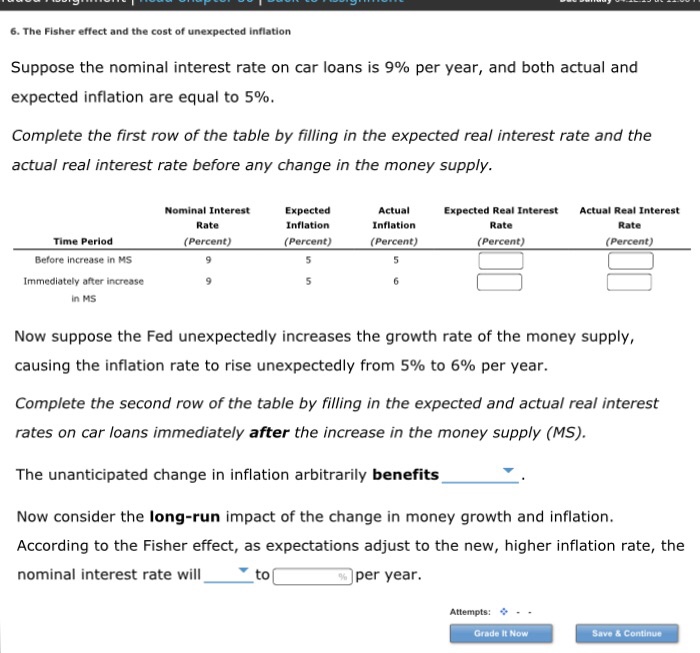
Who is hurt and who is helped by unanticipated inflation?
Unanticipated inflation hurts savers and creditors becausethe money that they lend out gets paid back in cheaper dollars over time. Unanticipated inflation helps borrowers and debtors because they borrow money at a fixed rate and pay it back in cheaper dollars over time.
Who is most likely to benefit from inflation?
When inflation causes higher prices, the demand for credit increases, raising interest rates, which benefits lenders. Which group is most likely to benefit from inflation? Inflation means the value of money will fall and purchase relatively fewer goods than previously. In summary: Inflation will hurt those who keep cash savings and workers with fixed wages. Inflation will benefit those with large debts who, with rising prices, find it easier to pay back their debts.
Who benefits and who loses from inflation?
The higher prices will drive salaries higher and allow a fixed debt and bills to be paid off faster. On the other hand, we find inflation actually harms lenders and savers. Lenders and savers harm the loans and savings that do not directly appreciate from inflation.
Why inflation can be good and bad?
That's why inflation, especially the sharp price increases we've seen in recent months, feels like a dirty word. But on the whole, inflation can actually be a good thing for many working-class Americans, especially those with fixed-rate debt like a 30-year ...
Who benefited in inflation?
People who have to repay their large debts will benefit from inflation. People who have fixed wages and have cash savings will be hurt from inflation. Inflation is a situation where the money will be able to buy fewer goods than it was able to do so as the value of money comes down.
Who benefits most from unexpectedly high inflation?
If unexpectedly high inflation occurs, who benefits more * borrowers or lenders? Borrowers, since the real value of the money they repay declines.
Who benefits from unexpected inflation borrowers or lenders?
One important redistribution of income and wealth that occurs during unanticipated inflation is the redistribution between debtors and creditors. a. Debtors gain from inflation because they repay creditors with dollars that are worth less in terms of purchasing power.
Who is affected by unexpected inflation?
One positive effect of unanticipated inflation is that it benefits employees and borrowers. Employees with increasing income do not suffer the negative consequences of a fixed income. Furthermore, debtors benefit from unexpected inflation because they save money on existing loans.
Who wins from inflation?
Anyone with large, fixed-rate debts like mortgages benefit from higher inflation, says Mark Thoma, a retired professor of economics at the University of Oregon. Those interest rates are locked in for the life of the loan, meaning they won't ebb and flow with inflation.
Who are the winners and losers from unexpected inflation quizlet?
Terms in this set (18) Unanticipated inflation creates winners and losers among borrowers and lenders.
Who benefits from inflation debtors or creditors?
The correct answer is 1 only. Inflation redistributes wealth from creditors to debtors i.e. lenders suffer and borrowers benefit out of inflation. Bondholders have lent money (to debtor) and received a bond in return. So he is a lender, he suffers (Debtor benefits from inflation).
Who are the gainers and losers of inflation?
Inflation means the value of money will fall and purchase relatively fewer goods than previously. In summary: Inflation will hurt those who keep cash savings and workers with fixed wages. Inflation will benefit those with large debts who, with rising prices, find it easier to pay back their debts.
What is unexpected inflation?
Unexpected inflation is the inflation experienced that is above or below that which was expected. Unexpected inflation affects the economic cycle. It reduces the validity of the information on market prices for economic agents. Over the years, unexpected inflation impacts employment, investment, and profits.
