. INFLATION is the general rise in prices of different commodities taken together comparable to the previous one. eg … suppose the price of rice in 2016 was 100rs/kg.
Who benefits from anticipated inflation?
Anticipated inflation, inflation that is expected, results in a much smaller redistribution of income and wealth. Click to see full answer. Regarding this, who benefits from inflation borrowers or lenders? Inflation is good for borrowers and bad for lenders because it reduces the value of the money paid back to the lenders.
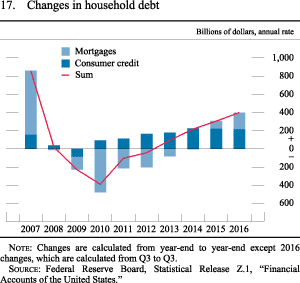
Who is benefited most from inflation?
People who have to repay their large debts will benefit from inflation. People who have fixed wages and have cash savings will be hurt from inflation. Inflation is a situation where the money will be able to buy fewer goods than it was able to do so as the value of money comes down.
Who is hurt by inflation creditors or debtors?
Inflation isn't as good for debtors as is commonly assumed, but it's unequivocally bad for creditors whose investments lose value proportionate to inflation. A U.S. dollar note is pictured alongside an Australian 10 dollar and 20 dollar bill in this picture illustration.
Are creditors benefits during inflation?
During periods of rising prices, debtors gain and creditors lose. When prices rise, the value of money falls. Though debtors return the same amount of money, but they pay less in terms of goods and services. This is because the value of money is less than when they borrowed the money.
Who benefits and who suffers from inflation?
Who Benefits From Inflation? While consumers experience little benefit from inflation, investors can enjoy a boost if they hold assets in markets affected by inflation. For example, those who are invested in energy companies might see a rise in their stock prices if energy prices are rising.
Who gains with inflation?
One important redistribution of income and wealth that occurs during unanticipated inflation is the redistribution between debtors and creditors. a. Debtors gain from inflation because they repay creditors with dollars that are worth less in terms of purchasing power.
What sectors benefit from inflation?
Which Are The Sectors That Benefit From Inflation?Wine. When inflation rises and purchasing power decreases, many investors turn to real assets for an inflation hedge. ... Real estate. ... Energy. ... Bonds. ... Financial Companies. ... Commodities. ... Healthcare. ... Consumer staples.
Why do a debtors benefit during inflation?
Inflation redistributes wealth from creditors to debtors i.e. lenders suffer and borrowers benefit out of inflation. Bondholders have lent money (to debtor) and received a bond in return. So he is a lender, he suffers (Debtor benefits from inflation).
Who loses from inflation?
“The losers from inflation include retirees on largely fixed nominal incomes, bond holders (whose financial income is largely fixed) and those whose compensation is relatively fixed in nominal terms,” Splatt said.
Who benefits financially from inflation?
Inflation allows borrowers to pay lenders back with money worth less than when it was originally borrowed, which benefits borrowers. When inflation causes higher prices, the demand for credit increases, raising interest rates, which benefits lenders.
Why do debtors gain from inflation?
Debtors gain from inflation because they repay creditors with dollars that are worth less in terms of purchasing power. 3. Anticipated inflation, inflation that is expected, results in a much smaller redistribution of income and wealth. Click to see full answer.
What is the benefit of inflation?
The key benefit of inflation is that it reduces the real value of government debt. It does this because tax revenues increase approximately in proportion to inflation. Government's fixed debt payments therefore become a smaller part of the tax take and more affordable.
What happens to debtors when prices rise?
During periods of rising prices, debtors gain and creditors lose. When prices rise, the value of money falls. Though debtors return the same amount of money, but they pay less in terms of goods and services. Thus inflation brings about a redistribution of real wealth in favour of debtors at the cost of creditors.
Is inflation good or bad?
Inflation is good for borrowers and bad for lenders because it reduces the value of the money paid back to the lenders. The inflation rate is built in to the nominal interest rate, which is the sum of the real interest rate and expected inflation.
Why won't creditors pay back their debt?
On the other hand creditors will have a hard time as their debtors won't be able to pay back because of the liquidity crunch and depreciation of the money value.
What happens if inflation is positive?
If there is a positive inflation, like in most of countries; then the debtor has an advantage.
What happens when interest rate falls short of inflation?
This means that the lender, would not be able to buy the basket of goods which he could have bought last year with the same money even after earning an interest over that amount due to high inflation rate .
What is a debtor?
DEBTOR is the person or any institution who takes money or loan from the creditor. Examples of debtors are Borrowers (individual or institution), Bond holders etc.
What is inflation in commodities?
INFLATION is the general rise in prices of different commodities taken together comparable to the previous one. eg … suppose the price of rice in 2016 was 100rs/kg. Now taking inflation @5%, the price of rice will be 105rs/kg in 2017.
Does inflation affect the debtor?
Hence the Debtor is more advatageous in times of inflation.
Who is at the most risk during inflationary times?
The business owner who NEEDS to borrow cash for a business with unknown elasticity (able to raise prices quickly or push out more product quickly) is at the most risk during inflationary times.
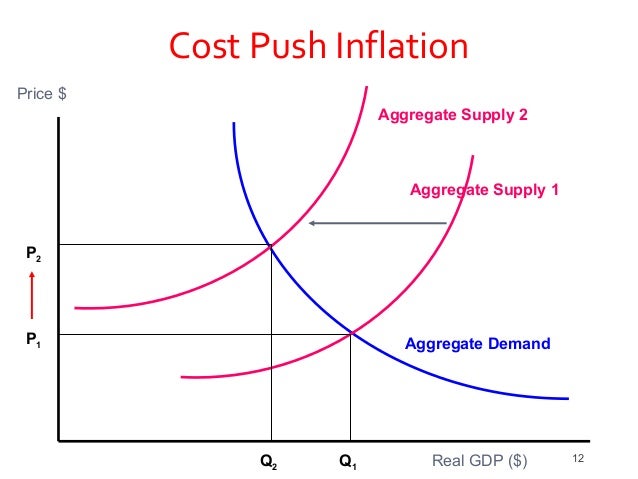
Inflation and The Quantity Theory of Money
- In the long run, the best way to think about money and inflation is with the quantity theory of money MV=PQ where M is the money supply, V is the velocity of money, P is the general price level, and Q is the real output of the economic system or gross domestic product (GDP) in real te…
Factors That Increase Money Supply
- Aside from printing new money, various other factors can increase the money supply within an economy. Interest rates may be reduced, or the reserve ratio for banks may be reduced (the percentage of deposits the bank keeps in cash reserves). Lower rates and reserves held by banks would likely lead to an increased demand for borrowing at lower rates, and banks would have m…
Inflation Can Also Help Lenders
- Inflation can help lenders in several ways, especially when extending new financing. First, higher prices mean that more people want creditto buy big-ticket items, especially if their wages have not increased–this equates to new customers for the lenders. On top of this, the higher prices of those items earn the lender more interest. For example, if the price of a television increases fro…
Inflation and The Cost of Living
- If prices increase, so does the cost of living. If people spend more money to live, they have less money to satisfy their obligations (assuming theirearnings haven't increased). With rising prices and no increase in wages, the people experience a decrease in purchasing power. As a result, the people may need more time to pay off their previous debts allowing the lender to collect interes…
Special Considerations
- If inflation is rising against the backdrop of a growing economy, this may result in central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, increasing interest rates to slow the rate of inflation. Higher interest rates may lead to a slowdown in borrowing as consumerstake out fewer loans. However, the rise in interest rates can help lenders earn more profits, particularly variable-rate credit products suc…