Who benefits from unexpected inflation quizlet?
Unanticipated inflation benefits debtors at the expense of creditors. You just studied 4 terms!
Who is harmed by unexpected inflation quizlet?
Unexpected inflation harms both debtors and individuals who live on fixed incomes.
Do borrowers benefit from inflation?
Do Borrowers Benefit From Inflation? Inflation actually can benefit borrowers. The way that this works is pretty simple, if you are a borrower and inflation occurs while repaying, the money you had borrowed will have more purchasing power and thus more value than the money you owe.
How does inflation affect the consumer?
Inflation erodes a consumer's purchasing power and can even interfere with the ability to retire. For example, if an investor earned 5% from investments in stocks and bonds, but the inflation rate was 3%, the investor only earned 2% in real terms. In this article, we'll examine the fundamental factors behind inflation, different types of inflation, ...
Why does inflation occur?
Inflation can occur when prices rise due to increases in production costs, such as raw materials and wages. A surge in demand for products and services can cause inflation as consumers are willing to pay more for the product.
What causes cost push inflation?
Cost-push inflation occurs when prices increase due to increases in production costs, such as raw materials and wages. The demand for goods is unchanged while the supply of goods declines due to the higher costs of production. As a result, the added costs of production are passed onto consumers in the form of higher prices for the finished goods.
What are the factors that drive inflation?
Typically, inflation results from an increase in production costs or an increase in demand for products and services.
What is the most popular measure of inflation?
Measures of Inflation. There are a few metrics that are used to measure the inflation rate. One of the most popular is the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures prices for a basket of goods and services in the economy, including food, cars, education, and recreation.
Why is consumer confidence so high?
Consumer confidence tends to be high when unemployment is low, and wages are rising —leading to more spending. Economic expansion has a direct impact on the level of consumer spending in an economy, which can lead to a high demand for products and services.
What happens when the unemployment rate is low?
When the economy is performing well, and the unemployment rate is low, shortages in labor or workers can occur. Companies, in turn, increase wages to attract qualified candidates, causing production costs to rise for the company. If the company raises prices due to the rise in employee wages, cost-plus inflation occurs.
Expected Inflation
Expected inflation is the inflation that economic agents anticipate in the future. Expected inflation leads to “menu cost,” which refers to a scenario in which businesses change their advertised prices constantly. The constant fluctuation of prices is due to inflation.
Unexpected Inflation
Unexpected inflation is the inflation experienced that is above or below that which was expected. Unexpected inflation affects the economic cycle. It reduces the validity of the information on market prices for economic agents. Over the years, unexpected inflation impacts employment, investment, and profits.
Differences Between Expected Inflation and Unexpected Inflation
Expected Inflation Unexpected Inflation 1 It is anticipated inflation by economic agents in an economy It is inflation experienced that is above or below what was expected 2 Wage negotiations and pricing into business and financial contrasts solve expected inflation When inflation is higher than expected, borrowers benefit at the expense of lenders because of the decline in the value of their borrowing.
Question
Which of the following is caused by unexpected inflation (as opposed to expected inflation)?
How does inflation help lenders?
Inflation Can Also Help Lenders. Inflation can help lenders in several ways, especially when it comes to extending new financing. First, higher prices mean that more people want credit to buy big-ticket items, especially if their wages have not increased–this equates to new customers for the lenders.
How does inflation affect the long term?
Many economists agree that the long-term effects of inflation depend on the money supply. In other words, the money supply has a direct, proportional relationship with price levels in the long term. Thus, if the currency in circulation increases, there is a proportional increase in the price of goods and services.
What happens when the cost of living rises?
When the cost of living rises, people may be forced to spend more of their wages on nondiscretionary spending, such as rent, mortgage, and utilities . This will leave less of their money for paying off debts, and borrowers may be more likely to default on their obligations.
What happens to the cost of living when inflation increases?
Inflation and the Cost of Living. If prices increase, so does the cost of living. If the people are spending more money to live, they have less money to satisfy their obligations (assuming their earnings haven't increased). With rising prices and no increase in wages, the people experience a decrease in purchasing power.
What is the rule of inflation?
A basic rule of inflation is that it causes the value of a currency to decline over time. In other words, cash now is worth more than cash in the future. Thus, inflation lets debtors pay lenders back with money that is worth less than it was when they originally borrowed it.
What is inflation in economics?
Inflation occurs when there is a general increase in the price of goods and services and a fall in purchasing power. Purchasing power is the value of a currency expressed in terms of the number of goods and services that one unit of the currency can purchase. Many economists agree that the long-term effects of inflation depend on the money supply. ...
What would happen if banks had lower rates?
Lower rates and reserves held by banks would likely lead to an increased demand for borrowing at lower rates, and banks would have more money to lend. The result would be more money in the economy, leading to increased spending and demand for goods, causing inflation.